
Chapter Four
- Organizational Chart
- The organizational structure is the formal framework through which management takes its place through an illustrative drawing that defines and clarifies relationships, through a description of the various centers that define the scope of responsibilities and authority, the scope of supervision, and the vertical and horizontal relationships between these divisions.
Types of organizational structure :
There are two types of organizational structure of the institution:
1 - The official organizational structure
2- The informal organizational structure
The official organizational structure and its preparation stages:
It is defined by the executive authority as a result of planning. It draws and clarifies the relationship between people and their positions and the classification of positions and responsibilities and the relationship between them .
The organizational structure requires several stages, the most important of which are:
Determine the main goal and sub-goals of the organization’s existence
Determine the activities necessary to implement these goals
Determine the responsibilities and duties required to carry out these activities
Grouping these responsibilities and duties into jobs such as (nursing jobs - technicians -...etc.) Grouping jobs into sections (similar and interrelated jobs that have a close relationship between them, such as nursing jobs). At the larger organizational level, departments are grouped into departments and departments are grouped into sectors.
Informal organizational structure:
It includes personal and social relationships that do not appear in the organizational structure drawing. Informal organization depends on personal relationships and not on respect for the authority vested in the center. It helps people achieve personal goals and provides them with social satisfaction . It comes from the natural respect of followers for the information and abilities of the colleague whom they follow, and the informal structure has its own channels of communication through which information is transmitted more quickly and spreads more quickly than in the formal way. Informal organizational structure is important for management and the manager must be aware of its existence, study its mechanism, avoid resistance to it and use it to achieve the goals of the organization.
Steps to prepare the organizational structure :
- Determine the purpose of the hospital.
- Determine the sub-goals necessary to achieve the goal.
- Determine the necessary activities and implement sub-objectives, for example (nursing/laboratory/nutrition activities...).
- Determine the work required to implement the activities.
- Grouping work into positions such as doctors/nursing personnel/technicians/heads/heads of units/specialties/supervisory/technical categories).
- Grouping jobs into sections, for example (nursing jobs).
- Grouping departments into departments and sectors and then grouping them under one executive body, such as the Directorate of Health Affairs/Treatment Institution/Health Insurance.
- Preparing an administrative organization guide that explains the rules, regulations, systems and instructions, the most important of which is the organizational structure .
1- The number of department supervisors is determined according to the organizational divisions of the hospital, according to the location of the departments, the number of beds, and the type of specialties.
2- The number of female department heads/heads is determined according to the organizational divisions of the different departments in the hospital.
3- The number of supervisors/supervisors, heads/heads of departments, and members of the nursing staff and their assistants in shifts and overnight hours is determined for each hospital according to the workload in each of them.
The following example illustrates the formal organizational structure of the nursing department in a large general or specialized hospital
The organizational structure of nursing management in a general or central hospital
Or my specialty is great
Organizational Chart
For the nursing department of a large general or specialized hospital
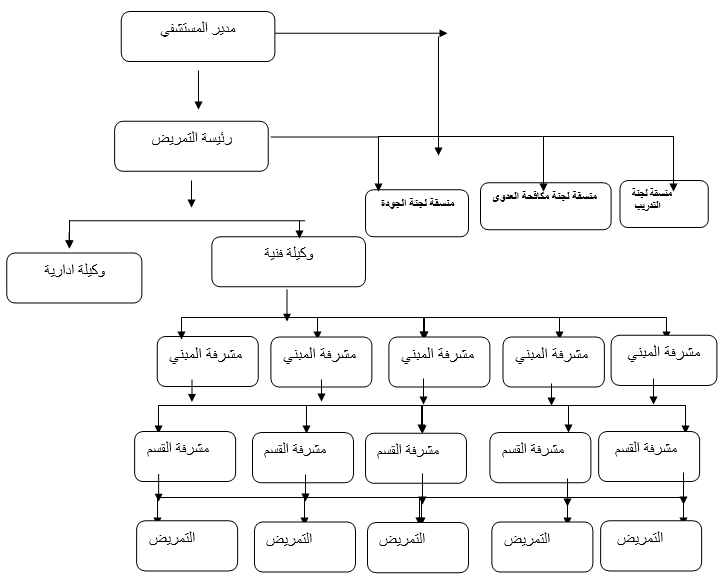
Notes on the previous example:
- The number of beds in the hospital is 150 or more
- The training and education agent in large hospitals must be responsible for continuous training of nursing staff members and coordination between the nursing institute and hospital systems.
- The number of nursing supervisors in the departments is determined according to the organizational divisions of the hospital, according to the location of the departments, the number of beds, and the type of specialties
- The number of department heads is determined according to the organizational divisions of the different departments in the hospital
- The hospital determines for you the number of supervisors, department heads, nurses and their assistants in shifts and evening hours according to the workload of each of them.
