
Part Three
- Installing a catheter and drawing blood
The Definition :
Evaluating the movement of blood vessels by knowing the volume of blood, the blood returning to the heart, the extent of resistance of peripheral blood vessels, and the elasticity of the arteries.
The Reasons :
Monitoring the patient's vital functions.
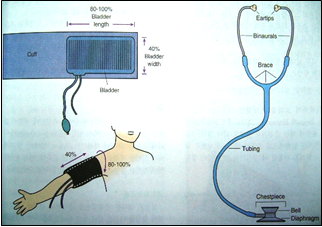
Normal rates:
80/110 mm/Hg.
The person in charge:
Nursing team.
Tools :
Blood pressure device and stethoscope.
Steps:
1. Getting to know the patient.
2. (Patient’s name and identification bracelet)
3. Explain the procedure to the patient.
4. Prepare tools.
5. Be careful not to measure pressure after muscular effort.
6. Place the patient in a comfortable position.
7. Maintain patient privacy.
8. Measuring blood pressure before and after giving high blood pressure medications.
9. Record your blood pressure measurement directly on the form designated for that purpose.
10. Determine the type of diet (low salt and fat).
11. Note the complications that may occur to the patient (nosebleeds).
Installation of intravenous cannula
the definition
It is a device that is connected intravenously to administer intravenous medications and solutions.
People most at risk: All patients treated with intravenous injections.
Working team:
Nursing team.
Tools :
Tray with lid - cannulas of different sizes - medical cotton - adhesive plaster strips - latex gloves - 70% alcohol.
Steps:
· Verify the patient’s identity and double-check the name.
· Explain the procedure to the patient to reduce his anxiety.
· Maintaining patient privacy.
· Wash hands and wear gloves.
· Tie the forearm with a compression bandage, preferably the forearm that is least used.
· Disinfect the catheter installation site with 70% alcohol and leave it to dry. Do not touch it after disinfection
· Inserting a cannula and monitoring the appearance of a spurt of blood in the place known as the cannula (as a sign of penetration of the vein wall) and completing the insertion slowly while pulling the metal insert out of the vein.
· Do not try to insert the same cannula again.
· Loosen the compression band from the forearm (tournament).
· Connecting the solution device to the cannula to test the efficient operation of the cannula.
· Fix the cannula with adhesive tape and write down the date of installation.
· Leave the installation site dry and visible.
· Dispose of the cannula tip immediately after use in the sharps waste safety box.
· Cleaning the used tools, putting everything back in its place, and preparing it for the next use.
Cannula removal should be considered in the following cases:
· Immediately after a blood transfusion.
· After completing the need for it, or after only 3 days have passed since installation.
When redness or inflammation appears at the cannula site
Urinary catheter installation
The Definition :
It is a procedure performed for the patient in medical conditions according to the doctor’s instructions.
The Reasons :
Bladder emptying - estimating the amount of fluid expelled - surgical operations
Working team:
Nursing team.
Exposed people:
Liver patients - kidney patients - urinary tract patients - bedridden patients
Tools :
Urinary catheter with a size suitable for the patient - urine collection bag - 10 cm syringe - salt solution - sterile gloves - gauze - Betadine for disinfection - KY gel - medical adhesive.
Steps:
1- To maintain the patient’s privacy, paraffin is placed or installed in the spare booth.
2- Tell the patient what you will do and explain the medical reasons for installing a catheter.
3- Gather the necessary tools to install a urinary catheter.
4- Surgical hand washing.
5- Wear sterile gloves.
6- Connect the urine collection bag to the catheter first.
7- Apply 3 ml of gel (or any anti-friction material).
8- He hands the sterile catheter to the doctor to install it.
After installing the catheter:
· Fixing the catheter in the thigh with plaster.
· Place the urine bag below the level of the patient’s bed and place it on a urine holder to prevent urine reflux.
· Bring the patient’s own urinal to empty the urine from the urine collection bag.
· Dispose of waste in its red bag.
· Wash hands routinely after removing gloves and dry them well.
· Recording in the nursing staff’s notes the type of catheter, the time of installation, and the doctor by whom the catheter was installed.
· Observe and record the amount of urine and any changes (blood - pus) and inform the doctor.

Drawing blood samples
The Definition :
It is a procedure done to obtain a blood sample for analysis.
Most exposed people:
Patients in departments.
Working team:
Nursing team.
Tools :
70% alcohol - sterile and dry cotton - syringes measured according to the required quantity - tourniquet
Steps:
1. Explain the procedure to the patient.
2. Washing hands.
3. Place the tourniquet above the elbow and tie it.
4. Feeling the location of the vein and cleaning and disinfecting the location of the vein and its surroundings.
5. Choose the appropriate place and tighten the skin below the area chosen to take the sample.
6. Inserting the tip of the needle into the vein at an angle of 30 degrees so that it enters the skin first and then enters the vein.
7. Raise the tourniquet and take the required amount of blood slowly.
8. Place a piece of sterile gauze over the place where the vein enters and apply pressure for 2-4 minutes until the blood stops.
9. Remove the syringe tip and place the amount of blood required for analysis into the tubes prepared for this purpose.
10. Place a sticker on each tube with the patient’s name and his file number (the department in which he is treated).
Dispose of used tools properly.
Do a sugar analysis
The Definition :
It is a procedure done to determine the blood sugar level.
Most exposed people:
Diabetics.
Working team:
Nursing team.
Tools :
Sugar analysis device - test strips with the same code as the device - sterile cotton or gauze - straws - alcohol - latex gloves.
Steps:
· Hand washing.
· Explaining the procedure to the patient.
· Wear a glove, hold the patient’s finger down and squeeze gently.
· Wiping the tip of the finger with a cotton ball containing alcohol, and the finger is suspicious.
· Place the tip of the strip or the designated place on the strip to place a drop of blood.
· Press the finger with a cotton ball until the blood stops coming out.
· Dispose of waste in the designated place.
· The nursing staff records the blood sugar level on the relevant form and gives the insulin dose according to the doctor’s orders.
Giving treatment orally
The Definition :
These are medications that are given orally (such as tablets and syrup).
The Reasons :
Treating the patient's signs and symptoms.
The person in charge:
Nursing team.
Tools :
Medications dispensed to the patient.
ten (10) It is important to follow the correct ten times before giving the medicine
Rights:-
1. The correct patient
2. The correct medication
3. The correct dose
4. The correct method
5. The correct time
6. Healthy repetition
7. Correct registration
8. Required effectiveness.
9. The right to refuse
10. The right to education
Steps:
1. Washing hands.
2. Review the doctor’s order for the medication and prepare the treatment, taking into account the time coordination, unless the time at which administration is required is specified
3. Verify the correct patient through the patient’s file and identification bracelet (full name and medical number).
4. Explain the procedure that will be performed to the patient.
5. Maintaining patient privacy.
6. Ask the patient to sit if possible so that he can take the medicine.
7. In the case of treatment with tablets, take the tablets to the patient with a glass of water, taking care not to touch the tablets with the hand.
Ensure that the patient takes the treatment dose on time in the presence of a nursing team member.
8. Notify the doctor if the patient refuses the medication to be given and write this down in the form designated for that purpose.
9. Securing the patient after giving medications that cause a change in the patient’s consciousness (narcotics, blood pressure medications, etc.) by raising the sides of the bed or warning the patient not to walk without assistance.
10. Notifying the treating physician in the event of any medication error, which is recorded in the form for reporting a medication error or the appearance of side effects of medications in the nursing registration form.
11. Recording the administration of treatment in the treatment implementation form
