
Part Three
- Gynecological and obstetric operations
1. Caesarean section.
2. hysterectomy
3. removal of the ovaries .
4. expansion and curettage .
1-Caesarean Delivery
Caesarean section is a type of abnormal birth, in which the surgeon performs a surgical operation, in which the abdomen and uterus are cut to extract the fetus when natural birth is not possible, and it is performed by a specialized surgeon, an 'obstetric surgeon'. Cesarean section is a surgical operation where one or more incisions are made in the mother's abdomen and uterus to have one or more babies. This operation is performed when vaginal delivery endangers the life or health of the baby or mother, this operation is performed before 39 a week of pregnancy .
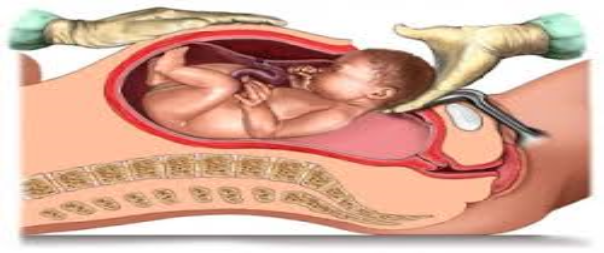
- Indications for cesarean section :
- When natural childbirth is impossible, as it carries a risk for the mother or child, one of the most important motives and positive conditions for performing a cesarean section is .
- Factors that hinder normal transvaginal delivery such as :-
- The length of Labor.
- Rupture of the uterine wall and an increase in blood pressure in the mother or child after rupture of the amniotic membrane, an increase in the heart rate of the mother or child.
- Problems with the placenta such as (placenta previa, or placenta accreta).
- Ineffectiveness of the divorce of childbirth several hours after its start.
- The fetus came by accident and could not be born naturally.
- Dyspareunia due to the large size of the fetus, its excess weight (more than 4 kg) and the narrowing of the mother's pelvis.
- Problems with the umbilical cord, such as advanced vessels, and the multi-lobed placenta, which includes the placenta with two lobes, the placenta with an additional lobe, and the sheath suture.
- Prolapse of the umbilical cord.
- Multiple births (a woman's pregnancy of more than one fetus inside the uterus ).
- The mother has AIDS.
- Infection of the mother with one of the sexual diseases such as herpes, which may be transmitted to the fetus during natural childbirth through the vagina.
- Previous rupture of the uterine wall.
- Previous classic cesarean section (longitudinal).
- Other reasons such as :-
1- the occurrence of traumatic bleeding that threatens the life of a woman during childbirth due to rupture of the placenta or the ends of the placenta.
2- preeclampsia, high blood pressure to high degrees pose a danger to the health of the expectant mother.
3- skipping the fetal age of forty weeks and not starting childbirth.
4- when the life of the fetus is threatened by a danger, which necessitates its birth before it dies in the belly of its pregnant mother.
5 - the uterus is lazy and the shooting stops.
6- the woman is tired and ceases to actively participate in the birth process.
7- if the woman is a virgin and has exceeded the age of thirty-five, and the child is desirable, as it came after being treated for long-term infertility
There are many steps that can be taken during abdominal or pelvic operations to reduce complications that occur after operations, such as the occurrence of adhesions. These techniques and principles may include:
1. handle all weaves with great care .
2 - uses of powder-free gloves .
3. spare parts for the wound.
4-bleeding control .
5-prevent the occurrence of infections
2-hysterectomy :-
Definition :
Hysterectomy is a surgical procedure in which surgery is performed to remove the uterus, usually performed by a gynecologist. Removal of the uterus may often include the removal of the cervix, ovaries, fallopian tubes.
Types of :
1-total hysterectomy (removal of the body, bottom, and cervix; called 'total hysterectomy')
2-partial (removal of the body of the uterus while leaving the cervix intact; called 'supracervical hysterectomy').
Important note :
This leads to the fact that the woman who has had the removal operation is unable to conceive and have children, so this procedure is performed only if there is a strong reason for the operation, such as there is a direct threat to the patient's life in the presence of the uterus, and there is no therapeutic alternative except for the removal procedure. A hysterectomy also stops the menstrual cycle, and if the ovaries are removed together with the uterus, you will feel the symptoms of a period of interruption of the cycle (menopausal symptoms). The uterus can be removed by making a surgical incision in the lower abdomen or through the vagina, and sometimes the uterus can be removed by laparoscopy.
- Causes:
1- hysterectomy is necessary when cervical cancer or uterine cancer itself is diagnosed, it is also recommended when ovarian cancer occurs .
2- severe metrorrhagia: previously, this was one of the reasons for the removal of the uterus, but with the advent of Interventional Radiology, bleeding can be stopped with a catheter and save the life of the patient and the uterus. But when bleeding continues with intensity and profusely during the menstrual cycle without knowing its causes, the uterus is removed.
2-uterine prolapse, prolapse, fall or prolapse of the Uterus (prolapse of the Uterus). (That is, the protrusion of the uterus outside the pelvis) may require such an operation as part of the lifting and tightening of the vaginal wall .
Species
- There are three types of hysterectomy :
1- vaginal hysterectomy is performed without opening the abdomen and does not leave a clear trace from the outside indicating that the woman has undergone a type of surgery called radical, basic or essential, in which the uterus, upper vagina, fallopian tubes and ovaries are removed, which causes an immediate interruption of menstruation. The ovaries may be left in place to avoid this happening.
2- complete: total or complete: in which only the uterus and cervix are removed and does not mean the removal of the ovaries ,where the hysterectomy is performed by the abdomen is the most common operation and is performed through an opening in the lower abdomen about 20 cm wide.
3- removal of the uterus through the vagina with the help of an endoscope by making small surgical openings in the abdomen to insert the endoscope from them and monitoring the primary surgeon who removes the uterus through the vagina for the purpose of finishing the operation and making sure the safety of internal organs. Only the uterus is removed while retaining the cervix to preserve the sexual sensation as it is thought or thought so.
- There are types of this operation according to the organs that are removed, which are as follows :-
- Complete hysterectomy with cervix and this operation is more common .
- Partial hysterectomy with retention of the cervix in place .
- Hysterectomy with the cervix and a small part of the upper section of the vagina and some of the surrounding tissues inside the pelvis, this operation is performed only in cases of cervical cancer .
3- ovarian resection
The purpose of the operation:
The purpose of oophorectomy surgery is to remove one or both ovaries, with or without fallopian tubes, which form a large and central part of a woman's reproductive system.
Causes of oophorectomy
1- ovarian cancer.
2 - when suspecting the presence of a cancerous disease in the ovarian cysts, as part of the process of diagnosing other abnormalities in the ovaries (swelling in the ovaries, for example), pelvic diseases such as adhesions (endometriosis)،
3 - when diagnosing the presence of contamination in the pelvis (cysts or pelvic inflammatory disease), in case of exposure to ovarian torsion that causes permanent damage to the ovaries, as well as for the treatment of other cancer diseases in the pelvis such as uterine cancer, fallopian tubes or cervical cancer.
4 – another reason to have an oophorectomy surgery is to take this step as a preventive measure – such as preventing pregnancy in women who do not want to give birth at all after that - or to prevent cancer in women at risk of ovarian cancer (BRCA gene carriers).
Preparation for the operation:
- Before undergoing surgery to remove the ovaries due to cancer, several proactive tests are usually performed, including a comprehensive blood count, a blood chemistry examination that includes tumor fingerprinting, coagulation tests, kidney performance, and urinalysis.
- Usually, an examination is also performed in order to detect cervical cancer - Pap pap smears
- Ultrasonic device (ultrasound).
– In some cases, computed tomography (CT) or positron tomography (CT-PET) is needed in order to check the extent of tumor spread.
4- dilation and curettage
Dilation and curettage
(D&C)
An operation is performed to empty the contents of the uterus in order to stop bleeding and take a sample for analysis .
Causes
1- dilation and curettage are used in the diagnosis and treatment of many gynecological diseases such as menstrual irregularities(menstrual cycle), whatever its form (increased blood loss during the cycle, lack of blood, or an increase in the number of cycles than usual).
2- curettage is also used to remove increases in the endometrium, which are caused by some diseases such as polycystic ovaries, which causes hormonal disorders that lead to increased growth of the endometrium.
3- curettage is used to remove other causes of vaginal bleeding,such as hidden or missed abortion(the fetus did not descend despite its death inside the uterus), and also postpartum bleeding, which is caused by the non-descent of the placenta or part of it after birth.
4-curettage is used in the procedure of therapeutic abortions.
Mastectomy
Two main objectives:
Excision of the entire tumor and all breast tissue from one or both breasts.
Examine the lymph nodes in the armpit to make sure that the tumor has not spread to them.
There are several types of mastectomy. They include:
1-modified radical mastectomy.
2-simple or complete mastectomy.
3-mastectomy with skin retention.
4-mastectomy with nipple retention.
Simple mastectomy, or complete mastectomy is aimed at removing the entire breast. This includes breast tissue, skin, nipple and areola. Mastectomy with skin retention removes all breast tissue, nipple and areola. The skin of the breast is not excised. This type of surgery is immediately followed by breast reconstruction surgery. A mastectomy with nipple retention only removes breast tissue. The skin, nipple, areola and chest muscles are not excised. This type of surgery is immediately followed by breast reconstruction surgery. Sometimes a mastectomy may be performed even if the woman does not have breast cancer. Preventive or risk-reducing mastectomy is the removal of both breasts to reduce the risk of breast cancer. It is performed only in women with a very high risk of developing breast cancer.
Important note
Several hours before the operation, the surgeon may give an injection near the tumor. The injection is either a special blue dye or a radially active safe dye. The tincture helps the surgeon to find out which lymph nodes he has to excise. One or two incisions are made, and in all types of mastectomy, at least one lymph node is removed. During surgery, the lymph nodes that have picked up the dye are excised, sent to the laboratory for examinations.
