Abattoir (Slaughterhouse or Meat Plant)
"last update: 9 May 2024"
- Main compartments of the abattoir
1. Qarantine (Lairage)
· The Lairage is designed for reception of living animals. It is used for performance of ante-mortem inspection and pre-slaughter rest (12- 24 hr.) before slaughtering and segregation of animals exposed to infection.
· It should be built far away from the slaughter halls, roofed to protect animals and staff, and has reinforced concrete divisions with iron gates built in each lairage. Water troughs or bowls and hay rack must be provided.
· Every species of food animal must have a separate lairage with the following pen size for housing of livestock: cattle (loose) 2.3-2.8m, cattle (tied) 3.3m, calves and sheep 0.7m.
2. Slaughter halls
· Every species of animal must have separate slaughter halls. Slaughtering, dressing, and post-mortem inspection take place in slaughter halls.
· There are two main types of slaughter halls which are traditional or old-fashioned slaughter halls and modern automatic slaughter halls.
· At the traditional slaughter hall, the slaughtering, dressing, splitting and inspection of carcasses and organs have been done while animal carcasses are being hung in the same place or on the floor, which is considered unhygienic.
· While at modern automatic slaughter halls the carcass is conveyed by gravity or power along an overhead rail, after bleeding. The process of dressing is divided up into various stages, each undertaken by a separate operator. A combination of several machines, tools, and equipment. The dressing line system consists of clean and unclean areas where slaughtering, dressing, splitting are performed in the unclean area, while washing, inspection, cooling and dispatching in the clean area. The production rate may be as high as 5000, 10,000, and 3500 Cattle, sheep and pigs every 10 hours, respectively.
· There are four main types of line dressing which are gravity rail system (10-40 cattle/hour), intermittent powered system (10-75 cattle/hour), continuous powered system (40-120 cattle/hour) and canpak system 50-150 cattle/hour.
1. Gravity rail system is used for lower slaughter rates with dressing occurs while hanging and moving through gravity.
2. Intermittent power system can be used for higher rates of slaughter than gravity rail system and the carcass suspended on spreader and trolley a long a level rail at intervals by means of a variable timing device which can be pre-set to suit the slaughter rate.
3. Continuous-power system is a continuous system and is used for higher rates of slaughter.
4. Canpak system where the carcass can be revolved 360 degrees while being on the rail, allowing the operator to work all sides from one position.
3. Emergency slaughter room or Sanitary slaughter unite (Isolation block)
· It is a very small abattoir consists of lairage for 4 cattle, slaughter hall, detained meat room for keeping the carcass until the results of laboratory examination and it should be situated near to the lairage and by-product unit to get rid of dead animals from lairage into render plant.
· If there is no isolation block in the abattoir, suspected and diseased animals should be isolated and slaughtered at the end of slaughtering of healthy animals to avoid cross infection and contamination.
4. Condemned meat room
· For keeping the carcass and organs unfit for consumption and then taken either into render plant (By-products unit) or general incinerator (Outside town).
5. Detained meat room
· For keeping carcass and organs required further examination at refrigeration temperature (-1ºC to +4ºC).
6. Chilling room
· For keeping carcasses fit for human consumption until dispatching at a temperature range from -1ºC to +4ºC and the relative humidity 85%.
· The carcass must be hung in such a way as to allow free movement of cold air around them, rail spacing should be 0.9 m for beef, 0.7m for pigs and 0.5 m for lambs with a minimum space between carcasses on the rail should be 0.3-0.4m.
· It is vital that chill or freezer doors be closed fitting, and be provided with an internal opening device to prevent personnel being closed in the rooms and temperature to be checked on a continuous basis using charts or computer-generated records.
7. Veterinary Laboratory
· A well-equipped laboratory is essential for diagnosis and confirmation of suspicious cases as well as for maintaining the overall hygiene standards.
· A small laboratory for trichinella examination should fit, connected with pig slaughter halls.
8. Accessory compartments
a. Hide and skin store
Hides and skin of slaughtered animals should be transferred directly after skinning either mechanically or manually to this store where they are prepared and stored.
b. Gut and tripe room
For emptying & cleaning of the stomach and intestines.
c. Red offal room
Edible offal such as liver, kidneys and lungs should be trimmed and placed in a chill or freezing room. Edible offal’s must be held at a temperature not exceeding 3ºC .
d. The edible fat room
This is a separate holding room, usually located near the gut room and where edible fat is held.
e. Cutting room
During the cutting process, the temperature of the building must be not exceed 10ºC (internal temperature of meat not more than 7ºC). Adequate facilities are necessary in the form of suitable equipment, hot water, potable water to keep the whole area hygienic and waste disposal system that meets hygienic requirements.
f. Inedible area
Materials unfit for human consumption except for hide and skin should be sited away from the edible areas, since improper handling of these organs can result in unhygienic conditions.
g. Fresh meat dispatch area
The fresh meat dispatch area must be located away from the dirty part of the abattoir and easily reached by vehicles associated transport of meat and offal for human consumption.
h. Facilities for personal
Enough water closets for both sexes are employed, with showers and washing hand basins must be provided (one for every 15 employees). A Laundry and car park are necessary for modern abattoir.
i. Veterinary office
An adequately equipped lockable room for the use of the veterinary service and a larger one for the meat inspectors. The rooms provided with hand washing and showers facilities. A convenient means of cleaning footwear before entry into changing rooms is an advantage.
j. Manure bay
This should be located near the lairages on the dirty side of the abattoir. Its floor and sides should be impervious, with provision made for overflow liquors to be drained
k. Vehicle washing
The cleaning of meat and animal transport vehicles is usually neglected, so the former should be done in the clean side of the abattoir with high pressure hot water and detergent with a good drainage for vehicles and wash area.
l. Freezing room
For keeping the carcass that requires special treatment.e.g. light infestation with C. bovis
m. By- product unit
By-product unit is used for further processing of all materials which are unfit for human consumption.


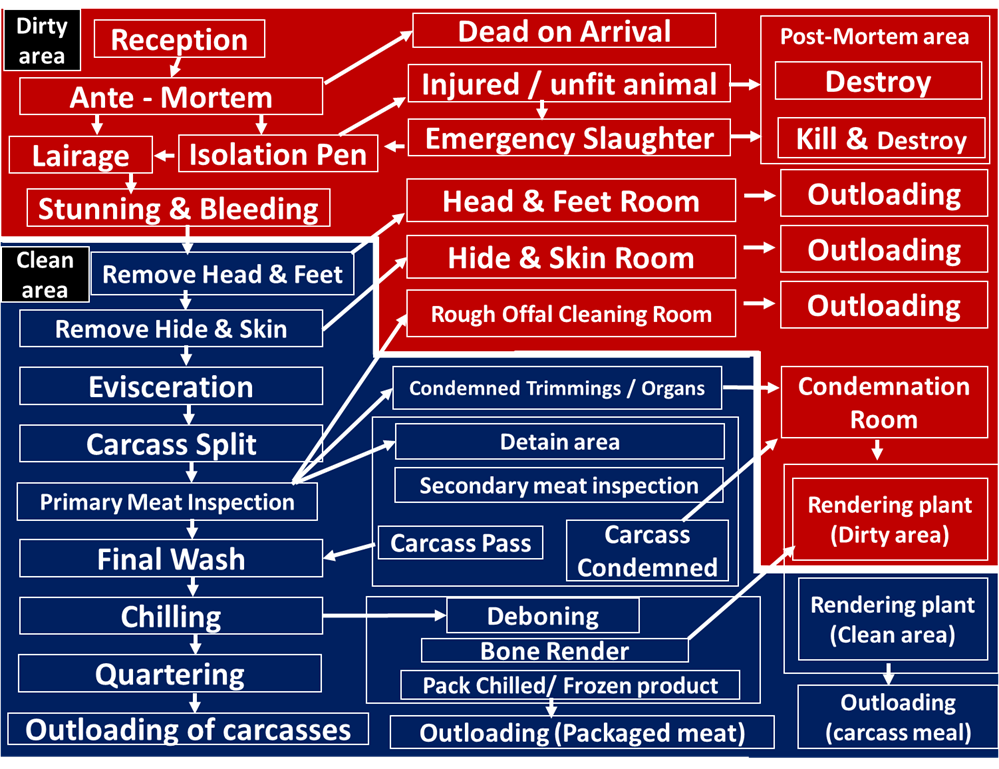
Slaughter Hall

Flow diagram for red meat abattoir