
First Part
- Quality
Definition of quality:
Definitions of quality vary depending on needs and habits, and these definitions may apply to many services. Therefore, there are many definitions of quality, as follows:
◼️ Quality is judging a specific thing based on specific specifications or conformity with needs and specifications.
◼️ Quality is doing the right thing in the right way.
◼️ Quality health care is the application of medical science and technology in a manner that achieves the maximum benefit for public health without exposure to risks.
Different dimensions of quality:
◼️ Effectiveness and impact : The more effective the service is, the more it can be described as being of high quality.
◼️ Efficiency: meeting societal requirements.
◼️ Professional empowerment of workers to provide the service.
◼️ Ease of access to the service: ensuring benefit from resources and achieving fair distribution of the service to the community.
◼️ The relationship between people: whether between workers and each other or between beneficiaries of the service.
◼️ Continuity: to ensure continued use of the service to reach a high level of quality.
◼️ Resources: Providing what is necessary to provide care so that it is an integrated service.
Quality assurance :
Quality assurance in the field of health services is the application of standards in a safe and acceptable manner to the community and at an acceptable cost, such that it leads to an impact on the incidence of disease rates, mortality rates, disability,
and malnutrition.
Quality assurance principles:
There are four principles for quality assurance, which are as follows :
1- Focus on client/beneficiary services: Service planning must depend on the needs and desires of the client or beneficiary, and there are two types of beneficiaries: internal and external.
(a) Internal beneficiary:
They are those individuals within the business who depend on each other to provide the service. An example of this is service providers, supervisors, and the rest of the team.
(b) External beneficiary :
He is the beneficiary of the service, such as the patient or the community .
2- Focus on the system or processes (procedures):
Processes are defined as a successive set of steps or tasks that transform people, methods, and materials into products or services. These operations are implemented within a system, where the system is defined as a group of interconnected operations. Quality problems may result in one process as a result of a deficiency in one or in several other processes belonging to the same system, or resulting from a failure to coordinate these interconnected processes. If the processes are incomplete, then the outputs will also be incomplete. Therefore, improving quality requires an understanding of processes and acceptable levels of their variation.
3- Focus on information-based decisions:
Information in the organization is like blood in the human body, so it must be accurate and timely, which ensures the correctness of decisions. Information is particularly needed in places that suffer from problems because of its importance in the following:
(a) Define the problem
(b) Identify the causes of the problem or the processes in which errors are expected to occur
(c) Measure the results of the solutions applied and ensure that they work correctly
4-Focus on participation and the work of quality improvement teams:
All employees must participate in implementing the correction plans resulting from the application of quality improvement steps, and this has advantages including the following:
(a) Workers have a more accurate sense of the errors that occur in their work and the best way to correct them
(b) Employees prefer to implement changes that they feel involved in decision-making.
The difference between quality assurance and quality improvement
There are three basic differences between quality assurance and quality improvement as follows:
1- The quality assurance system relies on quality control by reviewing patient files and verifying the implementation of treatment according to sound scientific foundations, then identifying deficiencies or errors and determining methods for correction, while quality improvement focuses on preventing errors before they occur.
2- The quality assurance process leads to accusing those who made a mistake and raising strong sensitivities among employees, while quality improvement focuses on increasing cooperation and participation among employees, which leads to determining the correct path to avoid mistakes.
3- Quality assurance processes are always carried out separately from administrative development, while the proper application of quality assurance achieves the integration of the two processes together, which leads to achieving the desired goals.
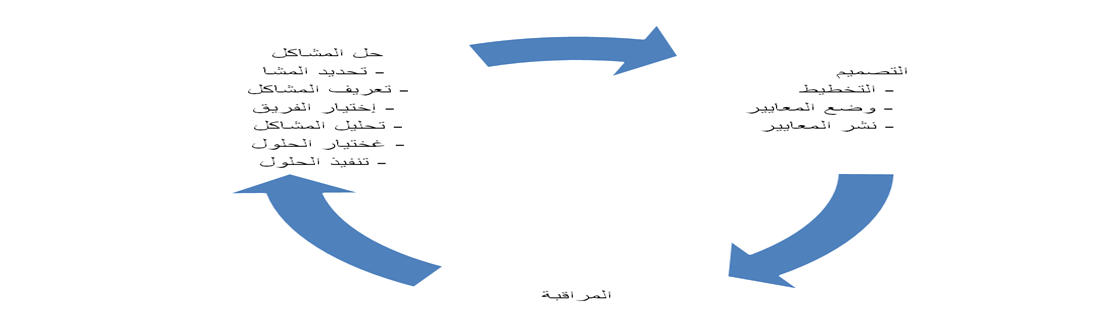
Quality assurance process
The quality assurance process includes steps that came as a result of many experiments and are called the steps of the quality assurance program or elements of quality assurance, and sometimes it is called the quality assurance cycle or quality improvement cycle. Whatever the title, this course includes three groups of activities, as in the following figure, Figure (1):
Figure (1)
Standards
Standards constitute a very important part of any quality assurance program at the levels of the organization. It is not enough for the organization to be aware of the dimensions of quality on which the quality of the services provided depends or to judge them, but rather the organization must help those who work in it to achieve the client’s expectations accurately by setting the standards for them. Which makes this easier for them.
The Definition:
The standard is a definition of expected quality, and its goal is to ensure that the service matches the needs and expectations of the customer and not the needs and expectations of the hospital.
Standard characteristics:
1- Credibility: means that there must be a strong relationship between the standard and the desired results, and that the standards be based as much as possible on research evidence.
2- Reliability (stability): means that the standard always gives the same results every time it is used under the same measurement conditions.
3- Realism: means the possibility of using standards within the resources available to the organization.
4- Clarity: The standards must be understandable to those who use them.
5- Modernity : The standard reflects the latest scientific information available.
Standards sources:
There are many sources of standards, some standards have been previously prepared, and sometimes it may be necessary to prepare new standards, as follows:
◼️ Standards previously prepared:
o Local standards.
o International standards.
o Standards from service bodies and institutions.
o Standards from educational institutes and institutions.
o International experts.
o Local experts.
◼️ Standards being re-established:
Sometimes it may be necessary to prepare a new work manual and prepare updated specifications. In such a case, there are many sources that can be relied upon, such as:
o The World Health Organization and other international organizations.
o Professional bodies such as unions and scientific societies.
o Educational institutes.
o Global experts.
o Local experts.
Nursing standards:
They are acceptable and honest definitions that express the quality of nursing care. Standards are not considered valid unless they have a means of measurement so that they are given the opportunity to measure the quality and effectiveness of nursing care.
Nursing standards have been set by multiple institutions concerned with the quality of nursing care, and these standards differ depending on the institution, as some consider the standards to be the minimum required level of service. Whatever the definition, the function of the standard is to provide the means by which the level of quality is measured.
Writing nursing standards:
In order to write nursing standards, seven steps must be followed as follows :
1- Choose the specialization that will be covered by the standards and type.
2- Determine the goal of setting standards and specify the purpose of achieving them if:
· Patient focused
· Focuses on the nurse
3- Determine the nursing actions necessary to achieve the goals.
4- Determine the time needed to complete nursing work.
5- The standard is written in an acceptable form.
6- Review each standard, taking into account that there are no ambiguous words or actions that are difficult to measure.
7- Measuring the availability of standards-specific characteristics in each standard that has been developed
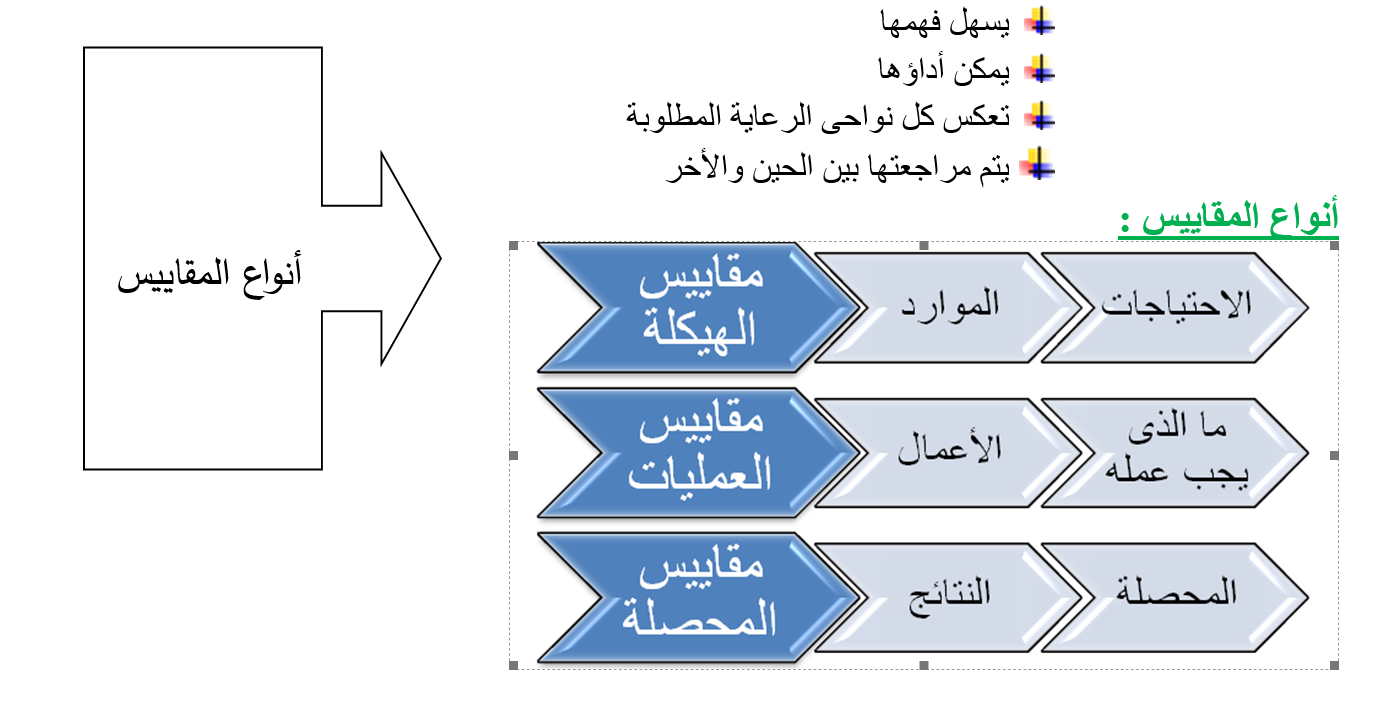
Measurements
The Definition :
The standard is a statement that describes performance and behavior, and expresses the academic or skill state that represents the positive level required for the thing. Standards are indicators of standards, and must be specific to a particular specialty or patient care.
Scale characteristics:
The standard must have:
· A detailed index of the standard
· Specific to a particular specialty or type of patient
· It can be measured
· It contains elements:
Improving the work environment
Definition of Kaizen philosophy:
It is a compound word of two parts that means “change for the better,” and it is a primary means of achieving Continuous improvement includes many of the improvement tools used in management, and one of these tools is 5S.
It is the philosophy of taking care of the workplace by organizing and cleaning it. It consists of five basic steps and each step is named in Japanese with a word that begins with the letter S Hence the name 5S . This philosophy became known worldwide by this name, and these five Japanese words were even translated into English words starting with the letter S For the designation to be valid. We can translate these five words into Arabic words that begin with the letter T, which are classification, organization, cleaning, standardization, and stabilization.
The five elements of this philosophy:
Five T consists of five elements:
1 - Sorting classificationIn Japanese, it is Seiri :
Taking care of the workplace begins with classifying everything in it.
Meaning of classification: Classification here means that we classify things into things that are necessary for work at the present time and things that are not necessary for work. After that, we get rid of the things that are not needed for work and keep those that are necessary for work. Such as: tools, files, materials, waste, papers, and equipment.
The classification process is the first step in this process
2-Organizing Set in OrderIn Japanese, it is Seiton :
After that comes the organization process, which aims to preserve the things that we decided to keep in an organized way that helps us perform the work efficiently. The organization process does not only include arranging tools or files on the shelves, but it also leads to reconsidering the general plan of the workplace itself. We have to think about the most appropriate way to organize the workplace based on our current work.
3- Cleaning or ShiningIn Japanese, it is Seiso :
The goal is a very clean work environment. This process is a process that occurs periodically, every shift or every day. There are things that must be cleaned by the person who uses them or handles them, such as work tools, including keys, tools, and supplies that he uses.
4- StandardiseIn Japanese, it is Seiketsu :
After all this effort and experience in organizing and cleaning, specific rules should be established for what the workplace should be like. This includes defining the responsibilities of each individual, setting standard methods for the cleaning process, and announcing all of this so that each individual knows what duty he has on a regular basis and how to perform it. This ensures that the situation will continue in this good manner and we will not return to old habits again.
5-Install SustainIn Japanese, it is Shitsuke :
We come to the final step, which is establishing systems to ensure the continuity of this entire process. For example, systems are put in place to review the cleanliness of places. An effective method is for one party to inspect another party, and a representative from one department inspects the process of filing files in another department or the cleanliness of the work site.
Five benefits:
There are many benefits including:
1- Reducing time wasted searching for documents or tools .
2- Reducing injuries due to the cleanliness of the floors, the absence of anything lying here and there, and the clarity of safe passage places .
3- Reducing equipment malfunctions due to their early detection.
4- Eliminate excess effort and unnecessary movements through the process of serious organization .
5- Feeling a beautiful work environment as a result of the cleanliness and organization process .
6- Replace damaged tools as soon as they are damaged, instead of discovering it late and disrupting work .
7- Discover lost things easily .
8- Reducing the malfunctions that occurred after maintenance operations as a result of some dust entering the delicate components (and this has been mentioned in other fields) .
9- Reducing quality problems that occurred due to pollution and dust.
