
BLADDER CANCER
"last update: 21 Nov. 2024"
- Annexes
|
Annex 1. Risk group stratification of patients with NMIBC and treatment recommendations (1) |
|
|
Risk group stratification |
Characteristics |
|
Low-risk tumors |
Primary, solitary, Ta G1 (PUNLMP, LG), <3 cm, no CIS |
|
Intermediate-risk tumors |
All tumors not defined in the two adjacent categories (between the category of low and high risk) |
|
High-risk tumors |
Any of the following: _ T1 tumour _ HG tumour _ CIS _ Multiple, recurrent and large (>3 cm) Ta G1-G2/LG tumours (all features must be present |
|
Subgroup of highest-risk tumors |
_ T1 G3/HG associated with concurrent bladder CIS _ Multiple and/or large T1 G3/HG and/or recurrent T1 G3/HG, T1 G3/HG with CIS in the prostatic urethra _ Some forms of variant histology of urothelial carcinoma, lymphovascular invasion |
|
Annex 2. American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM Staging System for Bladder Cancer 8th ed., 2017), (1). T Primary Tumor TX Primary tumor cannot be assessed T0 No evidence of primary tumor Ta Noninvasive papillary carcinoma Tis Urothelial carcinoma in situ: “flat tumor” T1 Tumor invades lamina propria (subepithelial connective tissue) T2 Tumor invades muscularis propria pT2a Tumor invades superficial muscularis propria (inner half) pT2b Tumor invades deep muscularis propria (outer half) T3 Tumor invades perivesical tissue pT3a Microscopically pT3b Macroscopically (extravesical mass) T4 Extravesical tumor directly invades any of the following: prostatic stroma, seminal vesicles, uterus, vagina, pelvic wall, abdominal wall T4a Extravesical tumor invades prostatic stroma, seminal vesicles, uterus, vagina T4b Extravesical tumor invades pelvic wall, abdominal wall N Regional Lymph Nodes NX Lymph nodes cannot be assessed N0 No lymph node metastasis N1 Single regional lymph node metastasis in the true pelvis (perivesical, obturator, internal and external iliac, or sacral lymph node) N2 Multiple regional lymph node metastasis in the true pelvis (perivesical, obturator, internal and external iliac, or sacral lymph node metastasis) N3 Lymph node metastasis to the common iliac lymph nodes M Distant Metastasis M0 No distant metastasis M1 Distant metastasis M1a Distant metastasis limited to lymph nodes beyond the common iliacs M1b Non-lymph-node distant metastases
|
|
Annex 3. AJCC Prognostic Groups (T N M), (1). Stage 0a Ta N0 M0 Stage 0is Tis N0 M0 Stage I T1 N0 M0 Stage II T2a N0 M0 T2b N0 M0 Stage IIIA T3a N0 M0 T3b N0 M0 T4a N0 M0 T1-T4a N1 M0 Stage IIIB T1-T4a N2,N3 M0 Stage IVA T4b Any N M0 Any T Any N M1a Stage IVB Any T Any N M1b |
Annex 4. Follow up and patient monitoring during treatment
· No single follow-up plan is appropriate for all patients. The follow-up tables are to provide guidance, and should be modified for the individual patient based on sites
of disease, biology of disease, and length of time on treatment.
· Reassessment of disease activity should be performed in patients with new or worsening signs or symptoms of disease, regardless of the time interval from previous studies.
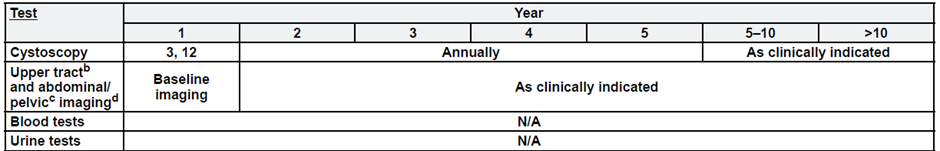
Low-Risk, Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
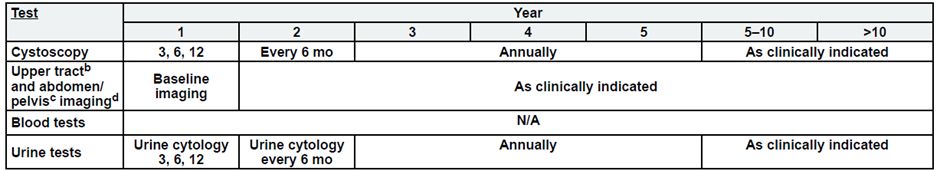
Intermediate Risk, Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
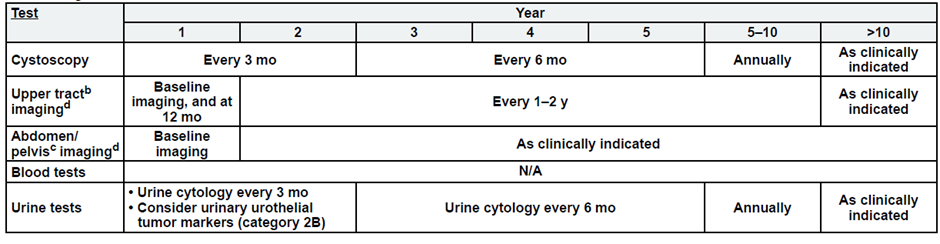
High-Risk, Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
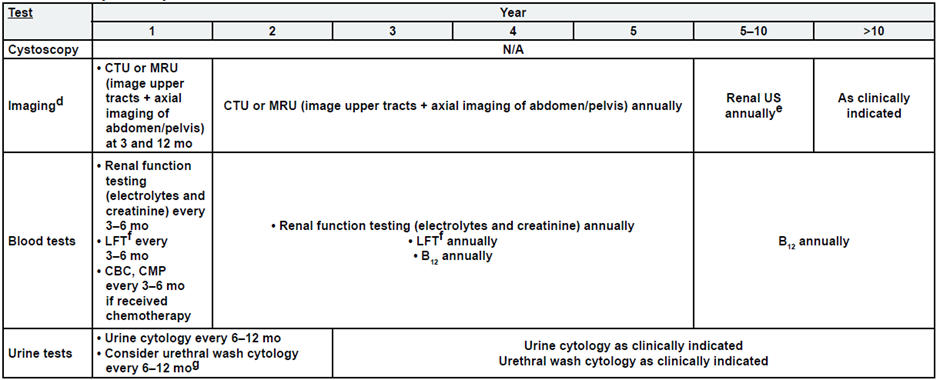
Post-Cystectomy Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
Post-Cystectomy Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
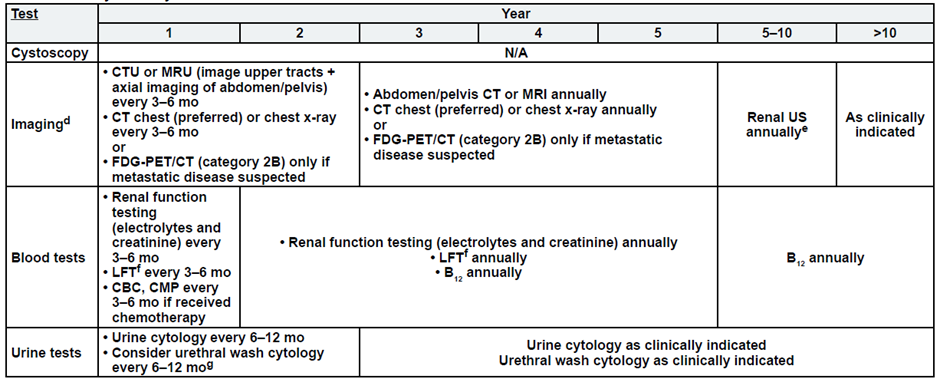
Post-Bladder Sparing
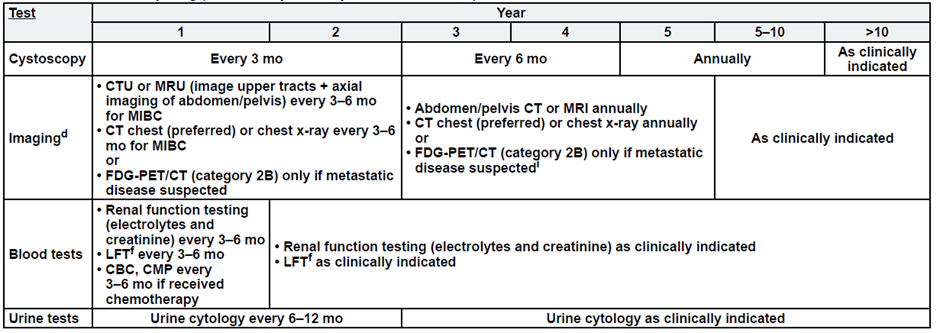
Metastatic Disease:
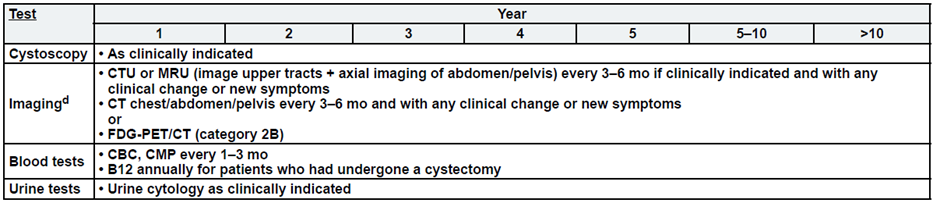
a. See risk classification
b. Upper tract imaging includes CTU, MRU, intravenous pyelogram (IVP), retrograde pyelography,
or ureteroscop.
c. Abdominal/pelvic imaging includes CT or MRI.
d. See imaging.
