
Acute Otitis Externa
"last update: 28 April 2024"
- Annexes
Table 4. Elements of the diagnosis of diffuse acute otitis externa. |
1. Rapid onset (generally within 48 hours) in the past 3 weeks, AND… 2. Symptoms of ear canal inflammation, which include: otalgia (often severe), itching, or fullness, WITH OR WITHOUT hearing loss or jaw pain, a AND… 3. Signs of ear canal inflammation, which include: tenderness of the tragus, pinna, or both OR diffuse ear canal edema, erythema, or both WITH OR WITHOUT otorrhea, regional lymphadenitis, tympanic membrane erythema, or cellulitis of the pinna and adjacent skin |
a Pain in the ear canal and temporomandibular joint region intensified by jaw motion. |
Table 5. Interventions considered in acute otitis externa guideline development. |
➡️Diagnosis ▪️ History and physical examination ▪️ Otoscopy ▪️ Pneumatic otoscopy ▪️ Otomicroscopy ▪️ Tympanometry ▪️ Acoustic reflectometry ▪️ Culture ▪️ Imaging studies ▪️ Audiometry (excluded from guideline) ➡️Treatment ▪️ Aural toilet (suction, dry mopping, irrigation, removal of obstructing cerumen or foreign object) ▪️ Non-antibiotic (antiseptic or acidifying) drops ▪️ Antibiotic drops ▪️ Steroid drops ▪️ Oral antibiotics ▪️ Analgesics ▪️ Complementary and alternative medicine ▪️ Ear canal wick ▪️ Biopsy (excluded from guideline) ▪️ Surgery (excluded from guideline) ➡️Prevention ▪️ Water precautions ▪️ Prophylactic drops ▪️ Environmental control (eg, hot tubs) ▪️ Avoiding neomycin drops (if allergic) ▪️ Addressing allergy to ear molds or water protector ▪️ Addressing underlying dermatitis ▪️ Specific preventive measures for diabetics or ▪️ immunocompromised state |
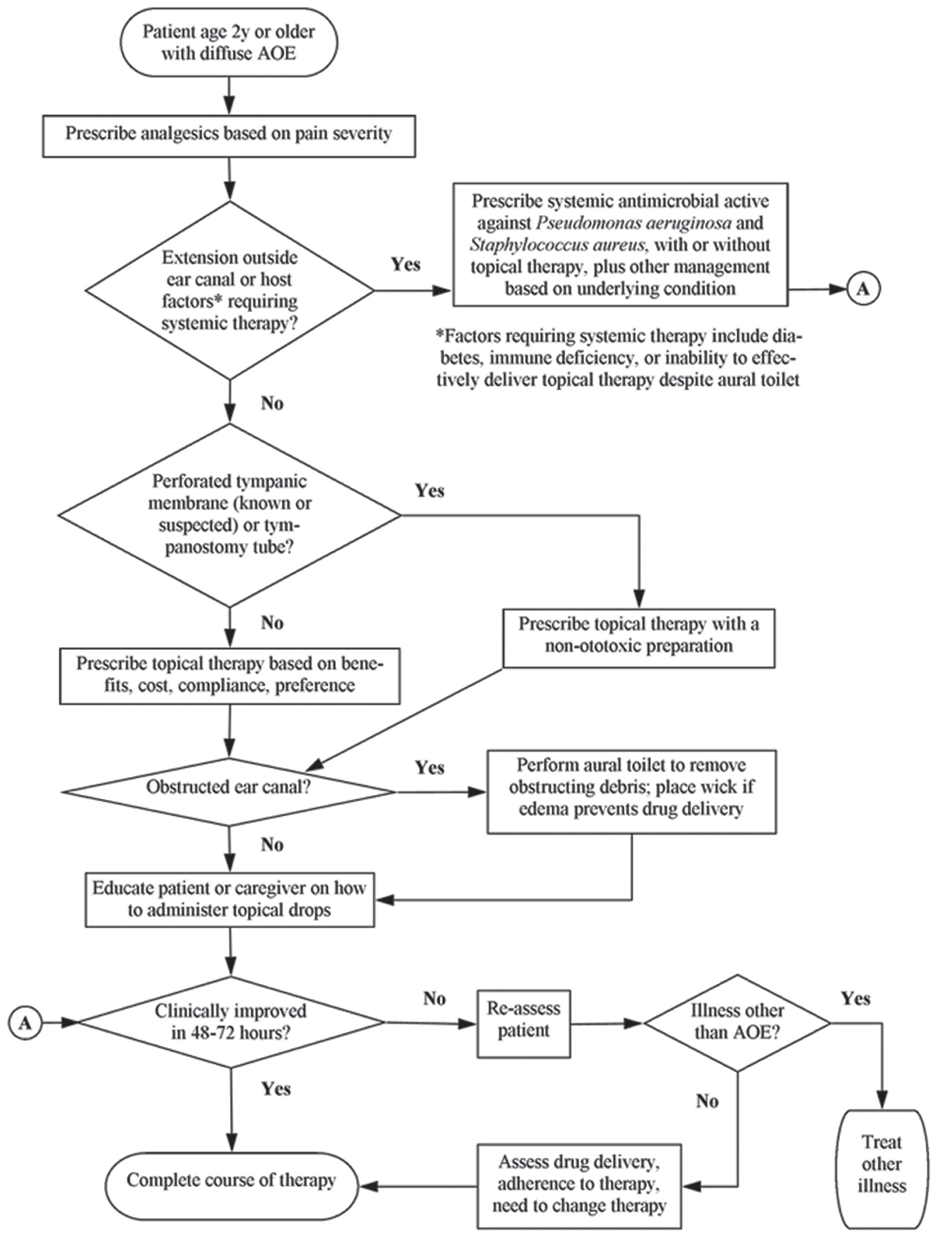
Figure 1: Flow chart for managing acute otitis externa.
