
Articulation Disorders (Speech Sound Disorders)
"last update: 29 August 2024"
- Annexes
Editorial Independence:
▪️ This guideline was developed without any external funding.
▪️ All the guideline development group members have declared that they do not have any competing interests.
Annex 1: Articulation disorders Flowchart
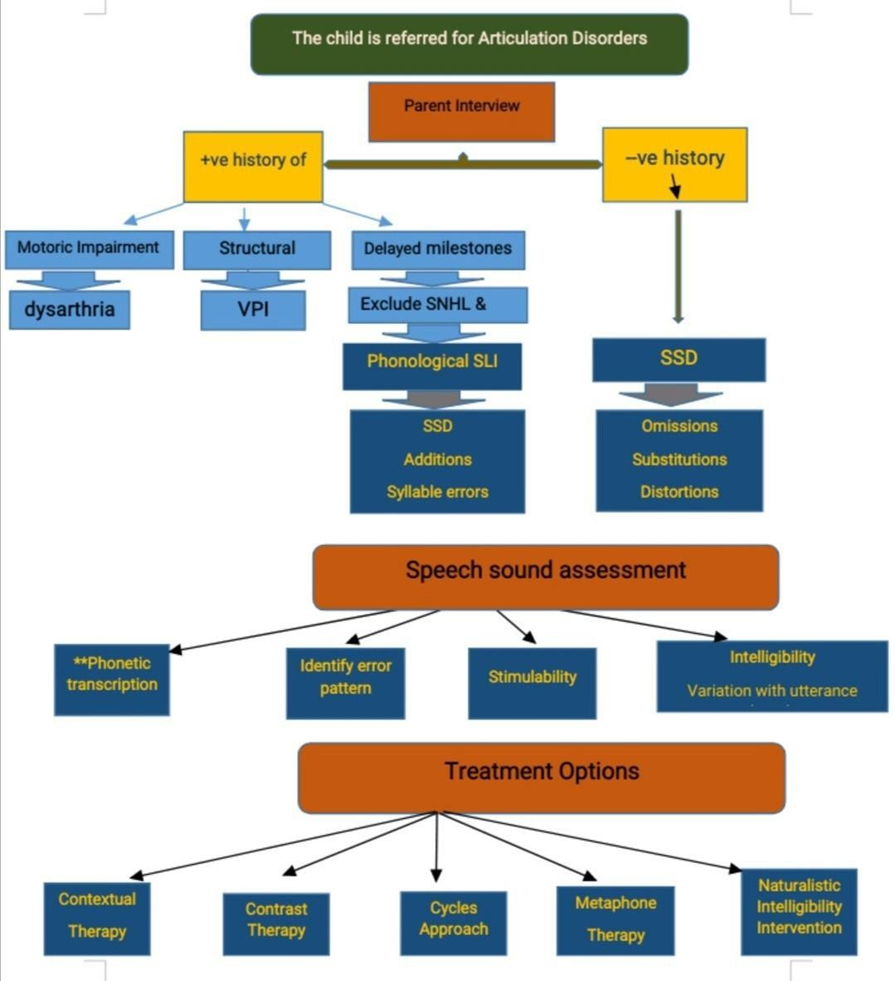
Annex 2: Tables of appraisal of selected guidelines: Currency (table 1), Content (table 2) and Quality (table 3) of the selected guidelines.
1- Currency (table 1)
|
Number |
Responsible Organization |
Date of Publication |
Review Date |
Original Details Date |
|
CPG1 |
Child lang. Teach. & Therapy |
2004 |
NR |
2001 |
|
CPG2 |
University of N Carolina |
2006 |
NR |
2011 |
|
CPG3 |
CSDRN |
2017 |
NR |
2013-2017 |
|
CPG4 |
Evicore |
2019 |
Annually |
2015-2018 |
2- Content (table 2)
|
Guideline 1 |
Guideline 2 |
Guideline 3 |
Guideline 4 |
|
|
Criteria |
Evidence-based management of ph. impairment 2004 |
University of N. Carolina 2006 |
Child Speech Disorder Research Network 2017 |
Clinical guideline Speech therapy 2019 |
|
Credibility |
9 |
8 |
5 |
8 |
|
Observability |
4 |
3 |
5 |
3 |
|
Relevance |
5 |
9 |
7 |
9 |
|
Relative advantage |
6 |
7 |
5 |
7 |
|
Easy to install and understand |
8 |
9 |
8 |
9 |
|
Compatibility |
6 |
9 |
7 |
8 |
|
Testability |
5 |
8 |
9 |
9 |
|
Total |
43 |
53 |
46 |
53 |
3- Quality (table 3)
|
Domain |
CPG1 |
CPG2 |
CPG3 |
CPG4 |
|
Transparency |
A |
A |
A |
A |
|
Conflict of Interest |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
|
Development Group |
C |
C |
C |
C |
|
Systematic Review |
A |
A |
B |
B |
|
Grade of Evidence |
B |
B |
B |
C |
|
Recommendations |
C |
A |
B |
B |
|
External Review |
NR |
NR |
NR |
A |
|
Update |
C |
B |
B |
A |
|
CPG2: 3A, 2B, 1C, 2NR CPG4: 3A, 2B, 2C, 1NR |
||||
Annex 3: The risks and benefits of added and/or modified statements
|
Statement |
Risk |
Benefit |
|
Apart from short term memory disorders, the exact cause of speech sound disorders in most children is unknown. The cause of other articulation disorders is known and can be the result of motor speech disorders (e.g., Apraxia and Dysarthria), structural differences (e.g., cleft-palate), syndromes (e.g., Down Syndrome) or sensory deficiencies (e.g., hearing loss). SSD have to be clearly differentiated from other organic articulation disorders as early as possible during preliminary diagnosis in order to direct the patient to the suitable diagnostic procedure |
Late diagnosis and subsequently interference leads to development of disarticulation strategies that will postpone response to therapy program later on. |
Early identification of the cause of articulation disorders (other than SSD) helps to manage the underlying cause in the developmental period. |
|
If SSD is not attributed to any other communication disorder, intervention should be started at the age of 5-6 years. Therapy should be postponed to give chance for completing the phonemic inventory and disappearance of all phonological processes including devoicing |
Interference before completion of phonemic inventory is not effective in most cases |
Waiting for phonemic inventory completion is important to facilitate targeting the correct place and manner of articulation of the affected phoneme |
