Third part
- Vital Signs
The Definition
These are indicators that health team members search for through a physical examination to determine the basic functions of the body, which include temperature, pulse, breathing, and blood pressure.
Oral temperature measurement
The Definition :
Temperature is a number that indicates the state of the body in terms of hotness and coldness.
The Reasons :
Monitoring the patient's vital functions.
Normal rates:
36.4 – 37.4 degrees Celsius.
The person in charge:
Nursing team.
Tools :
Mercury thermometer - alcohol - piece of gauze - timer.
Steps:
1. Getting to know the patient. (Patient's name and identification bracelet)
2. Explain the procedure to the patient.
3. Washing hands.
4. Prepare tools.
5. Maintain patient privacy.
6. Adjust the thermometer and move it vigorously until the mercury line reaches 35 degrees (the starting point).
7. Clean the thermometer from top to bottom with alcohol.
8. Place the thermometer at eye level to ensure that it reaches the starting point.
9. Place the mercury portion of the thermometer under the tongue for (three minutes) in the patient’s mouth.
10. Extract the thermometer from the patient’s mouth.
11. Clean the thermometer from bottom to top with a dry piece of gauze.
12. Reading the measurement Record the thermometer reading on the temperature recording form.
13. Move the thermometer vigorously to lower the mercury level.
14. Clean the mercury part of the thermometer from top to bottom with soap and water, dry it, and disinfect it with alcohol.
15. Place the thermometer in its designated container.
16. Hand washing.
17. Reassure the patient.
18. Record any emergency signs.
Measure the temperature through the armpit
The Definition :
Temperature is a number that indicates the state of the body in terms of hotness and coldness.
The Reasons :
Monitoring the patient's vital functions.
Normal rates:
36.4 – 37.4 degrees Celsius.
The person in charge:
Nursing team.
Tools :
Mercury thermometer - alcohol - piece of gauze - timer.
1. Steps:
2. Getting to know the patient. (Patient's name and identification bracelet)
3. Explain the procedure to the patient.
4. Washing hands.
5. Prepare tools.
6. Maintain patient privacy.
7. Adjust the thermometer and move it vigorously until the mercury line reaches 35 degrees (the starting point).
8. Clean the thermometer from top to bottom with alcohol.
9. Place the thermometer at eye level to ensure that it reaches the starting point.
10. Place the mercury part of the thermometer under the armpit, making sure that this place is dry for (five minutes).
11. Removing the thermometer from the patient’s mouth.
12. Clean the thermometer from bottom to top with a dry piece of gauze.
13. Reading the measurement Record the thermometer reading on the temperature recording form. Taking into account (half a degree increase when reading the thermometer) and signed.
14. Move the thermometer vigorously to lower the mercury level.
15. Clean the mercury part of the thermometer from top to bottom with soap and water, dry it, and disinfect it with alcohol.
16. Place the thermometer in its designated container.
17. Hand washing.
18. Reassure the patient.
19. Record any emergency signs.
Measuring temperature through the anus
The Definition :
Temperature is a number that indicates the state of the body in terms of hotness and coldness.
The Reasons :
Monitoring the patient's vital functions.
Normal rates:
36.4 – 37.4°C with half a degree increase.
The person in charge:
Nursing team.
Tools :
Mercury thermometer - alcohol - piece of gauze - timer.
Steps:
1. Getting to know the patient.
· (Patient’s name and identification bracelet)
2. Explain the procedure to the patient.
3. Hand washing.
4. Prepare tools.
5. Maintain patient privacy.
6. Adjust the thermometer and move it vigorously until the mercury line reaches 35 degrees (the starting point).
7. Clean the thermometer from the mercury part from top to bottom with alcohol.
8. Place the thermometer at eye level to ensure it reaches the starting point.
9. Place gel on the edge of the mercury part and place the thermometer for a minute, taking care that the patient is on his side.
10. Remove the thermometer and clean the mercury part from the bottom with a dry piece of gauze.
11. Read the measurement and record the thermometer reading on the temperature recording form. Taking into account (a decrease of half a degree when reading the thermometer).
12. Move the thermometer vigorously to lower the mercury level.
13. Clean the mercury part of the thermometer from top to bottom with soap and water, dry it, and disinfect it with alcohol.
14. Place the thermometer in its designated container.
15. Hand washing.
16. Reassure the patient.
17. Record any emergency signs.
Note: The anal measurement method is used in children and burn cases.
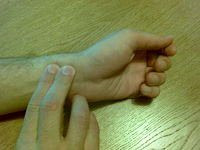
Pulse measurement
The Definition :
The pulse is the wave generated in the arteries as a result of the contraction of the heart. The pulse can be felt by feeling the large arteries in the human body, such as the neck and wrist. (As in the attached picture)
The Reasons :
Monitoring the patient's vital functions.
Normal rates:
70-100 N/Q per adult and 80-130 N/Q for children.
The person in charge:
Nursing team.
Tools :
Time timer.
Steps:
1. Getting to know the patient. (Patient's name and identification bracelet)
2. Explain the procedure to the patient.
3. Washing hands.
4. Prepare tools.
5. Choose a comfortable position for the patient.
6. Place the tip of two fingers of the hand (index and middle) on the artery (radial - carotid - femoral)
7. Using the watch with the other hand.
8. Count the pulse for one full minute. The normal pulse rate is 70-100 beats/s in an adult and 80-130 beats/s in children.
9. Record the pulse using the vital notes form and report if the pulse is (fast - slow - strong - weak - irregular).
10. Reassure the patient.
11. Hand washing.
◼️ Respiratory measurement
The Definition :
Evaluating the rate and regularity of breathing (which is the process of the body obtaining oxygen through breathing, which is necessary to carry out its activities and get rid of carbon dioxide).
The Reasons :
Monitoring the patient's vital functions.
Normal rates:
12-20 N/Q per adult and 24-40 N/Q for children.
The person in charge:
Nursing team.
Tools :
Time timer.
Steps:
1. Getting to know the patient. (Patient's name and identification bracelet)
2. Explain the procedure to the patient.
3. Preparing tools.
4. Be careful not to measure breathing after muscular effort.
5. Place the patient in a comfortable position, preferably half-sitting.
6. Ensure that the patient’s chest movement is clear to her.
7. Observe the rise and fall of the patient’s chest.
8. Each inhalation and exhalation is counted as one breath for a full minute.
9. Notice any abnormal signs in breathing.
10. Observe the patient’s color, especially around the lips and fingernails.
11. Record the respiratory rate on the patient’s form.
12. Inform the doctor of any abnormal signs.
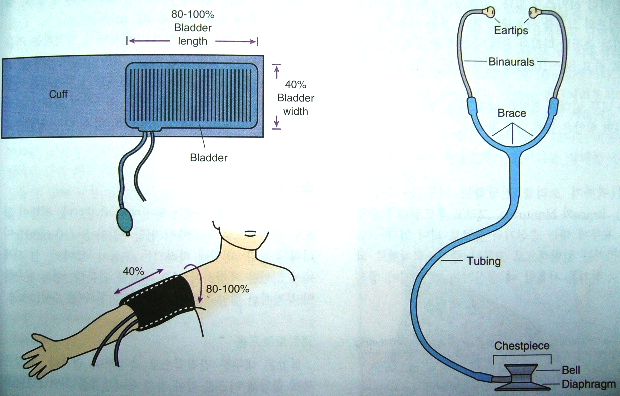
◼️ Measuring blood pressure:
The Definition :
Evaluating the movement of blood circulation by knowing the volume of blood, the blood returning to the heart, the extent of resistance of peripheral blood vessels, and the elasticity of the arteries.
The Reasons :
Monitoring the patient's vital functions.
Normal rates:
80/110 mm/Hg.
The person in charge:
Nursing team.
Tools :
Blood pressure device and stethoscope.
Steps:
1. Getting to know the patient. (Patient's name and identification bracelet)
2. Explain the procedure to the patient.
3. Prepare tools.
4. Be careful not to measure pressure after muscular effort.
5. Place the patient in a comfortable position.
6. Maintain patient privacy.
7. Measure blood pressure before and after giving high blood pressure medications.
8. Record your blood pressure measurement directly on the form designated for that purpose.
9. Determine the type of diet (low salt and fat).
10. Note the complications that may occur to the patient (nosebleeds).