Part Two
| Site: | EHC | Egyptian Health Council |
| Course: | Procedural work guide for the operations unit |
| Book: | Part Two |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Monday, 23 December 2024, 5:04 PM |
Table of contents
- - A brief overview of the policies
- - Evaluation policies
- - The policy of the time frame for completing the assessment
- - Registration policy and nursing plan
- - Policy of evaluation and identification of patient categories
- - The policy of unified and fixed content of the patient's medical file
- - The policy of who has the right to write and view the medical file
- - Medical records protection and disposal policy
- - Pathological examination process Policy and information
- - Patient management policy and coordination
- - Transfer, referral and discharge policy
- - Hospital Medical Emergency Response Policy
- - Health education policy for patients and their families
- - Unexpected events policy incident reporting policy
- - Patient rights and responsibilities policy
- - Policy of rejection of complaints and suggestions of patients
- - The policy of obtaining written consent and informing the patient of the result
- - The policy of correct identification of the patient
- - The policy of handing over patients ' conditions and the tradition of wrong access to catheters
- - Safe use policy and prevent the fall of patients
- - Standards for medicines
- - Policy of medicines that are similar in form and pronunciation
- - Transfer policy evaluation and follow-up of the patient
- - Policy of preparation, care and control of patient prevention
- - The policy of determining the place of surgery procedures before starting it
- A brief overview of the policies
The policies that will be displayed are just a sample and the hospital has the right to make the policy according to its operating system.
The policy is reviewed every three years unless there is any change in it during those three years.
At the beginning of each policy, the following table should be filled in :
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A brief overview of the policies
The policies that will be displayed are just a sample and the hospital has the right to make the policy according to its operating system.
The policy is reviewed every three years unless there is any change in it during those three years
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,2,3... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Evaluation policies
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
- The policy of the time frame for completing the assessment
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Politics :
* The hospital is committed to evaluating the patient and determining his needs in full within 24 hours of admission to the hospital.
Purpose :
* Determine the sufficient and permitted time to complete the evaluation of the patient and determine his needs.
Working procedures:
1. The resident evaluates the patient's condition upon admission to the hospital.
2. Emergency operations patient the Attending Physician assesses his condition immediately before the operation .
3. The nurse completes the nursing assessment when the patient is admitted to the hospital.
4. The evaluation of the patient's physiotherapy is done when he needs it and this is decided by the Attending Physician.
5. The consultant evaluates the patient for whom the presentation is scheduled within no more than 24 hours for stable cases / anesthesia presentations in the inpatient department.
6. The anesthesiologist evaluates the patient in emergency operations immediately before the operation.
7. The department supervisor calls the patient's social worker when he needs it.
References: Egyptian accreditation standards
|
Preparation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: re-evaluation of patients in critical and non-critical cases requiring long-term ( chronic)treatment
Purpose: to ensure the correct follow-up and continuation of patient care and evaluation
Working procedures :
First : in acute cases (care-premature babies):
The attending physicians of the departments evaluate and identify the following
1-the degree of awareness and Horizon.
2-vital signs .
3-the occurrence of complications .
4-the results of tests and treatment or( surgical interventions ) .
5-the extent of response to treatment .
o the evaluation rate is continuous and you call the deputy doctor when a critical result is issued (physiological – laboratory – radiology) and when there is pain, and the doctor re-evaluates .
o the patient's re-evaluation is documented, a follow-up observation is recorded at least once a shift ( every 24 hours), and any actions resulting from a call, emergency or important events of the patient are recorded by date and time .
Second : in non-acute cases :-
The attending physicians evaluate patients in non-acute cases and make sure
* Vital signs ·
* Occurrence of complications
* Results of tests and treatment
* Patient compliance with treatment and medical instructions .
This is done every 12 hours for the internal department by the specialist or the doctor on duty, unless the clinical evidence requires less and this is proved in the patient's file .
Third: cases that need a long - term (chronic diseases )
The attending physicians in the departments that care for patients who need long-term or (chronic) treatment and ensure :-
* Vital signs ·
* The occurrence of complications .
* Results of tests and treatment .
* The extent of the disease progression.
The rate of Re-evaluation is once a day by the doctor on duty or as required by clinical evidence and proof of this in the patient's file.
1. The specialist re-evaluates the patient from various specialties during the patient's stay in the hospital to find out the extent of response to treatment and how effective it is .
2. Shift nursing re-evaluates the patient every shift to determine the patient's needs .
Fourth: cases that need to be re-evaluated
* Treatment plan developed for the patient Individualized care plan
* Change in the patient's condition change inpatient condition
· Patient diagnosis
· Desired outcome of care, treatment or service
* The extent to which the patient has responded to previous treatment patient response to previous treatment
3. The reassessment is documented in the patient's file
The patient should be re-evaluated immediately before the administration of anesthesia
Fifth: the content of nursing reassessment
1-vital signs: every 6 hours in the internal departments, every two hours in the care, early, after blood transfusion, before surgery, during recovery, and when the patient complains that it needs to be re-measured or according to the doctor's instructions.
2-pain:
3-the probability of the patient's fall: every seizure.
4. skin condition: every shift (skin color during awakening).
5-nutritional evaluation: when the patient needs according to the doctor's orders.
6-measuring blood sugar: according to the doctor's instructions.
7-the patient's need for restriction or isolation: according to the doctor's orders .
Forms: medical follow-up form.
References: Egyptian accreditation standards
|
Preparation |
|
|
|
|
|
Assessment, reassessment and pain management policy
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: the hospital is committed to the process of assessment, reassessment and pain management .
Purpose: to clarify the process of assessment, reassessment and treatment of pain.
Actions :
1 - the nurse in charge evaluates the pain (according to the following table), finds out its intensity, describes the pain and its frequency by asking the patient and looking at the patient's facial expression (in case he is unable to speak or in case he is a child) and records this in the pain assessment form and saves in the patient's file when the patient is hospitalized.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
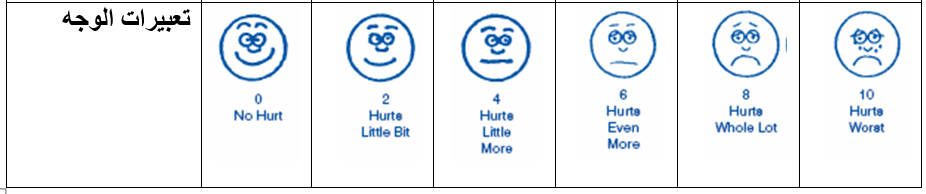
2-the Attending Physician draws up a pain treatment plan and records it in the patient's medical file .
3 - the responsible nurse implements the treatment and follow-up plan according to the pain model and the doctor's instructions .
4-the responsible nurse re-evaluates the pain and records it in the previous form and completes it with each nursing shift and can be re-evaluated more according to the patient's condition:
1. The responsible nurse will reassess the pain once before and after the surgeries, once every hour for 3 hours, and then every shift or as ordered by the doctor .
2. The responsible nurse re-evaluates the pain if pain is present and an hour after pain therapy is given.
Responsible :nursing staff-doctor .
Models: pain assessment model .
References: - approved Egyptian accreditation standards
Annexes: clinical evidence for the indications for the use of drugs used to treat pain
|
Preparation |
|
|
|
|
|
- Registration policy and nursing plan
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Politics :
The services department is committed to providing nursing care according to the patient's needs and documenting them in the nursing care plan for each patient.
Purpose :
1. Understand the patient's needs and meet them.
2. Providing high-quality nursing care.
Steps:
The nursing team performs :
1. Make a nursing assessment of the patient upon admission and identify the patient's problems.
2. Write down the patient's nursing problems in the nursing plan, including: (problems / needs - nursing intervention-evaluation-signature).
3. Write the necessary procedures to help solve nursing problems.
4. Re-evaluation to determine the patient's response to nursing interventions.
5. The supervisor of the department follows up the plan and implements its procedures.
In charge :
Department supervisor-responsible nursing.
Models :
Sample nursing care plan.
References :
Comprehensive hospital accreditation guides.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy:
the nursing services department is committed to accurate nursing registration 24 hours a day in a correct, accurate and readable manner
Purpose:
Registration of all patient data.
Teaching the members of the health team to register in the nursing forms in a correct, accurate and readable way.
Steps :
The members of the nursing team :
1. Registration of each activity performed for the patient from the moment of his entry in his form.
2. The team begins by evaluating the patient with the form prepared for this.
3. The main complaint of the patient is identified and the needs are identified.
4. Planning the care that will be provided to the patient.
5. Implement the plan carefully to get the desired results.
6. Evaluate the plan every shift to identify the development of the situation.
7. Repeat any of the steps of the plan in which the patient's condition has not improved.
8. Follow-up vital signs and inform the doctor when there is any change from normal rates.
9. The need to work and file a report on any emergency incident during the work period, such as (patient's fall-patient's escape _ error in giving treatment ).
10. The members of the health team should take care of recording the nursing development, including (the patient's condition-the doctor's recommendations-all medical procedures, analyzes and rumors-surgical interventions-nursing intervention-the patient's assessment has not been updated of signs and symptoms).
In charge :
Nursing staff members
Models :
Nursing notes-nursing assessment-vital signs-nursing care plan-treatment maps
References:
Operational Manual of Nursing Services at the Ministry of Health.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Policy of evaluation and identification of patient categories
Patient evaluation policy for abuse or neglect
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: the hospital is committed to preventing harm or neglect of patients while they are in the hospital and dealing with those cases as soon as they occur to remove harm from patients or neglect while dealing with them.
The purpose: is to develop methods of dealing with patients in case of abuse or neglect .
Ill-treatment: the patient while in the hospital, which leads to his exposure to physical, psychological or both harm/ injury, and there are types
Different types of mishandling can be divided into :
Mental abuse :
By influencing the mental state .
Manifestations of mental abuse:
* Verbal abuse .
* A threat .
* Intimidation .
* Isolation .
* Insult ·
* Humiliation .
* Deprivation .
Physical abuse :
By affecting the physical condition of the patient by exposing the patient to the ( beating - slapping - kicking ) .
Manifestations of physical abuse:
* The fall of the patient .
· The appearance of bedsores in the patient .
* The presence of wounds that are not well cared for .
* The presence of unexplained wounds .
* Physical pain when touched .
* The presence of marks as a result of biting, scratching, abrasions or bruises .
* The presence of signs of dehydration, unjustified malnutrition, patients, sunken eyes or the presence of eye injuries .
· The presence of blood stains in underwear .
Sexual abuse; :
The patient has been subjected to any form of sexual assault / harassment .
Physical abuse:
Manifestations of physical abuse :
* Theft .
* Misuse of money and property .
* Blackmail .
* Fraud .
* The presence of abnormal actions of the patient's bank account.
* Indifference in the disbursement of financial amounts .
Negligence :
It is any negligence [negligent treatment] harming a patient in need without an acceptable medical reason by a responsible person while the patient is in the hospital .
People in need :
A person who needs the help of another person due to (intellectual disability, lack of age, brain atrophy / dysfunction) which hinders the person's ability to protect himself or provide his own care.
Types of possible neglect to which the patient was exposed :-
* Negligence in medical and nursing care .
* Neglect of administration of treatment doses.
* Neglect of social and psychological needs .
* Lack of food/ water .
* Placing the patient in an unsafe or unattended place .
Actions : -
1. The doctor and the nurse assess the patient's condition and determine his treatment needs.
2. The doctor and the nurse introduce the patient to the treatment plan and how to implement it.
3. Nursing teaches the patient how to call her when needed
4. The social worker visits patients daily in the internal departments to monitor patient complaints to report them to the administration and those responsible for resolving their complaint
5. If a case of neglect or ill-treatment is detected, the patient's attending physician is informed:
- The Doctor assesses the patient's condition, identifies manifestations of abuse or neglect, a report is written with adherence to physical and psychological treatment of cases .
- The doctor asks the patient to write his complaint (for the damage caused to him ) if he wants it with an appendix with or without a signature.
- The head of the medical authority shall assign whoever he deems appropriate to investigate and follow up the complaint and then the results will be presented to him for necessary action.
Responsible : - doctor – nursing-social worker.
Forms: - the patient's rights and duties form-the form of confirmation of the existence of secretariats
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: the hospital is obliged to specify the minimum requirements for medical examination of the patient upon admission.
Purpose: to determine the minimum medical examination and medical history necessary to evaluate the patient upon admission to the hospital.
Working procedures:-
1. The department doctor takes the patient's medical history and examines the patient upon admission according to the medical history and examination form, which includes :
* Personal history of the patient and explains (name, gender, age, profession, marital status, national ID card, special habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. The doctor conducts a clinical examination of the patient and includes :-
* Measurement of vital signs (pressure – pulse – temperature ).
* Comprehensive examination of all parts of the patient's body .
* Local examination of the place of the patient's complaint by various manual examination methods.
* The doctor records the result of the examination, the results from the date of admission and clinical examination in the patient's file (preliminary diagnosis) .
* The doctor records the initial treatment plan
3. Based on what he has arrived at and according to the patient's need, the doctor will write the order in writing in the doctor's orders form to do the necessary tests and radiographs for the patient and specify the vital signs notes to be taken and the dates of registration by the nursing staff of the Department .
4. The doctor accurately writes out the drug therapy in the form of prescribing and carrying out treatment .
5. The doctor selects the appropriate type of nutrition for the patient in the doctor's order form.
6. The nurse records the patient's data in the food form to bring meals to the patient .
7. The Attending Physician informs the patient and his relatives about the initial diagnosis, the treatment plan or surgery, the possible results, the expected complications and the nutrition system .
Responsible: specialist doctor
Forms: medical history and medical examination form – food form-doctor's orders form.
References: Egyptian accreditation standards
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Politics:
Patients with critical conditions most at risk should be identified and followed up and then the medical team will start the evaluation process and the plan will be coordinated and applied with the patient and the family .
Purpose:
* Identify the most vulnerable patients such as children, individuals with special needs, the elderly and psychiatric patients in the hospital and the necessary special assessment for each of them.
* Patients who require special services regarding hospital care :
◾ Age 75 years or older .
◾ Alteration of the state of consciousness or related disorders (States of mental disorders).
◾ Injuries, multiple fractures, fractures of major joints.
◾ Malnutrition, dehydration, microbial poisoning.
◾ Patients with delayed cases.
◾ Children.
◾ Victims of violation, negligence or injuries.
◾ Patients of the dialysis department.
◾ Intensive care patients.
◾ Patients with chronic diseases.
◾ Patients prone to falls.
◾ Patients prone to bedsores.
* Patients taking sedative drugs and diuretics.
Actions:
* The medical team matches the high-risk cases for each patient within 24 hours of admission to the hospital and if the patient's condition matches one of the following conditions, the expected signs of severity for the patient are determined.
* Doctors and nursing staff record current and expected problems, Major and alternative solutions in care plans.
* Doctors and nurses follow up the cases and re-evaluate them according to the requirements of each case.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- The policy of unified and fixed content of the patient's medical file
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy:
Staff familiarity with the established composition of the patient's medical record .
Purpose :
* The presence of a medical record for each patient who has been examined and treated.
* The established composition of the patient's medical record contains sufficient information such as:
◾ Identify the patient by name – address-file number.
◾ Allows continuity of care .
◾ Confirm the diagnosis .
◾ Justification of treatment.
◾ Documentation of treatment steps and results .
* The components of the medical records of patients in the hospital are unified and specific in form, and doctors and nurses are committed to using the forms optimally and contain:
◾ Write treatment orders in a unified manner and in the same place.
* The nursing departments are committed to familiarizing the patient with all patient record forms, including:
Quadruple patient name-unified number
* It is done with examination reports, rumors, medical report and a copy of the discharge summary of the patient's file .
* The medical team corrects or amends one of the data recorded in the medical record by putting brackets around inaccurate data, taking into account ensuring that it can still be read, signing in front of it and recording the date and time of Correction, where it is not permissible to erase or delete erroneous data .
* Availability of consultation data as evidence that the consultant reviewed the patient's medical record and the results he reached when signing the medical examination, as well as the consultant's opinion and recommendations .
* Issuing oral diagnostic and therapeutic orders to a qualified nurse .orders must be signed within twenty-four (24) hours and all orders must bear the date , time, signature and applicable procedures.
* The clinical data recorded in the medical record and any other data and signatures are clear and legible .
* Send a referral form with the patient when he is transferred to another hospital, keeping a copy of the patient's file.
* Give the patient an updated discharge summary .
Actions:
The nursing staff members make sure that the file contains the following data when entering :
* Quadruple patient name-unified number-age .
* Name, address and phone number of a relative of the patient or who can be contacted in case of emergency.
* The nursing staff members do the following:
* Write the name of the quadruple patient and his unified number on all pages of the medical file .
* Registration of vital signs and the patient's satisfactory condition with the vital signs register and the nursing notes register
* Modify the treatment implementation plan according to the doctor's modification on the doctor's Orders page.
* Doctors do the following :
* Complete the patient examination record and the record contains the following data:
* The type of allergy suffered by the patient, if any .
· Whether the patient has any chronic infectious disease such as hepatitis .
* Diagnosis when the patient is hospitalized .
* The patient's complete medical history: previous, current and family medical history .
* A detailed statement of the clinical examination of the patient and a statement of the results and the action plan.
* Mention the results of laboratory tests and radiology
* Clearly write the type of treatment applied on the doctor's Orders page .
* Request all required examinations or tests on the clinical progress page
* Record all types of follow-up, consultations, routine and special treatments appropriately in the appropriate forms.
* Take notes of the development of the condition at least daily for patients with serious conditions, as well as for patients whose conditions are difficult to diagnose or control their clinical problems, and notes of the development of the condition should be recorded at the time of observation to allow continuity of care and the possibility of transferring the patient from one department to another, as well as On the other hand, comprehensive notes on the development of the condition during the surgery and immediately after the completion of the surgery should be made in the medical record in order to provide correct information for use by any caregiver who takes responsibility for the care of the patient afterwards
* Write all the reports of the operations immediately after the end of the surgical operation, including the patient's name, medical file number, date of the surgical operation, pre-and postoperative diagnosis, the name of the surgeon and his assistant, the name of the surgical operation, a detailed statement of the results and methods used during the operation, anesthesia, samples taken, the amount of fluids secreted, complications, and The reasons for the surgery and the patient's condition before the operation.
Writing a discharge or death summary in all medical files of hospitalized patients, including
◾ Entry and exit dates .
◾ Preliminary diagnosis-the final diagnosis .
◾ Analysis .
◾ The actions that took place .
◾ Medical drugs and other treatments .
◾ The patient's condition and the next stop at discharge .
Exit instructions include food, medication and follow-up instructions .
◾ The name of the doctor who discharged the patient .
Completing the referral form as follows:
◾ The reason for the referral
◾ The required means of transition and follow-up
◾ Case description
◾ The next stop
The medical file of the emergency patient contains :
◾ Patient arrival time and discharge time .
Final results at the time of completion of treatment.
◾ The patient's condition at discharge .
◾ The patient's destination at discharge .
◾ Medical care instructions for patient follow-up .
◾ Document the order of discharge from the Attending Physician .
Responsible: members of the nursing and medical staff .
Forms: patient records-the content of the medical file for each department.
References: directory of medical records of the Ministry of Health .
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- The policy of who has the right to write and view the medical file
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy:
the medical team of nurses and attending physicians is authorized to write in the patient's medical file with their clear and legible names and their job title, provided that the information is clear and in a legible font, with the date and hour written.
Purpose:
to determine who has the authority to write in the medical file.
Actions:
* The members of the nursing staff, when recording their performance in the patient files, are obliged to write their names (Triple name) and record the date and hour.
* When registering in patient files, doctors are obliged to write their names (Triple name), use cliches, write the date and hour.
* All researches, examinations and treatments that require the patient to sign from the attending physician with the writing of his Triple name and his seal.
* The person doing the medical and Radiological analyzes signs the results of the analyzes and the Radiological reports with his Triple name or his aclash and writing the date and hour.
Responsible members of the nursing and medical staff .
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Politics:
* The medical record is considered a legal document and therefore its confidentiality must be maintained and this confidentiality is the basis of the legal aspect of the medical record.
* Establish controls to maintain the confidentiality of information and determine who has the right to access the medical record and the data allowed to access them .
Purpose: -
maintaining and protecting the confidentiality of the patient's information and data .
Actions:-
* All hospital staff sign a declaration of confidentiality of patient information .
Conditions under which information in the medical file is allowed to be viewed :-
· If the file is requested from the medical team to view the patient's tests or information of clinical value, the doctor writes the request to extract the previous file in the current file and the doctor signs it clearly and with the date, then submits the file to the medical records officer to extract the medical file .
· In the case if the student is sick himself or his legal representative or external bodies such as (administrative prosecution - Public Prosecution-inspection bodies-Ministry of Health ), the hospital director or medical director will review the application and provide information in one of the following ways :
◾ Verbally .
◾ A photocopy of the original from the file.
◾ Summary of the case .
◾ The original file, and in this case, a representative from the hospital will forward the file and return it after the end of the decision .
· In case the patient is transferred to another hospital, the specialist fills out the transfer form with a summary of the case( diagnosis - reason for transfer ) .
· In case of requesting a medical report on a case, the patient or his legal representative submits an oral request to the medical records office official to address the Attending Physician to write the report on the case, which is done on the same day and delivered to the applicant .
* The hospital has the right to withhold some of the patient's medical information in the event that the information represents harm to the patient, such as ( the patient's knowledge of the nature of the patient's pathological condition may affect his psychological condition and lead to deterioration of his condition ).
* List of authorized persons to view the medical file at the hospital :
◾ The doctor in charge of the case .
◾ Doctors from other departments who are consulted about the patient's condition .
◾ The nurse in charge of the case .
◾ The patient or his legal representative with the authorization of the patient .
◾ The director of the hospital .
◾ Medical director .
◾ Coordinator of quality and performance improvement .
◾Judicial and supervisory authorities and the Ministry of health when needed .
◾ Medical Statistics Officer .
◾ The accounts officer.
|
|
ا |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Responsible: all employees of the hospital.
Forms: declaration of confidentiality of information
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Medical records protection and disposal policy
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: protection of medical records and information from loss, damage, tampering and unauthorized use
Purpose: to ensure the preservation of the medical file from being lost or damaged and to ensure the preservation of the patient's medical information for retrieval when it is needed .
Actions:
The medical record keeping room at the hospital meets the following specifications :
* Ventilation is sufficient .
* Lighting is sufficient .
* Fire Protection .
* Keep shelves intact .
* Offices for employees .
* Access to the place of filing is not allowed to non-authorized persons (patient affairs staff only) .
* The medical records bureau officer keeps the patient's medical records on the shelf in the order of the month for each department.
* The medical records office Officer repairs all records with loose papers or torn covers immediately before the important information recorded in them is further lost or damaged.
* The official of the medical records office saves all reports related to diagnostics, examinations, etc., such as medical reports or laboratory results... In the medical file, except for radiology, it is kept in the radiology department .
· There is a record of recording requests in the place of filing files, including borrowed files and the person who borrowed the file from authorized persons to view the file .
* The responsibility of maintaining the cleanliness of the place and the proper arrangement of files on the shelves lies with the medical records clerks assigned to work in the place of filing files.
Responsible : medical records office
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Purpose:
to dispose of medical files by legal methods and clarify the legal period for keeping records and files .
Politics:
* Disposal of records within the specified period in accordance with regulations and laws.
* Get rid of the records completely to prevent them from being viewed by anyone or extract identical copies from them.
* Records may not be disposed of except on the basis of an administrative order issued by the director general of the hospital.
Actions:
* Inactive medical records may be disposed of after the expiration of a certain period of time determined by the guidelines of the Ministry of Health.
* Records to be disposed of must be recorded according to the patient's name, medical file number and the last date of activity.
* Records must be completely disposed of to prevent them from being viewed by anyone or to extract identical copies from them.
* On the first of December of each year, the medical records officer and a clerk review the medical records to extract what has expired from the prescribed periods of preservation and deserves to be dispensed with Permanently' in accordance with' the guiding policies of the Egyptian Ministry of Health website.
* The medical records officer keeps all records related to lawsuits or other investigations of a confidential or serious nature and does not dispose of them until after the completion of lawsuits .
* On the first of January of each year, the medical records officer examines the dispensed documents and after confirming the validity of the dispensing, they are packed in bags by the Department's workers to be handed over to the Directorate of Health Affairs for disposal in accordance with the' archives regulation '.
* The schedule for maintaining medical files and records is as follows .
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In charge
* Medical records department
References
* Directory of medical records of the Ministry of Health
* Guiding policies of the Egyptian Ministry of Health website.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Pathological examination process Policy and information
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: the hospital is committed to conducting a priority assessment of patients ' needs for therapeutic and nursing services when the patient is admitted to the hospital and the appropriate department for the patient's condition .
Purpose: to provide medical care to the patient according to his condition and in accordance with the priorities and clinical work guides (therapeutic, diagnostic, analgesic), when the patient is admitted to the inpatient department of the hospital .
Working procedures:
* The nurse in charge of the internal department conducts the initial nursing assessment of the patient's condition using the nursing assessment form .
* The responsible internal department nurse performs pain assessment according to the pain assessment model .
* The nurse responsible for the case develops a nursing care plan according to the nursing assessment and documents it in the nursing plan form .
* The responsible nurse of the internal department contacts the competent doctor and informs him of the patient's condition .
· The specialist doctor will review the medical history, complete the medical examination and determine the patient's needs for medical care.
The specialist doctor will develop a treatment plan for the patient according to the priorities and treatment protocol of the case, including :
* Necessary examinations .
* Required analysis .
* Treatment according to the prescribed treatment model .
* Follow-up and observation required .
· Any other instructions .
The responsible nurse implements the treatment plan in the form of examinations and research, which is specified by the timing of the request and the execution hour
Responsible: attending physician-nursing staff
Models :
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
References :
* Approved Egyptian accreditation standards
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: the hospital is committed to familiarizing and informing the patient and his relatives upon admission with the necessary information to make the appropriate decision to treat the patient .
Purpose: to determine the information that is given to the patient and his relatives upon admission to the hospital, which helps to make the appropriate decision to treat the patient, N8 and achieve the preservation of patients ' rights, facilitate the period of stay and obtain the required medical care, and inform patients of their responsibilities towards the hospital, which achieves the satisfaction of patients and their families .
Working procedures:
* When the patient enters the hospital, the receptionist or the admission office will introduce the patient and his relatives :
* The bill of rights of patients .
* Document the duties and responsibilities of patients .
* Instructions of the hospital regarding visiting and food / and non-smoking .
* The receptionist / entrance office will inform the patient about the cost of accommodation and treatment and view the price list in accordance with ministerial decree 186 of 2001 .
* The Attending Physician introduces the patient / his relatives with the necessary information that will benefit them to make an informed decision, including :
* The nature of the disease and diagnosis .
* The expected result of treatment .
* Planned date of discharge from the hospital .
* Suggested treatment steps .
Responsible: attending physician-nursing staff .
Forms: conversion form .
References: approved Egyptian accreditation standards
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Patient management policy and coordination
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: the hospital is committed to finding an alternative solution for the patient in case there is no place for the required service in the hospital.
Purpose: to know how to act in case there is no place in the required service at the hospital .
Working procedures:
* When a case is discovered that there is no available place to provide the required medical service at the hospital, the attending physician provides first aid to the patient and writes a report on the case .
* The hospital helps the patient and his family to find an alternative place through the emergency department and the Directorate and give a report to the patient's parents about the situation .
* After confirming the approval of the hospital to which the transfer will be made, the doctor responsible for completing the transfer procedures .
* Providing an equipped means of Transportation suitable for the patient's condition.
* The attending physician writes the special data in the transfer form and keeps a copy of it and is attached to the report on the patient's condition with the provision of appropriate facilities for the patient .
* The attending physician provides medical instructions to the patient and his companions during transportation .
Responsible:
attending physician-nursing staff
Forms :
conversion form
References :
* Approved Egyptian accreditation standards
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: the hospital is committed to providing means of coordination and cooperation between all departments .
Purpose: to know how to coordinate the provision of medical care to all patients .
Working procedures
* Coordination between doctors and nurses .
* Timely execution of nursing doctor's orders .
* Registration of delivery and delivery for each category and execution of follow-up and required orders.
* Medical consultation .
* Coordination between departments during transportation or ordering diagnostic services :
* The use of policies that determine the appropriateness of patient transfer within the hospital :
* Surgical and non-surgical treatment services after medical consultation and acceptance of the case .
* Diagnostic and therapeutic services .
* Emergency services and internal department .
Responsible: attending physician-nursing staff
Director, his deputy or administrative deputy
Forms :conversion form .
References: approved Egyptian accreditation standards
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Transfer, referral and discharge policy
Policy name |
Patient transfer, referral and discharge policy |
|
|
|||
|
Issue date and number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Section |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Hospital Medical Emergency Response Policy
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: the hospital is committed to responding to medical emergencies .
Purpose: to equip the departments to deal with emergency cases that require emergency handling with the development of a system to respond to the emergency call .
Procedures:
* The nursing supervisor of each role equips an emergency vehicle with life-saving medicines and tools according to the attached list that specifies the components and arrangement of the emergency vehicle, provided that the vehicle is nearby and available for use 24 hours a day .
* A supervisor of each role reviews these vehicles daily .
* The pharmacy department at the hospital assigns a pharmacist to pass on the emergency vehicle and check its contents and validity daily .
* The medicines used from the emergency trolley are replaced immediately after use from the emergency cupboard of the department that used them, and if these medicines are not available in the emergency cupboard of any department, they are replaced from the intensive care emergency cupboard until they are dispensed from the hospital pharmacy.
* The hospital ( training officer ) is committed to the existence of training courses on cardiorespiratory resuscitation for all employees (doctors and nurses) in the hospital on a one-day basis every two years.those who receive the course are granted a certificate stating this and it is specialized to follow up the access of employees to the courses by their direct superior.
* Any of the hospital staff suspected of having a cardiac arrest condition will call the cardiorespiratory resuscitation team by calling the intensive care and nursing home or by switch to make a call and indicate the role/ Department and the number of the room to be moved to.
* Nursing role calls the rest of the team in case the Switch is not available.
* Cases of cardiac arrest that occur in intensive care, in which the care doctor is called and the cardiorespiratory resuscitation team is not required unless the care doctor requests it and his responsibility is to supervise the resuscitation of the patient.
* Cases of myocardial arrest that occur in operating rooms and units where the patient is supervised by an anesthesiologist, the cardiorespiratory resuscitation team is not called unless the anesthesiologist requests it and he is responsible for supervising the resuscitation of the patient.
· The first to arrive at the patient performs CPR.
* The cardiorespiratory resuscitation team consists of an intensive care doctor and a nurse from the care in addition to the case doctor, the nurse of the floor/ Department or room and a security individual (depending on the subject schedule).
* Bringing the emergency vehicle with the responsibility of nursing the role in which the cardiac arrest occurred.
* The team leader is the intensive care doctor who is responsible for giving electric shocks, obtaining a clear airway and respiratory passage, and participating in cardiac resuscitation operations.
* The case doctor is responsible for explaining the patient's condition, reviewing the patient's files and informing the team leader of any information he needs.he is also involved in the work of cardiac resuscitation and is responsible for communicating with the patient's parents and informing them of the patient's condition developments and involving them in any medical decision that needs their participation.
* The intensive care nurse is responsible for giving medicines and withdrawing samples requested by the team leader and assisting the rest of the team members according to the instructions of the team leader.
* The nurse of the role/ Department is responsible for recording the events of cardiac arrest, the dates of administration of medications, The Shape of the heartbeat and the date when the heart returns to beat in the form provided for that, and is also responsible for giving breathing to the patient in the manner determined by the team leader.
* The security officer provides the appropriate atmosphere for the work of the team and is present when informing the patient's parents of any developments in his condition.
* It is necessary to work on providing places of care on an ongoing basis in order to receive post-myocardial infarction cases that may occur in the hospital after first aid work in the internal department and stabilize his condition.
* The medical team is trained to respond quickly and immediately upon call, and all members of the medical team must be present in the emergency room and deal with the case in accordance with the policy of cardiorespiratory resuscitation.
* The callback system is tested unexpectedly by The Unit Manager/ Quality Coordinator at the hospital to ensure that the doctors and nurses respond to the call and calculate the time between the call and response as a kind of performance assessment within the unit with the results being submitted to the hospital quality coordinator.
* Cardiorespiratory resuscitation is performed according to the attached protocol.
* All hospital staff are trained to deal with cases of myocardial arrest (basic level), while the doctors of care and anesthesia are trained at the advanced level.
In charge:
· All hospital staff - cardiopulmonary resuscitation team .
Models:
Table of Contents and arrangement of the emergency vehicle
Monthly CPR team schedule
Cardiorespiratory resuscitation protocol
References:
Egyptian quality standards.
Cardiorespiratory resuscitation protocol
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Health education policy for patients and their families
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: providing health education to patients visiting the hospital and their families ensures that patients are provided with important information that helps to heal and prevent them from diseases when they enter the hospital, while they are in the hospital and after discharge, and this is evidenced in the hospital's commitment to educating the patient and his related relatives as follows:
* Pathological diagnosis of the patient .
* Tests, diagnostic tests and treatment .
· The use of medicines and possible side effects .
* Nutrition.
* Interactions between food and medicine .
* Physical therapy and rehabilitation .
* Special information on how to reduce the risk of diseases through nutrition .
* The harms of smoking and the need to stay away from active and passive smoking .
* Exercise and health-related behaviors.
* The relationship between the patient and the community .
* Exit and follow-up instructions .
Purpose: to improve health care outcomes by educating the patient and his relatives to help in recovery and to enhance the value of health behavior by providing health information about the various medical specialties necessary for the patient.
Actions:
* According to the professional ethics regulation 238 of 2003, health education for patients and their families is one of the tasks and responsibilities of the doctor and the medical team.
* The attending physician and the responsible nurse use a special Record form to educate patients and their families.
* The Attending Physician, the responsible nurse and the patient's medical service provider assess the patient's educational level and determine the educational needs upon admission of the patient.
* Any department participating in the seminars registers its seminar with its signature and date in the educational register of patients
· If abbreviations are used, an explanation is provided for each abbreviation to clarify the information.
* The attending physician and the responsible nurse make sure that the patient's educational record contains the type of information provided to the patient and to whom the information was provided, the extent of the patient's response or his relatives, and the summary of the educational episode that was done to the patient.
* The attending physician and the responsible nurse make sure that the forms of the departments participating in the educational seminars are placed in the educational register of patients.
* The attending physician and the responsible nurse make sure that the patient's questions are given the opportunity.
* The attending physician and the responsible nurse make sure that the patient understands the exit instructions and follow-up steps, provided that this is recorded in the patient's file.
* The hospital provides a special place for receiving educational seminars for patients in inpatient and outpatient departments.
* The hospital is committed to developing a standard educational material for chronic diseases / dialysis patients .
In charge:
* Attending physician-nursing staff-medical service provider from any department involved in patient education
Models :
* Patient and family education model
References :
* Professional ethics regulation-Egyptian quality standards
|
Preparation
|
Review
|
The trusted |
|
|
|
|
- Unexpected events policy incident reporting policy
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Politics :
A policy clarifying a reporting system for near misses / incidents that enables employees to report them in order to assist in continuous performance improvement.
Purpose :
Provide an organized mechanism in the hospital to identify problems that lead to negative outcomes for both patients, visitors or employees in order to detect them early and prevent their occurrence.
Definitions :
* Near fault: an unplanned accident with the potential to cause damage that was intercepted in time or by chance resulted in no harm to the person.
* Incident / accident: any incident that occurs in the hospital (not representing routine patient care) that negatively affects or could affect the health or life of patients, visitors or hospital staff.
Procedures
General procedures :
* The report must be written and completed by the person who discovered the incident or the person involved in this incident.
* The report must be written immediately after the discovery of the incident and submitted to the quality coordinator no later than 48 hours .
* The quality coordinator presents the report to the head of the relevant department and the hospital director to take corrective measures .
* Confidentiality must be observed in dealing with or maintaining these reports, limiting access to them to persons with authority for this.
* Do not use the information contained in this report as a means of taking disciplinary action against anyone.
* These reports should generally be discussed at meetings of the quality Committee and the medical board committee for educational purposes or to develop instructions that limit their occurrence.
Constituent items of the report
* Information about the infected person and the department in which it is located.
* The type of unexpected incident / event that is significant.
* Information about the near error / incident / unexpected event that is significant.
* A description of the incident with an indication of any action taken immediately after the discovery and the factors that led to this incident.
* Corrective actions that have been taken.
* The data of the person who discovered the unexpected incident / event that has significance and filling this part is not mandatory.
* The head of the department checked the report.
* Instructions of the hospital director.
The persons responsible for writing the report
* All hospital staff, including doctors, nurses, pharmacists, chemists, radiology technicians and non-medical service personnel .
Plan corrective actions and assigned responsibilities in case of unforeseen accidental events :
· After the report reaches the quality coordinator at the hospital (within 48 hours of the incident), he reviews it and refers to the head of the department where the incident occurred and the person or persons who discovered the incident to find out the reasons that led to the incident, and this is done within 48 hours of the report's arrival to the quality coordinator.
* The quality coordinator (or whoever is assigned by the quality team) classifies this incident in terms of being (environmental safety - medication - patient safety)
* The quality coordinator ( or whoever is assigned by the quality team) will refer to the ( environmental safety officer – pharmacy manager – Patient Safety and security officer ) according to the classification of the incident to make recommendations with the quality coordinator (or whoever is assigned by the quality team) not to repeat this incident again.
* After making the necessary recommendations to avoid the occurrence of this incident, a corrective plan is developed to implement these recommendations by the quality coordinator and the responsible person according to the classification of the incident and the head of the department where the incident occurred.
* The corrective plan includes the recommendations, who is responsible for the implementation of each recommendation, the time frame for implementation and the required resources.
* The quality coordinator (or whoever is assigned by the quality team ) follows up the implementation of the set corrective plan and submits a report on it for discussion at the meeting of the quality Committee.
Responsibilities
The employee discovered the incident:
* Rapid intervention to protect or support the patient's health condition.
* Immediate notification to the existing doctor
* Write the report before the end of the lip.
The doctor who was informed of the incident
* Registration of the result of medical examination and required medical care.
Hospital director
* Review the case and ensure that corrective actions have been implemented and provide any required assistance.
Quality coordinator
* Monitor all reports and ensure that all important steps to solve the problem have been taken.
* Write a monthly summary of all reports.
* Writing a quarterly report for the quality committee to discuss.
* Keep a file of all reports that is kept for three years.
Occupational Safety and health officer
* Examine all reports related to occupational safety and health to review safety-related incidents.
* Formation of a team from the Occupational Safety and health committee to review safety-related incidents.
* Record the results of the examination and the corrective actions taken in the report.
* Return the updated report to the quality coordinator.
* Writing a monthly summary and presenting it to the Occupational Safety and health committee.
Responsible for implementation:
* Employee incident Finder .
* The doctor who was informed .
* Head of Department .
* Director of the hospital .
* Quality coordinator.
* Responsible for Occupational Safety and health.
References
* Egyptian accreditation standards-regulations and laws
Models
* Incident report form
Annexes
* Near accidents and errors that need to be reported at the hospital.
|
Preparation
|
Review |
The trusted
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
* Escape of the patient
* The patient's suicide, suicide attempt and violence.
* Unexpected mortality and complications, including those resulting from infections acquired from the institution.
* Confirmed transfusion reactions (routine adverse reactions such as chills and fever are excluded from this).
* Significant events in anesthesia and analgesia that caused harm to the patient.
* Significant differences between preoperative diagnosis and postoperative diagnosis including the results of surgical pathology.
* Adverse reactions to significant drugs that caused harm to the patient.
Significant medication errors that have caused harm to the patient, such as :
◾ Giving the wrong medicine.
◾ Giving the wrong dose.
◾ Giving medicine the wrong way.
◾ Giving medicine to a patient is wrong.
Related to operations :
◾ Cancel the operation .
◾ Unexpected removal of any organ .
◾ Wrong patient .
◾ Wrong counting of tools .
◾ Cases of error in the operation (patient – operating entity – procedure) .
◾ Leaving a foreign body in the patient.
Related to the lab :
◾ Wrong sample data .
◾ Sample it wrong .
◾ Inappropriate storage .
◾ False lab results .
Related to the hospital :
◾ Injury of a visitor .
◾ Bed sores .
◾ Wrong needle injury .
Security neutrality :
◾ theft or loss of personal property .
◾ Fight with a visitor or a patient .
◾ Failure to follow hospital policies .
◾ Suicide attempt .
Fire and safety :
◾ Fire .
◾ A chemical spill .
◾ Blockage of one of the emergency exits .
◾ Expired fire extinguisher .
◾ Gas leak .
◾ Water leakage .
◾ Unsafe electrical wiring .
* Serious physical or psychological harm to a patient, employee or visitor (nerve damage – loss of limb or organ – death).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: The existence of standards and processes for intensive analysis of significant and undesirable unexpected events.
Purpose: To increase public knowledge about events, their causes, and strategies to prevent them, and focus the hospital's attention on understanding the reasons behind this event and changing hospital systems and processes in order to reduce the possibility of such an event occurring in the future.
Definitions
◾ A significant unanticipated event is any unexpected event in health care that results in death or serious physical or psychological injury to a patient.
Procedures:
◾ A report on the occurrence of the event is written as in the policy.
◾ The quality coordinator selects a team consisting of people close to this event and a member of the hospital’s quality team to analyze the reasons and determine the basic factors behind the occurrence of this event, provided that this is done within a month of the formation of the team.
◾ The analysis identifies changes that could be made in systems and processes (either through redesign or development of new systems or processes) that would reduce the risk of such events in the future.
The analysis must be accurate, documented, and comprehensive, including the following:
◾ Identify the human factors and other things that are directly related to the event and the processes and systems relevant to its occurrence.
◾ Analyze basic systems and processes through a series of questions.
◾ Identify risks and their potential contributions to this type of event.
◾ Identify potential improvement in processes or systems that would lead to a reduction in the likelihood of such events occurring in the future.
◾ After identifying the root causes, the team will develop a corrective plan to avoid these causes in the future, provided that the time frame for implementing this plan does not exceed three months.
Time Frame :
◾ The root causes must be analyzed and a corrective plan must be developed within a month of the event occurring.
◾ The corrective plan must be implemented within a period not exceeding three months.
◾ The root cause analysis and the implementation of the corrective plan are reviewed by the hospital’s Quality Committee.
Responsible for implementation:
Quality Committee
work team
Persons responsible for implementing the plan
The Reviewer
Egyptian accreditation standards
Regulating laws and regulations.
Models
Incident report form
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Patient rights and responsibilities policy
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: the hospital provides multiple medical services and the hospital management, doctors and staff are committed to the performance that preserves the patients ' rights and familiarizing them with them from the time they enter and during the performance of various services until they leave in commitment to the hospital's mission and to achieve the patient's needs in health care.
Purpose: to preserve the rights of patients and their relatives.
Working procedures:
* The hospital adheres to all the regulations and laws issued by the Ministry of Health and the Federation of medical professions unions with regard to the rights of patients and their families, as stated in the professional ethics regulation issued by the minister of Health Decision No. 238 of 2003 as well as ministerial decision 186 of 2001, accordingly, the hospital takes the following policies :
* The right to receive care if it is available in the hospital .
* The right to know the name of the Attending Physician, supervising physician and / or responsible physician
* The right to receive care that respects the patient's personal values and beliefs .
* The right to know and participate in decisions related to their care.
* The right to refuse or discontinue treatment: the following doctor must .
* The right to security, personal privacy, confidentiality and dignity, the patient has the right to have the following.
* The right to receive appropriate treatment for pain
* The right to make a complaint or suggestion without fear of being persecuted
* The right to know the prices of services and procedures .
First: an explanation of the patient's rights clauses:
* Rights defined by regulations and laws:
* The existence of the professional ethics regulation resolution 238 of 2003 by the hospital administration and the quality coordinator as a reference in training on the rights of patients, the regulation includes the following points:
* The first section : doctors section
* The second part: the duties of the doctor towards
* Community .
* Profession ·
* Patients.
* Colleagues.
Third: medical interventions of a special nature
* Gender correction procedure .
* Assisted fertilization operations..
* Operations of Excision and transfer of human organs and tissues
Part IV: conducting medical experiments and research on human beings
A copy of resolution 186 of the year 2001 at the emergency manager of the hospital, which includes the following:
* Patient insight into the cost of surgical operations at all stages.
* It is prohibited to detain the body of an inmate or exploit a death to obtain material benefits.
A copy of the Prime Minister's decree 1063 of 2014 at the hospital emergency manager, which includes the following:
* All medical facilities are obliged to provide emergency and accident treatment services free of charge for 48 hours, after which the patient chooses to stay at his own expense or treatment in the free Department of the hospital, provided that the state bears the costs from the budget of treatment at state expense .
* The right to receive care if it is available at the hospital in order to ensure that the hospital is able to provide the necessary medical care to the patient, and this depends on obtaining information about the patient's needs and condition through a screening and selection process by the medical team:
* Assessment of the patient's Anamnesis .
* Physical examination.
* Previous evaluations and examinations with the patient .......Etc
* The medical team provides medical care to the patient after obtaining the results of the medical examination and the necessary tests as long as the service the patient needs is available and a bed is available for this patient in the hospital.
Usually this is done at the first point of contact:
· When the patient arrives at the hospital .
· During ambulance transportation .
* Before transferring from another place.
* The right to know the name of the Attending Physician, supervising physician and/ or responsible physician.
· This is by introducing the doctor himself to the patient before dealing with him .
* An identification card drawn up by the doctor containing the name, specialty, personal photo and the name of the hospital
* Doctors wear a white Balto, blue or green suit.
* Put the names of doctors and their specialties on the door of each clinic .
The right to receive care that respects the patient's personal values and beliefs:
* Hospital staff should respect the patient's personal religious and cultural beliefs and the freedom to practice them
* Hospital staff should not prevent the patient's parents from using a clergyman in cases that need spiritual support, such as patients who are about to die .
* Hospital staff should respect the desire of Coptic patients to determine the quality of food on fasting days as long as this food does not interfere with the patient's care plan .
* Hospital staff must ensure that the patient receives the highest possible level of health care without discrimination due to age, gender, religion, race, nationality, origin, opinion, socio-economic status, disability, special needs or any other type.
* The right to know and participate in decisions related to their care.
This is done by the following:
* Taking the patient's consent (by the doctor) by signing a consent form before the following procedures: surgery and surgical interventions.
* Moderate or deep anesthesia.
· The use of blood .
* Gastrointestinal endoscopes
He also has the right to know the treatment plan and participate in its selection by the following:
* The attending physician explains the patient's medical condition, the various proposals for treatment and the various medical examinations that this entails.
* The doctor must also involve the patient / his family when drawing up a treatment plan.
* The right to refuse or discontinue treatment: the doctor must:
* Clarify the health consequences of the patient / his family resulting from the refusal of treatment.
* Clarify that the patient or those who have the legal right to do so bear full responsibility in case of persistent refusal.
* Informing patients about available care and treatment alternatives / customized discharge despite doctors ' advice
· The doctor supervising the treatment registers the refusal of treatment
The right to security, personal privacy, confidentiality and dignity, the patient has the right to have the following:
* Security: security personnel and the medical team are responsible for protecting patients from harm, theft, destruction, tampering, entering a place or using something unauthorized. This is done according to the security plan within the environmental safety plans.
* Privacy: the hospital administration is responsible for providing curtains, barriers or a sheet that ensures the privacy of the patient during :
* Medical examination.
* Conducting examinations.
* Care and treatment.
* Transportation .
* Confidentiality: members of the hospital's medical team sign an agreement to maintain the confidentiality of patient data and information.
* The medical team is responsible for not posting confidential information at the patient's door or at the nursing station.
* The medical team is responsible for not discussing the patient's condition in public places.
* The medical team asks patients for permission to release information that is not covered by laws and regulations.
* The right to access the patient's file.
While the file was in the internal departments of the hospital:
* The doctor (therapist, radiologist, laboratory doctor), the head of the department, the members of the nursing staff and the pharmacist have the right to see the patient's file.
* After saving the file, the file is reviewed by:employees of the Medical Registration Department to complete the entry and exit data.
* Judicial or prosecutorial bodies in the event of an attempt to obtain some information about the patient.
* The patient or his relatives of the first degree (after submitting an official request and approved by the hospital administration, provided that the request explains the reason for the patient or his relatives to view the file).
* Scientific studies (whether from inside or outside the hospital), and this is also after submitting an official request and approved by the hospital administration (according to the quality of the study and its compatibility with the existing cases in the hospital) provided that no personal data of the patient (such as name and address) is viewed.
* Dignity: the medical team must treat the patient in an appropriate ethical manner that preserves his dignity and prevents the wasting of any of his moral rights ( without humiliation – humiliation – deprivation ) .
* The right to receive appropriate treatment for pain: the patient has the right to receive appropriate treatment for pain at the right time according to his condition, where the nurse assesses the severity of pain and informs the doctor to review the assessment and prescribe the appropriate treatment for the patient, and this is done through a special form with details about the patient, his condition, the degree of pain, appropriate treatment and dosage (Pain assessment and treatment model )
* The right to make a complaint or suggestion without fear of being persecuted .
* The patient has the right to complain about any shortcomings he sees, as well as his suggestions for improving the service, provided that it is clarified how the patients and their families can submit a complaint or suggestion according to the terms of the complaints policy set by the hospital.
* The right to know the prices of services and procedures: the patient has the right to know the prices of various services provided by the hospital in various departments and their prices, and this is through the administration announcing the prices of some services through billboards in public places at the hospital, such as reception, provided that a person responsible for inquiries explains.
* The clerk of the admission office informs the patients or their relatives about the estimated cost of the required health care and the patient signs a general admission declaration that includes the patient's knowledge of the cost of the service after reviewing the price list.
Second: familiarizing patients and their families with their rights through the following:
* The hospital administration hangs the items of the patient's rights and duties in the boards in the patient waiting areas and in the departments.
* The admission or reception officer takes the patient's signature on the patient's rights and duties form after familiarizing him with them.
* The department supervisor makes sure that the patient understands these rights and in case the patient does not know them fully for any reason (ignorance of reading, forgetfulness, lack of ability to absorb or understand, etc.)...) The supervisor re-clarifies these rights.
* A list of patients ' rights is installed on the door / wall of all patient rooms.
* The person in charge of the Citizens Service office collects data on patient complaints daily and delivers it to the person responsible for the solution and analyzes it monthly to identify weaknesses to take corrective actions.
In charge:
· - All employees of the hospital. - Nursing department or unit.
* - Employee of the entrance office. - Citizens Service officer
Models:
* The bill of rights of patients.
* Unified emergency form .
* Sample declarations of consent .
* Pain assessment form .
* Price lists of hospital services .
References:
* Professional ethics regulation 238 of 2003.
* Ministerial Resolution 186 of 2001.
* Egyptian accreditation standards
* Prime minister's decision 1063 of 2014.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: the hospital is committed to informing patients of their responsibilities and following up the implementation of these responsibilities, and in case of violation, the necessary measures are taken according to the hospital system.
Purpose: to familiarize the patient with his own responsibilities while in the hospital.
Working procedures:
At the very least, the patient's duties include the following:
* Preservation of hospital property.
* Do not keep any personal belongings.
* Commitment to the specified visit dates.
* It is forbidden to introduce any food from outside the hospital, as the hospital provides the appropriate food for each patient.
* Stay calm and follow the regime while visiting patients.
* Adhere to the non-smoking policy.
* The possibility of having a companion for the patient if this patient is a child under 6 years of age, provided that the hospital takes a copy of the companion's ID card.
* The facilities are paid, except in some special cases where free accompaniment is allowed, and this is after taking the approval of the hospital director.
* Financial commitment in accordance with the law, regulations and hospital policy.
* Providing information: the patient is obliged to provide correct, accurate and complete information about his current illness, treatment methods and his frequency of treatment in any hospital.
* The patient is obliged to provide the required legal documents.
* Show respect to other patients and healthcare workers, help not to make noise and adhere to the visiting instructions.
* Financial commitment in accordance with the law, regulations and hospital policy.
* Following the proposed treatment plan: the patient is obliged to follow his own treatment plan, which was developed for him by the doctors, and in case of non-compliance, the nurse in charge informs the doctor in charge of the treatment, writing it in the transfer.
The patient is informed about his responsibilities by the following means:-
* The patient signs a general declaration upon admission by the admission desk employee or the receptionist stating his commitment to the hospital policy, respect for others , financial obligations and his commitment to the treatment plan.
* The nurse in charge of the internal departments reads the patient's responsibilities to him and introduces him to them with his signature in case he is unable to realize or sign his duties during his admission.
* The list of patient responsibilities is installed on the door / wall of all patient rooms.
In charge:
* Receptionist.
* Responsible nursing in the internal departments.
* Employee of the Citizens Service office .
Models:
* Document the duties of patients.
References:
- Regulation of professional ethics
- Ministerial Decree No. 186 of 2001.
- Egyptian accreditation standards.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Policy of rejection of complaints and suggestions of patients
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: the hospital is committed to ensuring the right of the patient, his family or his legal representative to refuse treatment or continue it, after making sure that he or his legal representative is informed of the results related to the refusal or non-continuation of treatment and the related responsibilities.
Purpose: to respect the patient's right to refuse treatment or not to continue treatment with the definition of the consequences of this and to hold the patient fully responsible in case he insists on refusal.
Action steps:
· The specialist doctor will inform the patient of his condition in a clear and appropriate way and introduce him to the types of treatment used for him, whether medication or surgery.
The refusal of the patient or those who have the legal right to do so for treatment or continuation of treatment is proved by the following:
* The nurse supervising the implementation of treatment for the patient registers the refusal in the patient's file.
* The nurse supervising the implementation of treatment for the patient informs the doctor of the patient's refusal or continuation of it.
* The doctor supervising the treatment explains the effect of refusing treatment or not continuing it and the health consequences resulting from this to the patient or to those who have the legal right to do so.
* The doctor will change the treatment or continue it, if possible.
* The doctor supervising the treatment clarifies that the patient or who has the legal right to do so bears full responsibility in case of insistence on refusal.
* The doctor supervising the treatment records the refusal of treatment or continuation of it in the patient's file in case the patient continues or whoever has the right to do so on the refusal with the recording of the summary of the patient's dialogue.
* The doctor registers the patient's refusal of treatment with documentation from him and the nursing staff.
· The doctor supervising the treatment makes sure to do the following steps:-
* Accommodate the patient or whoever has the right to it to describe the patient's general condition.
* The patient or whoever has the right to it understands the expected result of the refusal and the ensuing consequences.
* Understand the patient or those who have the right to it how dangerous it is to refuse treatment.
* Accommodating the patient or those who have the right to do so to bear full responsibility when refusing treatment.
* Write the statement of the patient's refusal of treatment despite the doctor's advice (the name of the attending physician) and the patient signs this refusal.
* The patient's signature on the refusal of treatment in the file and in case the patient refuses to sign, the attending physician and the responsible nurse sign this refusal as witnesses .
* The nurse responsible for carrying out the treatment records that the patient refused the treatment and left the place before the doctor came in case the patient was discharged without permission.
* The specialist doctor will prove the patient's desire to leave the hospital despite the advice of the treating team with the patient's file and prove that the risks of this procedure have been explained to the patient or who has the legal right to do so.
* The patient or the one who has the legal right to do so signs his wish to leave against the advice of the treating medical team and records the date and hour.
* The patient or the person who has the legal right to this undertakes to be shown to one of the specialized doctors outside the hospital as soon as possible.
* The employee of the Citizens Service office fills out the patient's opinion form about the medical service and clarifies any complaints to them.
* In case the patient leaves the hospital and refuses treatment despite the advice, the nurse reports the patient's escape from the hospital .
In charge:
§ The Attending Physician.
§ Nursing staff
§ Employee of the Citizens Service office.
Models:
§ Customized exit declaration form.
§ Sample patient opinion questionnaire.
References:
§ Egyptian accreditation standards.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: the hospital is committed to developing a system or procedures to ensure that patients know how to submit their complaints and suggestions to work on examining and removing the causes of complaints and studying the proposals submitted by patients and their families.
Purpose: to clarify how patients and their families submit a complaint or suggestion and to ensure that the complaint is examined, its causes are removed, and the submitted proposals are studied for the continuity of the performance improvement process at the hospital.
Means of submitting complaints and suggestions:-
- First: complaints received from outside the hospital.
- Second: complaints issued from within the hospital.
Actions:
First: complaints received from outside the hospital.
1. The secretarial employee receives the complaints received by the hospital from abroad by phone and reports them to the Citizens Service office.
2. The secretariat employee directs the complainant to the Citizens ' Service office.
3. The chairman of the complaints committee shall review the complaint and identify the responsible department or persons to verify and respond to it.
4. The person responsible (citizens ' service ) for verifying the complaint writes the appropriate response for presentation to the chairman of the Complaints Commission.
5. The chairman of the complaints committee determines the necessary action to be taken on the complaint.
6. The chairman of the complaints committee determines who sends the response to the concerned body of the complaint or calls the complainant by phone / Telegraph to schedule an appointment to meet with him and to inform him of what has been taken regarding the complaint.
Second: complaints issued from within the hospital.
1-complaints submitted through complaint boxes:
* The hospital administration sets up boxes to collect complaints from customers by distributing them in different areas in the hospital (administration building-reception)
* The Complaints Committee opens the complaint boxes, classifies them and hands them over to the chairman of the committee.
* The chairman of the complaints committee examines the complaint and writes a summary of it, if the name of the complainant is not mentioned, to be presented to the director to discuss what came of it, and if the name of the complainant is mentioned, the chairman of the committee assigns the person who answers what came of the complaint.
* The results of complaints are submitted to the manager weekly.
* The director of the hospital shall take the necessary measures according to the result received by him.
2-complaints submitted by phone call:
* The patient or his representative calls the internal number of the hospital.
* The director's Secretariat listens to the complaint and registers it in the special register, provided that at the end of the working day it informs the chairman of the complaints committee of all complaints in the register.
* Complaints are received by phone during the morning working hours (eight in the morning to two in the afternoon)
3-receiving patient complaints during personal interviews with them:
* First: the patient or his representative submits a complaint:-
The patient or his representative submits his complaint to The Citizen Service officer.
* Second: the passage of the employee of the Citizens Service office to the internal departments:-
i) the employee of the Citizens Service office visits the patients, hears their complaint, registers it in the special form and works to resolve it by contacting the official, and in case of inability to do so, he submits it to the chairman of the complaints committee.
ii) the employee of the Citizens Service Office presents the complaint form daily to the chairman of the complaints committee to discuss the problems and what has been done about them.
* Third: the passage of the coordinator of patients ' rights:-
1. The Patients ' Rights Coordinator visits a random sample of patients to hear their complaints and suggestions, make sure that the Citizens Service office employee passes by them, and record those complaints, if any, in his traffic record.
2. The Citizens ' Service officer examines the complaints he found .
3. The Citizens Service officer fills out the patient satisfaction form in the relevant department of the complaint if the complaint or proposal needs to be followed up.
Actions taken with complaints
* The chairman of the complaints committee shall address the relevant sections of the complaint or proposal either orally or in writing.
· The department concerned with the problem or proposal is obliged to research it and respond to it within a specific time period determined by the chairman of the committee.
* When the specified period of time has elapsed, if no appropriate decision has been made in the relevant department, the subject is presented to the director for a decision on it with the hospital administration.
* The recommendations of the hospital manager are followed up by the Citizens Service officer and the complainant is informed of the result .
* The confidentiality of the person reporting the complaint is maintained without exposing him or trying to harm him.
In charge:
- Head of the director's Secretariat.
- Complaints committee.
- Citizen Service officer
Models:
- Sample passage of patient complaints
- Inpatient complaint form.
- Patient survey form.
Documentation:
- Register of complaints.
References:
Egyptian accreditation standards .
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- The policy of obtaining written consent and informing the patient of the result
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy:
the hospital follows the policy of obtaining the patient's consent in accordance with the regulations and laws.
Purpose:
Maintaining the patient's rights and obtaining the patient's consent before providing a health service to him in accordance with the regulations and laws.
A-the patient's attendance at the hospital is considered an implicit consent to the medical examination and treatment, in accordance with the text of Article No. 28 of the regulation of ethics and honor of the profession of Human Medicine issued by the decision of the minister of Health and population No. 238 of 2003.
B-the patient or the person who has the right to sign legally must sign the general declaration of consent to be admitted to the hospital and receive treatment when the patient is admitted to the hospital ( general declaration form of admission to the hospital ).
C-doctors and members of the hospital nursing staff must obtain written informed consent from the patient or his legal representative in all the following cases (except for life-saving reasons):
* Surgical intervention.
* Renal dialysis.
* General anesthesia, migraine or deep sleep.
* Transfusion of blood and its derivatives.
* Surgical and diagnostic endoscopes.
Action steps:
1. The declaration of consent to the therapeutic procedure is filed in the relevant part of the patient's file after the signature of the patient or who is legally entitled to it.
2. The Attending Physician clarifies the reasons, advantages and risks of the procedure to be performed, explaining the consequences and alternatives resulting from it to the patient or who has the legal right to do so.
3. Doctors are obliged not to perform this procedure before confirming the existence of the patient's location acknowledgement or who has the right to it legally.
4. The doctor must be obliged to clarify the procedure and its details, mentioning (reasons –advantages – risks ) to the patient or his relatives .
5. The patient or those who have the legal right to do so shall sign the above-mentioned declaration, writing down the date and hour of signing.
6. The surgeon and the anesthesiologist sign their commitment to the said procedure with a declaration.
7. Determine the validity period of the approval of the therapeutic procedure thirty days from the date of signing the patient or who has the right to do so legally, and if the patient's condition requires emergency circumstances or on the instructions of the attending physician based on the patient's follow-up forms, perform another procedure in addition to the first procedure or change the type of So legally approve a new consent form.
8. The declaration required to be signed by the patient must contain:-
* Patient name
* Name of the process / procedure
· Type of planned anesthesia.
* Name / signature of the anesthesiologist.
* Name / signature of the surgeon .
* The date of approval must be earlier than the date of the operation.
* Signature of the patient / guardian / Guardian
9. In case of inability or incapacity of the patient to sign the declaration ( minor, incompetent or unconscious), the following order is followed with the submission of documents indicating this:
- The Guardian, guardian or trustee by virtue of the law (provided that proof of this is provided).
- Husband / wife.
- One of the parents.
- One of the adult sons.
- One of the grandparents or adult grandchildren.
- An adult third-degree relative who must prove the degree of kinship
10. In the event that the patient is unable to read and write or is unable to understand the information explained by the doctor, the patient's fingerprint or stamp must be taken on the declaration, provided that one of the relatives indicated in the previous paragraph signs as a witness to the declaration of consent and proves this to the doctor .
Due to the nature of the hospital's work and the frequent handling of serious and critical cases, the approval must include allowing blood transfusion and its derivatives .
11. In cases of loss of consciousness and critical situations affecting the patient's life, the medical team can perform some surgical interventions to save the patient's life before obtaining the patient's consent or it was not possible to obtain consent from his relatives that the hospital director or his representative form a committee of the attending physician, another doctor and the anesthesiologist Speed in conducting it before obtaining the declaration referred to in the previous item.
In charge:
- The Attending Physician.
- Nursing the responsible Department.
- The director of the hospital or his deputy (head of the department-consultant-deputy director of the hospital-administrative deputy-head of the medical authority
Models:
Sample declaration of consent
References:
- Regulation of professional ethics
- Ministerial recommendations to maintain patient safety during anesthesia.
- Egyptian accreditation standards .
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: the commitment of the medical service provider to inform the patients and their families about the result of the treatment and medical care provided to them and the expected costs .
Purpose: to create a system to inform patients and their families about the result of medical care or treatment provided to them and the expected costs.
Actions:
1. Doctors and medical service providers who have the right to evaluate the patient conduct the required examinations and analyzes.
2. The diagnosis of the patient's condition is investigated by doctors or other categories therapists.
3. Doctors draw up a treatment plan or the required care for the patient.
4. Doctors and medical providers familiarize the patient with the treatment plan, alternative plans, complications, collateral damage, if any, and the expected result of each plan.
5. According to Article (21 in the code of professional ethics), it is permissible for humanitarian reasons not to inform the patient about the serious consequences of the disease, and in this case he must inform the patient's parents in a decent humane way about the seriousness of the disease and its serious consequences, unless the patient has expressed his desire not to inform anyone about his condition or has identified certain people to inform them about it with no danger to those around him.
6. Doctors and medical service providers inform the patient and his family about the expected costs of Service and treatment.
Responsible:
the Attending Physician
References:
- Clinical manuals-professional ethics regulation-approved Egyptian quality standards
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy:
the hospital management is committed to preserving patients ' belongings and encouraging patients to send all their belongings to their homes or friends.
- Determine the role of the hospital and its responsibilities for the property of patients.
- The patient's belongings (money, jewelry, watch, checkbook, wallet) are examined....Etc.) and recorded and saved as safes in the hospital in case the patient is unidentified or unconscious.
Purpose:
- Preserving the patient's property and determining the hospital's role to preserve it to ensure that the hospital is not held accountable.
Working procedures:
* Patients should not keep any private property during their hospital stay.
* The patient or the one who is legally entitled to do so signs a declaration stating that he does not have any property in case he does not have any property with him.
The condition of the unidentified patient ( inability to identify the patient):-
1. The responsible employee (hospital assistant) collects the patient's belongings in a portfolio in the presence of an emergency nursing supervisor.
2. The assistant writes down the contents of the portfolio ( if the property is jewelry, it is not described as gold or silver, but it is described as a yellow ring with a white lobe or silver jewelry... Etc.) with the patient's trust list form.
3. The person in charge of the emergency secretariats, together with the nursing supervisor in charge of the emergency or her representative, shall sign the contents of the list of secretariats.
4. The person in charge of the emergency trusts writes the patient's name, date and patient's access authorization data on the clipboard in which the patient's belongings are kept.
5. The emergency safety officer records the patient's data in the safety register and places the number of the patient's safety list in the place specified for it in the safety register.
6. The person in charge of the emergency safes keeps and secures the wallet in a special cupboard in the safes with a tight closure until requested by the patient himself or whoever has the right to do so legally upon request.
7. The patient is handed the contents of the clipboard according to the existing list when he requests it, with his signature receiving it and taking his fingerprint in the Register of the secretariats.
· When the patient is discharged from the hospital.
1. The nurse supervising the patient's treatment notifies the person responsible for the secretariats to bring the portfolio after making sure that the numbers and contents match the receipt list that is with the patient or whoever is legally entitled to receive it.
2. The employee in charge of the secretariats opens the wallet in front of the patient or whoever is legally entitled to do so and the contents in the wallet are counted separately (money-jewelry-etc.)
3. The patient or the one who is legally entitled to do so shall recover the entire contents of the wallet and sign this in the Register of the secretariats with the date and hour of recovery recorded and the responsible employee shall sign as a witness to this.
4. A photo from the patient's trust list is placed with his file.
Determine the role of the hospital and its responsibilities for the patient's property
The employee in charge of the secretariats informs the patient or his legal representative that the hospital is considered responsible for the unconscious patient's property only upon arrival and receipt of the patient's secretarial officer, registration and signature on receipt, until the patient or his legal representative is handed over to the secretariats and signs for receipt.
In charge:
- Hospital assistant.
- Nursing the responsible Department.
Models:
The decision of the absence of property.
References:
Egyptian accreditation standards.
|
|
|
|
- The policy of correct identification of the patient
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Politics :
Identify the patient using two means before giving him a treatment, blood or one of its derivatives, taking samples from the patient or any diagnostic or therapeutic procedure.
Purpose:
Achieve patient safety and reduce the risks that the patient may be exposed to during any procedure within the hospital.
Working procedures:
1-everyone who deals with the patient from the health team must include :
* Doctors .
* Nursing.
* Pharmacists.
* Laboratory technician.
* Radiology technician.
* Physiotherapist.
Use at least two means of identification for the patient to verify his identity, namely:
* The name is quaternary.
* File number.
* The nurse makes sure that the data of the identification bracelet is correct before placing it in the right arm by matching it with the patient's data and being legible and clear. If the bracelet cannot be placed in the right arm for any reason, such as the presence of a plaster cast, it is placed in the left arm.
* The responsible nurse will put a new bracelet if the original is lost or becomes illegible.
* The nurse verifies the patient's quadruple name as in the patient's medical file and does not rely on another name (such as a nickname) and verifies the file number even if she is sure of the patient's knowledge .
2-the identity of the patient is confirmed before each treatment with him, such as:
◾ Give treatment.
◾ Blood transfusion or one of its derivatives.
◾ Taking a blood sample or any other samples necessary for medical analysis and laboratory examination.
◾ Transfer of the patient.
◾ Conduct diagnostic examinations.
◾ Or when taking any other actions.
Note: the identification label is not placed before the sample is taken or on the package, which is empty.
3-when taking any actions, the nursing staff should ask the patient for his name and introduce the patient to herself and the procedure that will be done taking into account ensuring the presence of the patient's bracelet and written on it two means of identification clearly, namely the patient's name and file number.
4 - then the nurse will compare the patient's data on the bracelet with those carried by the medical file to confirm the patient's identity before any procedure will be taken.
5-when taking a sample, the laboratory technician or nurse puts a sample identification sticker that includes the patient's name and file number, immediately after taking the sample and before leaving the place.
Note: the laboratory technician performs the same identification procedures as the patient before withdrawing any sample.
6-in the case of patients for premature babies, a bracelet is placed on the right leg of the baby.
7 - in the case of patients who are confused in consciousness and have a coma and who There is no way to prove their identity, their identity is confirmed by the following ( Unknown / Unknown - Patient Number - Date and hour of admission )
· If it is an accident, an accident proof report is made.
8-for newborns, they are identified by a bracelet placed at the foot of their following registered:
* Mother's name
* Male / female
* File number
9-dialysis patients: they are identified by an envelope with the name of the quadruple patient
10-patients who are in the emergency room or recovery room with the patient's name and the number of the reception ticket
11-outpatient patients their test tubes and radiographs are identified by the name of the triple patient and the outpatient ticket number
12-the radiology technician marks the radiology with the quadruple patient's name, File Number, Date and hour
13-none of the hospital staff will remove the bracelet of any deceased patient until he is discharged from the hospital
14-in case of an error in the patient identification process, the incident report requirements policy is referred to
Responsible: medical team
References: - world standard standards for patient safety.
- Egyptian accreditation standards.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
ه |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The policy: explains the following:
* Definition of critical significant results.
* When the results with critical significance are reported.
* How to report critical results.
* Who reports the results with critical significance.
* Who receives the communication of the results with critical significance.
* Documentation of reporting of critical significant results.
Purpose: to maintain the safety and security of the patient and take appropriate action when there are critically significant findings that require the intervention of the attending physician or any member of the medical team quickly.
Definition: critical values (Panic Values): are the results that may indicate a life-threatening situation that requires an urgent response or rapid intervention by the Attending Physician.
Working procedures:
1-each department shall draw up its own list of critical results, including the following:
* Results of critical laboratory tests (laboratory).
* Results of critical diagnostic examinations (radiology department).
* Critical medical examination results (inpatient departments / wards / dialysis ......).
2-in case of any critical result according to the previous lists, the official (laboratory doctor/ radiologist / resident doctor /nursing officer/laboratory technician or radiologist) will immediately inform the attending physician or nursing department.
3-the amount makes sure to confirm the Triple name of the one who was informed.
4-the recipient of the communication (the attending physician)- (nursing) will do:
* Record the critical score immediately in the critical score log.
* The recipient of the communication re-reads the patient's data and the result of the test on the amount in order to ensure that everything received and recorded in the patient's file is correct and accurate.
* The attending physician has the right to accept or reject the result in light of its suitability to the patient's condition, which may require a re-examination or procedure of the amount.
5-document the reporting process through the following:
* The recipient ( attending physician ) – (responsible nursing) documents in the critical results register the following data immediately upon receipt of the communication
(Today's date - reporting time (hour, minute) - test result).
The action taken in terms of accepting the result, rejecting it or requesting a re-examination.
(The Triple name of the laboratory / radiology officer who made the report - the Triple name of the recipient of the communication (doctor-nursing))
In charge:
* Laboratory doctors and radiologists.
* Resident doctors.
* Nursing staff.
* The Attending Physician..
Models:
* List of critical results for each section.
* Critical results model.
References:
* World standard standards for patient safety.
* Egyptian accreditation standards.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
- The policy of handing over patients ' conditions and the tradition of wrong access to catheters
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: the hospital's medical team is committed to the process of delivery and receipt of patients ' conditions in various departments, including:
* Identify the necessary duties to be handled during the delivery and delivery process.
* Identify the person responsible for delivery and delivery.
* Determine how to document the delivery and delivery process.
Purpose:
The process of delivery and receipt is vital in order to maintain the safety and security of patients by rationalizing the circulation of patient information among the medical team while in the hospital for the continuity of providing medical care to patients.
Responsible for delivery and delivery:
• Between doctors of the same specialty by using the delivery and receipt form.
* Among doctors with different specialties, for patients whose condition requires consulting doctors from more than one specialty using the medical consultation form.
* Emergency doctors when transporting the patient to and from the hospital departments (patient transfer form).
* Between the members of the nursing staff with each shift change (status book).
* Members of the nursing staff when transferring the patient to and from operations, care or to another department (time-out form )
Working procedures:
* The head nurse or her representative, upon admission of a new patient, receives the patient from the paramedic and the operator of the admission or reception office and records all the patient's data and what the attending physician requested in the patient's case record.
* The nurse records the patient's conditions throughout the lip in the patient's condition register.
• After the end of the lip and the attendance of the next lip nursing, the nurse delivers the conditions of all patients in terms of the development of their pathological condition, especially critical cases, Operations, treatment given to the patient, any change that has occurred, and any requests such as bringing test results or rumors about the patient and preparing the patient for operations, if any............With the documentation of delivery and receipt of the nursing signature in the notebook .
* In cases of operations, the nurse prepares the patient for the operation according to the doctor's instructions, and the nurse delivers the patient and the patient's dossier to the operations nurse and the patient's treatment if requested by the doctor according to the patient's preparation form for operations and the patient's receipt part of the time-out form.
• After the completion of the operation, the operations nurse calls the nursing role to come to receive the patient and the patient's dossier.
* When the patient needs to be transferred, the nurse transfers the patient and hands over the patient's file after updating it to the nursing department of the transferred patient inside the hospital.
* Resident doctors pick up and receive the patient at the start of the work shift according to the patient delivery form, which includes: ) patient name - file number - diagnosis - positive medical examination results - positive test results - follow-up and notes ).
* When the patient needs to be offered a consultation, the consultation form is used and the required data is recorded according to the form.
In charge:
* Members of the nursing staff.
* Doctors.
Models:
* Medical file.
* Record of patient conditions.
* Consultation form.
* Delivery and delivery form for doctors.
* Sample time-out operations.
References:
* World standard standards for patient safety.
* Egyptian accreditation standards.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy:
specifies the necessary data that must be placed on the catheters as well as those responsible for handling them to avoid the wrong connection or use of catheters.
Purpose:
* Achieving patient safety by avoiding the wrong connection of catheters and tubes in all departments of the hospital.
Working procedures:
* Patients, their families or hospital staff do not have the right to disconnect, install and reinstall any type of tubes or catheters, except:
* The doctor .
* Nursing.
* Supervisor.
Informing the patient about this is the responsibility of the nurse responsible for the patient's room.
· The department makes a policy for each type of tubes and catheters in the department, explaining :
o responsible for the installation.
o installation and installation method.
o ensure the integrity of the installation.
O follow-up and care of the link.
* It is required to indicate on each catheter the following data: the name of the installer, date and hour.
* Installation and ensuring the correct installation of each type is carried out according to its own policy.
* The doctor must specify the name and type of tube through which the drug will be administered.
* The nurse must check all the connections before giving any medicine and before and after performing any procedure according to the policy for each type .
In charge:
* Members of the nursing staff.
* Doctors.
References:
* International standard standards for patient safety.
* Egyptian accreditation standards.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Safe use policy and prevent the fall of patients
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: the probability of the risk of falling of each patient upon admission to the hospital, including the potential risk associated with the patient's treatment regimen, is assessed in the form for this in the nursing assessment part.
* Measures must be taken to prevent falls.
Purpose: to prevent the fall of patients by assessing and re-evaluating cases with regard to the possibility of falling and taking the necessary measures and precautions to prevent this.
Definition:
Falling: is the occurrence of any change in the patient's position from a level to a lower level, which leads to the patient's contact with the ground or any surface at a lower level.
Precautions to be followed to prevent patients from being at risk of falling:
* Environmental factors
* Distinguish patients who are at risk of falling.
* Educating patients at risk of falling and their families.
* Environmental factors:
The hospital / department takes into account various environmental factors and influences that provide security and safety to the patient and prevent the possibility of falling, therefore, the department nurse or her representative periodically make sure that:
* The safety of patients ' beds and free from any breakage or malfunction.
* The safety aspects of the patients ' beds and that they do not have a malfunction.
* Safety brake beds of patients and they work efficiently.
* Safety of the trolley used to transport patients between departments.
* Not to move patients while the department workers are doing the cleaning process to avoid patients from falling in the meantime.
* Ensure the safety and quality of lighting.
* Ensure that there are no obstacles in the corridors.
* Ensure that the bell in the toilets is working properly.
* Ensure and keep the floors dry and clean so as not to increase the risk of slipping and falling.
1-distinguish patients at risk of falling
The nurse evaluates the patient for the risk of falling according to the items in the nursing assessment form when the patient is admitted.
In the case of a patient who may be at risk of falling, nursing does the following:
* Raise the sides of the bed.
* Placing the symbol (F) on the patient's identification bracelet .
* Put the symbol (F) on the door of the patient's room and/or his bed if the room contains more than one patient.
* Repeatedly asking about the desire to go to the toilet.
2-educating patients at risk of falling and their families through treating doctors and nursing
* Alerting the patient to the need to notify the nursing in case of feeling dizzy, falling or unbalanced............Etc
* Warning the patient not to resort to sudden movements when changing the position from sleeping to standing or sitting.
* Warning the patient not to bend down to pick up anything from the floor.
* Consider the use of comfortable shoes without heels and not conducive to slipping.
* Consider keeping the bell near the patient's bed.
* The need to commit not to leave unwanted things on the comodino next to the bed or in the bathroom .
* Alert the patient to ask for help while walking and moving.
* Do not place any sharp instruments near the patient.
* Ease of movement of the medical team, patients and their families in the roads and rooms of the hospital by not occupying them with any tools or equipment.
* Encourage the patient to use wall supports while walking to prevent falls, if any.
* Registration of health education for patients and their relatives in the patient's medical record.
3 - in the event of a patient suffering from a fall, the following should be followed:
* The nurse measures vital signs before moving or helping the patient to move or stand.
• When the patient may be injured or broken, the patient is not permanently moved.
* The nurse notifies the doctor to examine the patient and determine the method of lifting him.
* The nurse assists the patient and puts him in the wheelchair after making sure that the brakes are lifted to prevent movement.
* The nurse records the incident in the incident report form.
* The responsible nurse will re-evaluate the patient when there is any change in the condition of the patient who is prone to falling, provided that she documents any change in the condition as follows :
o the Triple name of the nursing evaluator.
o valuation date.
o hour of evaluation.
o The New result of the assessment.
List of patients prone to falls:
* A patient with a disorder of the degree of awareness of all its types and causes
* Patient convulsions of all kinds and causes.
* Patients with limb fractures.
* Diabetic coma patient.
* High blood pressure patient a, low.
* Geriatric patient.
* A psychiatric patient, especially if he has suicidal tendencies.
* Disequilibrium patient (stroke patient + hemiplegia).
* Pediatric patients.
* Patients treated with sedative drugs, diuretics, blood pressure reducers.
In charge:
* Members of the nursing staff.
* Doctors.
* Maintenance.
* Responsible for environmental safety.
References:
- world standard standards for patient safety.
- Egyptian accreditation standards
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Politics :
The safety and security of the patient is maintained and his right not to restrict his freedom is preserved only if there is harm to the patient or those around
The patient is restricted for as little time as possible after evaluating the patient and making sure that the restriction is necessary using the least means
The patient is restrained on the order of a qualified attending physician
Purpose:
to preserve the patient's rights and dignity and prevent harm to himself or others.
Restriction: it is a means that reduces or prevents the patient's movement, and there are two types:
Either physical: it is a method of restraining the patient from the hands, feet and trunk of the body .
Or pharmacological: it is a drug given with the aim of reducing the patient's movement and calming his behavior .
Isolation: it is the determination of the patient's stay in a special room or area in cases of violence and aggressive behavior of the patient towards himself or those around him from workers, patients and others .
Reasons for restriction:
* A patient who suffers from mental disorders that make him capable of harming himself or those around him.
* A patient with neurological diseases who suffers from a cerebral trauma and in a state of agitation makes him capable of unconscious movement and capable of harming himself and others.
* A postoperative patient in a state of agitation, which leads to harming himself and others.
* A liver patient suffering from a state of pre-hepatic coma and in a state of agitation.
* The patient is conscious but has a history of harming himself before or taking off the devices installed in him, such as the monitor - the central vein - or injection and pumping devices.
Reasons for isolation: the patient in the presence of behavioral diseases is isolated in a room alone until he is transferred to another hospital and the patient's parents are informed.
Actions :
First: evaluation of the patient :
Responsible nursing determines the patient's need for admission based on his behaviors
The Attending Physician registers the restriction order in the patient's medical file, indicating the following :
* The reason for the restriction
* Type of restriction required
* The time of giving the restriction order / the specified duration of the restriction
The restriction began:
The restriction is carried out by the fastest available method, whether pharmacological or physical, only after consulting a consultant, but in some cases it is forbidden to use the pharmacological method .
Method of restriction:
Nursing uses a leather belt, gauze and cotton bands, or other means to restrain parts of the body, and the four limbs are often used for restraint, except in cases such as when eating diets and personal hygiene .
Female: the nurse in charge rolls the legs together and then handcuffs them to the foot of the bed.
Male: the responsible nurse restricts each leg of the patient individually at the foot of the bed.
The oral restriction order is signed by the attending physician within 24 hours from the time he was informed about the case .
Nursing takes care not to harm the patient psychologically or physically during the restriction .
Nursing takes into account the preservation of patient privacy .
Patients whose freedom is legally restricted are prohibited from participating in their restriction except when there is a purely medical necessity (Article 35 of the ethics of the profession-resolution 238 of 2003)
Second: follow-up of the patient :
The nurse registers the follow-up of the patient with the form for this, including the following data :
* Patient behaviors-vital signs - blood circulation - skin condition
The responsible nurse follows up the patient under restriction and for medical and surgical reasons at least every two hours with documentation in the patient's medical file .
The nurse follows up the patient under restriction for psychological reasons at least every half hour and the observations are recorded in the patient's medical file with the form for the patient's restriction .
Third: renewal of the restriction order:
Restriction orders that are made for medical and surgical reasons, the attending physician must renew the order at least every 24 hours based on the continuing need
Restriction orders that are made for psychological reasons the attending physician must renew the order at least every 6 hours based on the continued need
Fourth: termination of the restriction:
Specifications of ending the restriction: it either completely improves the patient's state of consciousness or its deterioration and the occurrence of a coma .
The trained nurse terminates the patient's restriction according to the doctor's orders, according to the patient's condition and according to medical evidence, provided that the time and date of termination of the restriction are recorded .
Fifth: training:
The person responsible for the hospital's patient care policies provides practical training to doctors and nurses in the internal and care department on how to perform the policy.
Sixth: health education of the patient and his relatives : the doctor / members of the nursing staff responsible for familiarizing the patient and his relatives with the following
* The extent to which the patient needs to be restrained
* Duration of restriction
* Average rating during the restriction .
Responsible: - the Attending Physician.
Forms: restriction and follow-up order form.
References:
- Egyptian quality standards
- Joint International Committee standards
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Standards for medicines
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
High-risk medications
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Policy of medicines that are similar in form and pronunciation
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: separation of similar drugs in form and form to reduce the risk.
Purpose: to achieve patient safety while in the hospital by adhering to the system of separation of drugs that are similar in form and pronunciation.
Working procedures:
* The pharmacy prepares a list of medicines that are similar in form and pronunciation, with the responsibility of renewing and updating this list every 6-12 months.
* The pharmacy manager distributes the list to all therapeutic departments and units of the hospital.
* The pharmacist separates them and writes clear addresses on the container packages of each of them in the storage places.
* Drugs that are similar in form and pronunciation are highlighted in green.
* The pharmacist, when dispensing medicines of similar form and pronunciation, alerts those who will receive the medicine from the pharmacy to the need to separate them for the safety of the patient.
* Nursing supervisors in the departments and roles separate and write clear addresses on the container packages for each of them in the storage places.
In charge:
* Pharmacists.
* Nursing staff.
Models:
* List of drugs that are similar in name and pronunciation.
References:
* International standard standards for patient safety.
* Egyptian accreditation standards.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Medicines that are similar in appearance and pronunciation
|
|
DRUG names |
Serial |
|
|
|
1 |
|
Ampoule |
|
2 |
|
Ampoule |
|
3 |
|
Ampoule |
|
4 |
|
Ampoule |
|
5 |
|
Ampoule |
|
6 |
|
Ampoule |
|
7 |
|
Ampoule |
|
8 |
|
Ampoule |
|
9 |
|
Vial |
|
10 |
|
Vial |
|
11 |
|
Vial |
|
12 |
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
List of abbreviations that should not be used in writing medicines
· U/ UI
· Q.D, QD, q.d, qd
· Q.O.D, QOD, q.o.d, qod
· MS, MSO4
· Mg SO4
· Trailing zero
· No leading zero
· Dose x frequency x duration
· › greater than
· ‹ less than
· Abbreviation of drugs names
· cc
· µg
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Transfer policy evaluation and follow-up of the patient
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: organizing procedures and securing the transfer of the patient from the patient's room to the operating room
Purpose: to adjust the workflow during the transfer of the patient from the patient's room to the operating room
Working procedures:
1. The department nurse informs the operational nurse of the receipt of the summoned patient (hour and date ) .
2. Inform the anesthesia consultant to discuss the case, review the medical file, re-evaluate the patient and document the evaluation in the medical file
3. The patient is transferred to the concerned operating room after the approval of the anesthesia consultant by the knowledge of the worker and handed over to the operating nursing
4. The operations nurse reviews the file and makes sure of the patient's personality and his knowledge of the quality of the surgical intervention, the place of intervention and the surgeon's name
5. The medical team follows the instructions to maintain the patient's safety before performing the operation according to the form prepared for this, explaining:
- Re-confirm the patient by asking the patient for the Triple name and reviewing the data match with the bracelet and patient file
- Confirm the type of operation planned to be performed
- Confirm the position of the planned operation
- Confirm the name of the surgeon.
In charge:
- Department nursing-operating room nursing
- Consultant anesthesiologist-surgical consultant or his representative
- The room worker
Models: safe surgery model
References: Egyptian accreditation standards.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: patient assessment for anesthesia and sedatives .
Purpose: evaluation of the patient for anesthesia and sedatives before anesthesia for surgeries and interventions to ensure patient safety .
Working procedures:
1. The day before the surgery, the anesthesiologist reviews the patient's file, signs the examination, and reviews the laboratory and diagnostic tests in order to assess his health condition and make sure that the patient is medically fit for anesthesia and record this in the patient's file (see AP.2.1 )
2. After the examination of the patient, the anesthesiologist takes the patient's consent to anesthesia, indicating the type of anesthesia planned to be used /sedatives in accordance with the possible condition / complications and the expected results, and this is recorded in the declaration of consent to perform a surgical intervention and both the anesthesiologist and the patient sign the declaration in the prepared declaration form
3. The anesthesiologist re-evaluates the patient immediately before surgery in the operating unit in the patient preparation area to make sure that the patient is fit for anesthesia and make sure that the necessary precautions are taken for the patient and recorded in the patient's medical file .
Responsible: anesthesiologist.
Models:
- Patient evaluation form before anesthesia . - Confirmation of the patient's consent to surgical intervention .
References:
Egyptian accreditation standards.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Patient follow-up policy during anesthesia
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: follow-up of the patient during anesthesia .
Purpose: to ensure patient safety during anesthesia
Working procedures:
- All patients receiving total, partial or analgesic anesthesia are regularly observed in the operating room by an anesthesiologist.
- Monitoring is an essential part of the proper handling of the patient during surgery.
- Basic follow-up criteria during anesthesia
1. Blood circulation: it is necessary to ensure the regularity and safety of the patient's blood circulation during all stages of anesthesia
- An electrocardiogram is performed continuously for each patient receiving anesthesia and this is followed up from the beginning of anesthesia until the readiness to leave the anesthesia site.
- Venous blood pressure and heart rate of each patient receiving an anesthetic are monitored at least every five minutes with an assessment of the readings.
- Circulatory functions are constantly assessed for each patient receiving an anesthetic by one of these methods: pulse palpation - hearing heart sounds, remote monitoring of blood pressure inside the veins, monitoring the peripheral pulse with ultrasound or by measuring the oxygen percentage.
2. Body temperature :the body temperature should be kept under control during all periods of anesthesia
- There is a ready-made means of continuously measuring the patient's body temperature when changes in body temperature occur, are expected or suspected to occur, and the temperature is then measured.
3. The vital functions of the patient are constantly monitored by follow-up devices throughout the anesthesia process and this is recorded in the patient's follow-up form during anesthesia in the medical file and includes the following points:
* Pulse speed.
* Regularity of the pulse.
* Blood pressure.
* Respiratory rate.
* The level of oxygen saturation.
* Medicines and liquids that have been given to the patient.
* Giving blood and its derivatives.
· The drug used.
* Unforeseen events or complications that have occurred to the patient, if any.
· The patient's condition at the end of the operation.
* Start and end time of anesthesia.
* Signature of the anesthesiologist.
In charge:
- Anesthesiologist.
- Nursing operations .
Models:
- Patient follow-up form during anesthesia .
References:
- Egyptian accreditation standards.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: patient care after the procedure
Purpose: observation of the patient until he is fully awake
Definition: admission of all patients receiving any type of anesthesia to the recovery room for a predetermined period of time in order to ensure their safe and proper care after receiving the anesthetic
Actions:
1. In case of total anesthesia
· All patients receiving total anesthesia should be monitored regularly for reactions.
* Vital signs should be recorded every 15 minutes, as well as the degree of consciousness, until he leaves the recovery room.
2. In case of partial anesthesia
* All patients receiving partial anesthesia should be monitored in the same way as patients with total anesthesia.
· They should stay in the recovery room until vital signs stabilize and sensation and the ability to perform functions return to the injured limb.
3. In case of local anesthesia
* All patients receiving local anesthesia should be monitored in the same way as patients receiving total anesthesia
* They can be discharged if the vital signs are stable, the level of pain tolerance is acceptable and as directed by the surgeon or anesthesiologist.
4. Post-operative pain relievers
· In the case of patients receiving hypnotic pain-killing drugs after the operation, the patient is observed in the recovery room after taking the drug until the vital signs become stable and the level of pain tolerance is also acceptable, and then transferred to the patient's room in the Department
As directed by the surgeon and anesthesiologist.
In charge :
- Anesthesiologist.
- Recovery nursing .
Models :
- A sample of patient follow-up after anesthesia (awakening) .
References :
- Egyptian accreditation standards
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Policy of preparation, care and control of patient prevention
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy:
preparing the patient's skin before operations
Purpose:
- Clean the skin as much as possible, remove skin fat, and all possible microbes from the operation site, so that the skin is incised with the least risk of contamination coming from this side.
- Leaving residues of antimicrobials on the skin that prevent the multiplication of microbes during the procedure.
- Reduce the presence of microbes in the shortest period of time with the lowest percentage of skin irritation
Working procedures:
A-pre - ' sterilization”
* The nurse in charge reviews the doctor's orders regarding the quality of the pre - “ sterilization” procedures (sterile or non-sterile), the quality of the soap to be used, the duration of the preparation and the patient's history of allergy is reviewed before using any chemicals on the patient's skin.
* The patient is transferred from the department to the operating room, then the patient is placed on the operating room table and anesthetized, the operation site and the area around it are cleaned with gauze 4×14 (10 cm × 10 cm) in a circular motion in circles widening and starting from the center to the extremities.
* The operation nurse starts to clean the operation site and then pass on the surrounding area, receiving the sponge gauze piece, never bring the 4×14 (10cm × 10cm) gauze contaminated towards the center.
· The “ sterilization ' process is repeated with 4×14 (10 cm × 10 cm) clean gauze each time.
* The area to be 'sterilized' is prepared in a time period according to the request.
B-preparation
* The responsible nurse reviews the doctor's preference for the quality of the solution and the preparation that should be used.
· After the nursing handler finishes the pre-sterilization stage, and before it is covered, the doctor or the person responsible for the sterilization process uses a sterile method to add antiseptic solution to the operation site and the surrounding area.
* The excess solution is squeezed out of a spongy gauze
* Sponge gauze is used on the patient's skin in a circular motion, starting from the operation site in a movement towards the surrounding area, the sponge is discarded, it is forbidden to use a contaminated sponge towards the center.
* Repeat the previous stage with a new sponge.
The type of solution used is recorded on the patient's own record.
C-sterilization by type of operation:
1. Abdomen
* Laparotomy-from the nipple to the bottom of the pubic bone
* Full - from the nipple line to the anus
· A special point-the navel is well cleaned with a thin rod, the tip of which is wrapped with something cotton.
2. Vaginal-all hair is removed at the confluence of the pubic bones, pubis, anus area, inner part of the thigh, if requested, do not use alcohol.
3. Anal cases-the area around the anus is prepared.
4. Venous ligation (vein to the thigh) - the origin of the thigh, vagina, pubic area, the area of the man where the operation will be performed is shaved, wiped and cleaned, if requested. If there are marks on the legs, please do not remove the marks (as they will be used by the surgeon during the operation) (the operating body).
5. Chest conditions-shaving, wiping and cleaning of the arm and chest is done from the affected side starting from below the back armpit line, to the nipple line of the uninjured side and from the clavicle to the navel, be sure to shave the armpit.
6. Behind-the-ear osteotomy and ear microsurgery-shaving, wiping and cleaning are done two inches above the ear to the back of the hairline from behind. All hair located at the site of the operation is braided or shaved.
7. Lumpectomy - a six-inch radius (except for the scalp) is prepared around the location of the tumor.
8. Capillary vesicle (coccygeal fistula) - is shaved, wiped and cleaned from the middle of the back to the bottom of the anus. If requested.
9. Amputation-six inches of skin is prepared below and six inches above the position to be amputated, whether it is a back or front part.
10. Preparation for bone sterilization (for all orthopaedic surgeons) - the position is cleaned with a soapy sponge (gauze) - depending on the selected area. A soap foam is applied and the area is shaved with a razor, if requested. Be sure to remove all hair, including thin ones. The site is wiped and cleaned for ten minutes with a soapy sponge (gauze), left to dry. The position is covered with sterile towels and the towel is fixed with a gauze bandage (an adhesive belt is used if necessary, do not use a pin). If the process involves a hand or foot, be sure to cut and clean the nails of the hand or foot, they are also wiped, cleaned and with a brush. If there is a part that is fixed with corsets or a splint, do not prepare it unless the doctor asks for it.
11. Arthroscopic examination of the knee joint: - preparation is carried out from the middle of the thigh to the heel with the front and back sides.
12. Foot and heel surgery-the man is prepared starting from (6) six inches below the knee to the end of the limbs, cleaning and manicure are done.
13. Hand and wrist surgery-the arm is prepared starting from (2) inches below the elbow to the fingertips.
14. Open splinting of the ulna and radius bone-the arm is prepared from the armpit to the wrist.
15. Open splinting of the humerus - the upper arm is prepared from the shoulder to just below the elbow.
16. Shoulder surgery (clavicle) - the shoulder is prepared from the upper middle part of the arm to the neck, the front and back of the chest and up to the middle line, the armpit hair is shaved.
17. Special points to remember:
* The doctor's orders on the patient's record are always checked to see if the preparation has been requested and to find out any special orders related to the preparation of the skin.
* Make the patient feel confident and discuss the operation with him within the limits allowed.
* Avoid cutting the patient with a razor.
* Make sure the navel is clean.
* Regular shaving is done in the case of patients undergoing operations around the face and neck.
* Limbs are sterilized in cases of orthosis.
D-types of disinfectants used :
1. Eudophore (Betadine):
* Compositions of cleanser and iodine do not cause irritation of the skin or mucous membranes.
* Iodine 1% is applied slowly to ensure the effectiveness of its bactericidal effect, and it is noted that iodine leaves a brown color on the skin that determines the place of the operation.
* Has an effective effect on Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria
2. Chlorhexidine gluconate :
* It is considered an alternative suitable for patients with allergies to iodine compounds .
· It has an effective effect on Gram-positive bacteria, and a less effective effect than iodophor compounds on Gram-negative bacteria.
3. Alcohol ( ethyl and isopropyl ) :
* It is used if the surgeon wishes to see the normal skin color and not the brown color of iodine.
· It should not be used for disinfection of mucous membranes.
* Loses its deadly effect when evaporating
* Alcohol can be used after Betadine
Responsible: nursing operations
Models:
References: Egyptian accreditation standards.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Objective
Making sure the surgical procedures are safe for the patient
Nursing care before the operation :
1. receiving the patient and confirming the data written on the ticket and making bracelets for the patient
2. preparation of the medical file, including (signing the necessary declarations of operations)
3. conducting the necessary tests as recorded in the medical file
4. determining the blood group of the patient by taking a blood sample from the patient
5. Prepare the patient fasting 6-8 hours before the operation
6. prepare blood for the patient if necessary
7. determining the place of the operation by the doctor
8. give the necessary treatment before the operation according to the doctor's instructions
9. measuring vital signs and recording them with the file
10. preparing the patient psychologically
Nursing care during the operation :
1. confirm the patient's name and the place of the operation
2. measuring vital signs and recording them with the file
3. wearing the patient's Operation Clothes and handing him over to the surgery nurse with the medical file
4. preparing the patient psychologically
5. ensure the safety of devices and connections
6. ensure the safety of surgical instruments
7. help the doctor during the operation
8. observe the patient and notice any changes that occur to the patient
9. ensure the counting of pads and machines before the end of the process
10. recording and recording the consumables of the process
11. transfer the patient from the operating room to the recovery room
Nursing care after the operation :
1. the patient is transferred immediately after the completion of the operation and the approval of the anesthesiologist
2. placing the patient in the appropriate position according to the operation
3. connecting the patient to the monitor device
4. observation of vital signs
5. note The Color of the skin
6. note the degree of awareness
7. note all connections and inform the doctor
8. review and implement the treatment plan written in the file
9. after the patient completely wakes up, when the anesthesiologist decides to transfer him to the internal department, the following is performed :
* Notifying the nursing department to come to receive the patient
* Receive the nursing to the patient at the clean area of the operating room and sign the receipt and the date of receipt in the operations statement
* The responsible nurse delivers all the patient's papers and the medical file to the nursing department
* Record all observations in the observation map and inform the doctor of any abnormal symptoms
Executive Officer :
Operational nursing (sterile and Palliative Nursing )
Operating doctor
Anesthesiologist
References :
Surgical Nursing textbook for Technical Secondary Schools of nursing
Manual of procedural work in the operations unit
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy:
adjust the patient's position for surgery
Purpose:
- Providing an appropriate possibility for the surgeon to reach the surgical position while maintaining the following physiological functions:
* Breathing
* Blood circulation
* Nerves
* Muscles
Working procedures:
1. The surgeon chooses the position in which the patient is fixed for the surgical procedure.
2. Consultation is carried out with the anesthesiologist responsible for administering the anesthetic
3. The following are the parameters for adjusting the patient's posture:
* Achieve maximum safety and comfort.
* No interference with breathing
* No interference with blood circulation.
* No pressure on any nerves.
* Accessibility of Operation positions.
* Accessibility of Drug Administration sites.
* Meet individual needs and requests.
4. Supine position on the back
* The head is on the same line with the body
· The arms are on the side of the body or stretched out on padded armrests.
* A safety belt is fastened across the patient's body.
* The patient lies completely supine (straight).
5. Setting the 'trend for lenberg'
* The patient's head is at a lower level than the level of the knees.
· The patient is placed on his back.
· The arms are on the side of the body or stretched out on padded armrests.
* A safety belt is fastened across the patient's body.
6. The 'Lindenberg trend' situation is reversed
* The patient is placed on his back
* A safety belt is fastened across the patient's body
* The head should be higher than the lower ends
7. 'Fuller / or semi-Fuller' position (sitting / or semi-sitting)
* Supports the patient's head with a headrest, if necessary
* Fix the arms in a comfortable position
* A safety belt is fastened across the patient's body
8. 'Lithotomy'mode
* The patient is placed so that his buttocks are above the rear brake (joint) of the table.
· Both legs are placed in padded stirrups and secured in position with belts (thongs)
· The arms are placed on armrests fixed down at the sides or resting on the patient's stomach.
* Reduces the portion reserved for the feet at the table.
9. Lateral position
* The patient is placed on his right or left side and his back is at the edge of the table, the butt and shoulders are on one line.
· The lower leg is bent (at the pelvic and knee joints), while the upper leg is on the same line with the shoulders with pillows placed between the legs
* Arms are placed along the body
* Support the abdomen and back with sandbags or any other supporting tool.
* A safety belt is placed over the patient
10. The situation is down
* The patient is given total anesthesia in the supine position and then turned over on the abdomen.
* Chest cylinders are placed under the sides of the chest to lift the weight of the body off the chest
· Arms extended on armrests
* Feet and ankles rest on cushions.
Responsible: nursing operations
References: Egyptian accreditation standards
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: training nurses on the use of a defibrillator, which is the main pillar in cases of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in emergency departments .
Tools used :
* Generation.
* Emergency vehicle and be equipped under any circumstances.
* Anesthesia, as directed by the doctor.
Steps: make sure that all tools are prepared and make sure that the shock device is loaded.
In case of cardiac arrest :
* Ensure that the environment is safe for all those around and for the patient (no water - no contact with the bed during the discharge of the charge).
* Put a gel on the patient's chest where the charge is discharged to prevent the patient from being burned .
* Carry out the doctor's instructions regarding the unloading of the shipment specified by the doctor after making sure aloud that it will start with the observation of Al-Monitor .
The conscious patient :
* Introduce the patient to the reception Department and calm the patient .
* Connect the patient on the monitor device with the measurement of vital signs in a regular way to follow his condition moment by moment while monitoring the degree of awareness of the patient .
* Carry out the doctor's instructions in charging the device according to the doctor's instructions .
* The patient was placed on oxygen according to the doctor's instructions after the shock was given .
* Note the degree of consciousness after shock administration .
* Making an electrocardiogram of the patient after trauma .
References: Manual of procedural work in intensive care (Nursing Guide Line).
- The policy of determining the place of surgery procedures before starting it
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: the commitment of doctors to the need to put a distinctive sign indicating the place of surgical intervention in order to preserve the patient's safety
Purpose: to keep the patient safe by placing the marker to determine the place of the correct surgical intervention.
Actions:
1-the surgeon, provided that he is a participant in the operation, determines the place of surgical intervention by placing a distinctive sign (circle or dash ) with a non-removable marker on the place of the operation in the Department.
2-the nurse in the Department verifies the mark before the patient goes to the operations after asking the patient or pointing with his hands to the place of the operation.
3-the operating nurse receives the patient and once again confirms the location of the mark in the part to be intervened in.
In charge :
* Doctors.
* Nursing.
Models:
* Sample preparation of the patient before the operation.
* Safe surgery model.
References:
* Patient safety standards according to international quality and health organizations.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Politics:
Use a documented method to confirm the correct patient, the correct procedure and the correct part before starting the operation or any other interventional procedure.
Purpose:
Achieve patient safety by making sure the right patient and the right place for surgical intervention or other interventions.
Working procedures:
1. The members of the nursing staff responsible for receiving the patient in the operations receive the patient's medical record and confirm the patient's basic data .
2. The nursing staff members ask the patient about his name and match the writing on the identification bracelet with his file and ask the patient about the procedure required for him and specify the place of the procedure prescription .
3. The nursing staff matches the patient's information with what is recorded in the medical record and has six procedures ( operations - endoscopes – interventional radiology- .....Etc.).
4. The surgeon, anesthesiologist and operation nurse ask the patient his name, the operation and the place of the interventional procedure ( operations – radiology – endoscopes - .....Etc.) before anesthetizing the patient on the operating table.
Responsible: doctors and nursing staff.
Models: safe surgery model.
References: universal standard precautions for patient safety.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Policy: use a checklist to make sure that all the documentation and all the equipment needed to perform operations and other interventional procedures are available, correct and working efficiently before starting any of them.
Purpose: to achieve patient safety when performing surgery or any other interventional procedure.
Working procedures:
1. The responsible nurse will obtain a copy of the list of operations ( for six operations ) .
2. The nurse in charge makes sure that the operating rooms are clean, including the operating room lights, the operating table, and all the room furniture and appliances .
3. The operating supervisor makes sure the safety of anesthesia machines, electric shocks , operating tables , air conditioning, lighting.
4. The operating supervisor makes sure that the various surgical instruments and packages are received according to the needs of the six , and reviews the safety of sterilization individually.
5. The operations supervisor ensures the safety and availability of devices, equipment and supplies for each operation in the list of operations.
6. The operations supervisor makes sure that the dates of operations are properly arranged and organized.
7. The suction machine is checked for the safety of its operating conditions by the responsible nurse .
8. The operating nurse receives the medical record of the operating patient from the nursing department .
9. The operating nurse together with the department nurse checks the patient's medical record before the operations to make sure :
* Patient name and file number
* Sample patient preparation for operations .
* Declarations of surgical procedures and presentation of anesthesia before operations .
* The results of the patient's tests .
* Patient-specific radiology reports .
* Carrying out preoperative treatment of the patient .
* Matching the previous data with what is included in the six operations .
10. The department nurse asks the patient about the presence of artificial dentures or rarefied natural teeth and about contact lenses .
11. The nurse performs the operations with the support and psychological rehabilitation of the patient in preparation for the operation.
12. The anesthesiologist, surgeon and nurse make sure the patient's personality before performing anesthesia and the patient's knowledge of the surgeon's name, the type of operation required and the place of the operation.
13. The hand washing policy is applied in accordance with the infection control policies.
14. The Chief Operating Officer or the nurse in charge together with the anesthesiologist will confirm the preparations related to anesthesia :-
* It is forbidden to use any narcotic substances that are flammable, inflamed or lead to an explosion in the anesthesia areas .
* Ensure that the ground electrode of all electrical devices is connected properly .
* Outerwear made of cotton is used only at the site of anesthesia .
* Wires, switches, electrical and electronic tools are regularly checked by the engineering department and the head of operations for follow-up .
* The equipment and anesthesia devices used in the operations are checked by the anesthesiologist who will use the device to ensure its safety .
In charge:
* Doctors, members of the nursing staff of operations, members of the maintenance department and cardiac catheterization.
Models:
* Department status Record-Safe Surgery form.
References:
* Universal standard precautions for patient safety.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Politics:
Use a documented method to confirm the correctness of the number of cotton, gauze, abdominal pads, surgical instruments and needles used before or after surgical intervention.
Purpose:
Achieving patient safety by protecting him from leaving any foreign object in his body after surgical intervention
Working procedures:
1. Surgical Nursing makes sure that the operating theater is free of any cotton or gauze, abdominal pads, surgical instruments and needles used other than those equipped for the current operation .
2. Sterile nursing and handler nursing before the surgery begins, after the instruments, bandages and needles are put together and loudly and each item is separated in the counting process.
3. This basic count is recorded immediately after the nursing handler takes it in the form of the number of instruments, bandages and needles.
4. All instruments, bandages and needles added to the operating area during the surgery procedure are counted by the sterile nursing and the nursing handler and recorded by the nursing handler immediately.
5. The nursing handler during the surgical procedure performs the following:-
* Conducting a count of all dressings excluded from the area of operation in conjunction with sterile nursing aloud.
* Separation of dressings into modules.
* Put the numbered bandages according to their units in sterilization bags.
6. Handler nursing and sterile nursing in front of the surgeon before starting to close the peritoneal cavity count together and loudly for the following:-
* All instruments, bandages and needles located in the operation area that were counted before the surgery and those that were added during the surgery.
* All instruments, bandages and needles that have been excluded from the operation area
* The nursing handler records the number in the required column 'before closing the peritoneum'.
* The nurse in charge reports aloud to the surgeon about the results of the counting.
7. Before starting to close the skin, the handling nurse and the sterilizer conduct a loud count together of all the instruments that were used after the closure of the peritoneum and all the items listed in the section from the record of counting instruments, bandages and needles:-
* This final count is recorded by the handling nurse in the required column with the 'final count'.
* Sterile nursing and handler nursing write their names in the designated place in the counting register.
8. The difference in counting tools :-
When reporting a difference:-
- The surgeon is notified immediately
- Careful research is carried out as follows:-
o the position of the operation by the surgeon and assistants.
o the area sterilized by the person responsible for sterilization.
o operating room by nursing handler.
When the difference cannot be ironed out :-
- The person who detects this difference completes the accident report on the occurrence of an accident
- An X-ray of the operation site is taken before the patient leaves the operating room.
In charge:
* Doctors and nursing staff
Models:
* Counting list
References:
* Universal standard precautions for patient safety.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|