
Part Two
- The policy of the time frame for completing the assessment
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Politics :
* The hospital is committed to evaluating the patient and determining his needs in full within 24 hours of admission to the hospital.
Purpose :
* Determine the sufficient and permitted time to complete the evaluation of the patient and determine his needs.
Working procedures:
1. The resident evaluates the patient's condition upon admission to the hospital.
2. Emergency operations patient the Attending Physician assesses his condition immediately before the operation .
3. The nurse completes the nursing assessment when the patient is admitted to the hospital.
4. The evaluation of the patient's physiotherapy is done when he needs it and this is decided by the Attending Physician.
5. The consultant evaluates the patient for whom the presentation is scheduled within no more than 24 hours for stable cases / anesthesia presentations in the inpatient department.
6. The anesthesiologist evaluates the patient in emergency operations immediately before the operation.
7. The department supervisor calls the patient's social worker when he needs it.
References: Egyptian accreditation standards
|
Preparation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: re-evaluation of patients in critical and non-critical cases requiring long-term ( chronic)treatment
Purpose: to ensure the correct follow-up and continuation of patient care and evaluation
Working procedures :
First : in acute cases (care-premature babies):
The attending physicians of the departments evaluate and identify the following
1-the degree of awareness and Horizon.
2-vital signs .
3-the occurrence of complications .
4-the results of tests and treatment or( surgical interventions ) .
5-the extent of response to treatment .
o the evaluation rate is continuous and you call the deputy doctor when a critical result is issued (physiological – laboratory – radiology) and when there is pain, and the doctor re-evaluates .
o the patient's re-evaluation is documented, a follow-up observation is recorded at least once a shift ( every 24 hours), and any actions resulting from a call, emergency or important events of the patient are recorded by date and time .
Second : in non-acute cases :-
The attending physicians evaluate patients in non-acute cases and make sure
* Vital signs ·
* Occurrence of complications
* Results of tests and treatment
* Patient compliance with treatment and medical instructions .
This is done every 12 hours for the internal department by the specialist or the doctor on duty, unless the clinical evidence requires less and this is proved in the patient's file .
Third: cases that need a long - term (chronic diseases )
The attending physicians in the departments that care for patients who need long-term or (chronic) treatment and ensure :-
* Vital signs ·
* The occurrence of complications .
* Results of tests and treatment .
* The extent of the disease progression.
The rate of Re-evaluation is once a day by the doctor on duty or as required by clinical evidence and proof of this in the patient's file.
1. The specialist re-evaluates the patient from various specialties during the patient's stay in the hospital to find out the extent of response to treatment and how effective it is .
2. Shift nursing re-evaluates the patient every shift to determine the patient's needs .
Fourth: cases that need to be re-evaluated
* Treatment plan developed for the patient Individualized care plan
* Change in the patient's condition change inpatient condition
· Patient diagnosis
· Desired outcome of care, treatment or service
* The extent to which the patient has responded to previous treatment patient response to previous treatment
3. The reassessment is documented in the patient's file
The patient should be re-evaluated immediately before the administration of anesthesia
Fifth: the content of nursing reassessment
1-vital signs: every 6 hours in the internal departments, every two hours in the care, early, after blood transfusion, before surgery, during recovery, and when the patient complains that it needs to be re-measured or according to the doctor's instructions.
2-pain:
3-the probability of the patient's fall: every seizure.
4. skin condition: every shift (skin color during awakening).
5-nutritional evaluation: when the patient needs according to the doctor's orders.
6-measuring blood sugar: according to the doctor's instructions.
7-the patient's need for restriction or isolation: according to the doctor's orders .
Forms: medical follow-up form.
References: Egyptian accreditation standards
|
Preparation |
|
|
|
|
|
Assessment, reassessment and pain management policy
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: the hospital is committed to the process of assessment, reassessment and pain management .
Purpose: to clarify the process of assessment, reassessment and treatment of pain.
Actions :
1 - the nurse in charge evaluates the pain (according to the following table), finds out its intensity, describes the pain and its frequency by asking the patient and looking at the patient's facial expression (in case he is unable to speak or in case he is a child) and records this in the pain assessment form and saves in the patient's file when the patient is hospitalized.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
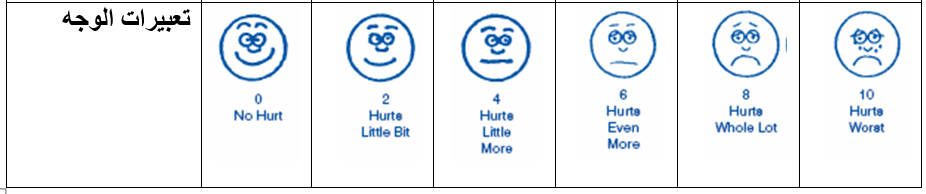
2-the Attending Physician draws up a pain treatment plan and records it in the patient's medical file .
3 - the responsible nurse implements the treatment and follow-up plan according to the pain model and the doctor's instructions .
4-the responsible nurse re-evaluates the pain and records it in the previous form and completes it with each nursing shift and can be re-evaluated more according to the patient's condition:
1. The responsible nurse will reassess the pain once before and after the surgeries, once every hour for 3 hours, and then every shift or as ordered by the doctor .
2. The responsible nurse re-evaluates the pain if pain is present and an hour after pain therapy is given.
Responsible :nursing staff-doctor .
Models: pain assessment model .
References: - approved Egyptian accreditation standards
Annexes: clinical evidence for the indications for the use of drugs used to treat pain
|
Preparation |
|
|
|
|
|
