
Paediatric Aggressive Mature B Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (Burkitt lymphoma)
"last update: 14 Oct 2024"
- Methodology
A comprehensive search for guidelines was undertaken to identify the most
relevant guidelines to consider for adaptation.
◾ inclusion/exclusion criteria followed in the search and retrieval of
guidelines to be adapted:
- Selecting only evidence-based guidelines (guideline must include a
report on systematic literature searches and explicit links between
individual recommendations and their supporting evidence).
- Selecting only national and/or international guidelines.
- Specific range of dates for publication (using Guidelines published or
updated 2015 and later).
- Selecting peer reviewed publications only.
- Selecting guidelines written in English language.
- Excluding guidelines written by a single author not on behalf of an
organization in order to be valid and comprehensive, a guideline
ideally requires multidisciplinary input.
- Excluding guidelines published without references as the panel needs
to know whether a thorough literature review was conducted and
whether current evidence was used in the preparation of the
recommendations.
◾ All retrieved Guidelines were screened and appraised using AGREE II
instrument (www.agreetrust.org) by at least two members. the panel decided
a cut-off points or rank the guidelines (any guideline scoring above 50% on
the rigour dimension was retained)
The NCCN guidelines are the main source used while formulating the national guidelines for Burkitt lymphoma (NHL).
◾ Evidence assessment
According to WHO handbook for Guidelines we used the GRADE (Grading
of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation) approach
to assess the quality of a body of evidence, develop and report
recommendations. GRADE methods are used by WHO because these
represent internationally agreed standards for making transparent
recommendations. Detailed information on GRADE is available through the
on the following sites:
. GRADE working group: http://www.gradeworkingroup.org
. GRADE online training modules: http://cebgrade.mcmaster.ca/
. GRADE profile software: http://ims.cochrane.org/revman/gradepro
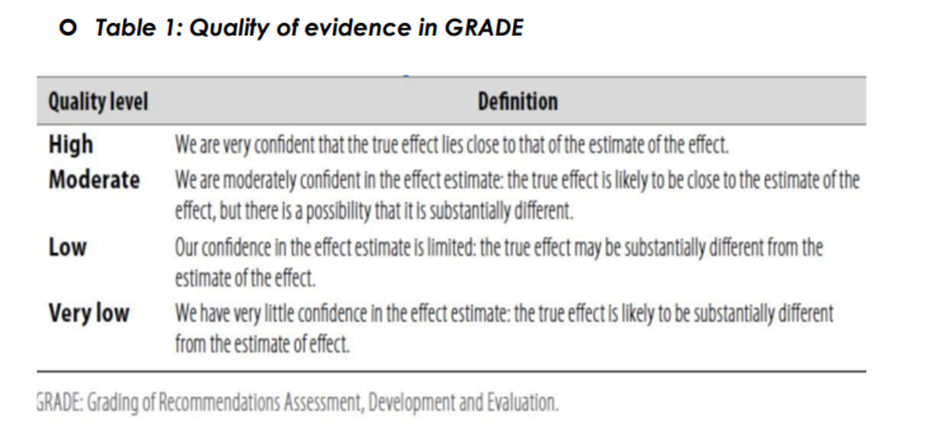
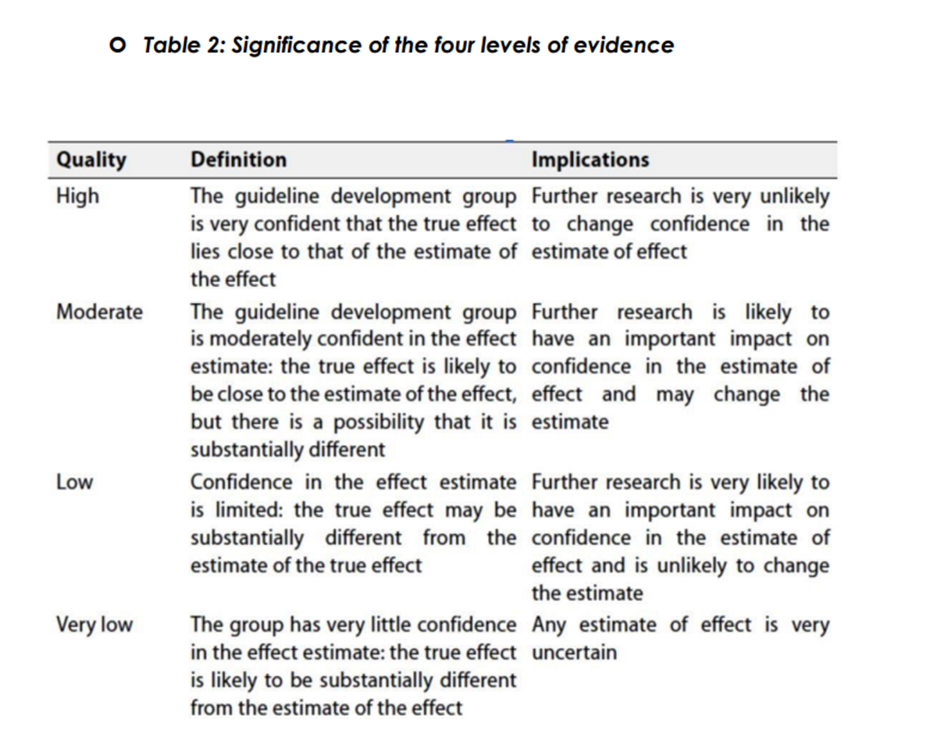
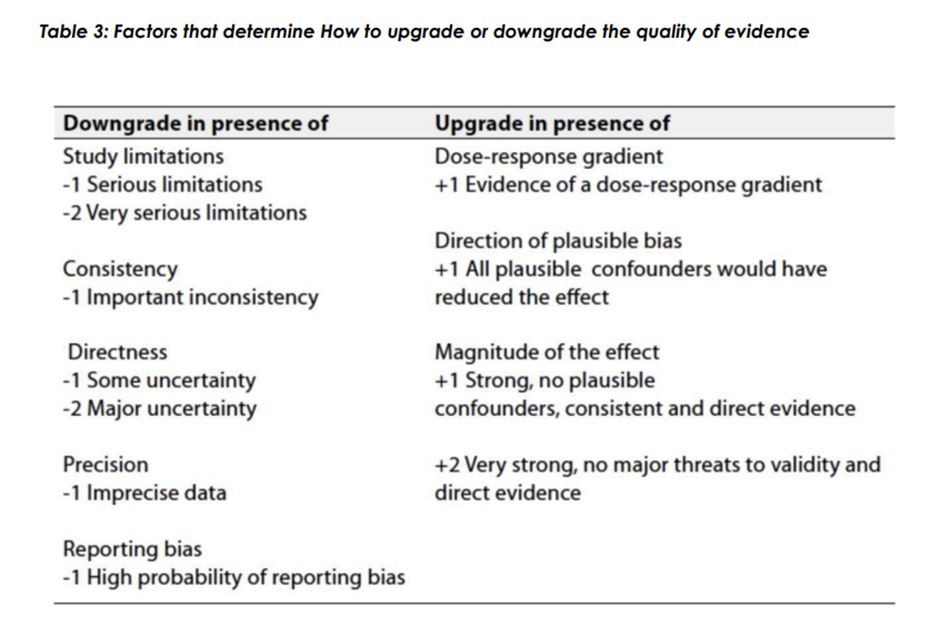
◾ Table 1: Quality of evidence in GRADE
The strength of the recommendation
The strength of a recommendation communicates the importance of adherence to the recommendation:
➡️Strong recommendations
With strong recommendations, the guideline communicates the message that
the desirable effects of adherence to the recommendation outweigh the
undesirable effects. This means that in most situations the recommendation
can be adopted as policy.
➡️Conditional recommendations
These are made when there is greater uncertainty about the four factors
above or if local adaptation must account for a greater variety in values and
preferences, or when resource use makes the intervention suitable for some,
but not for other locations. This means that there is a need for substantial
debate and involvement of stakeholders before this recommendation can be
adopted as policy.
When not to make recommendations.
When there is lack of evidence on the effectiveness of an intervention, it may
be appropriate not to make a recommendation.
