Quarantine and Isolation
"last update: 26 NOV 2024"
- Management of farm traffic
Bacteria, viruses or other agents of disease are infectious when they are capable of causing infection in exposed animals. Farm visitors wearing boots or clothing freshly contaminated with infectious agents can spread diseases within a farm and among farms. Birds, rodents, pets, people, equipment and vehicles contaminated with manure (or other bodily excretions including urine, milk, saliva, uterine discharge or calving fluids) are potential disease carriers.
➡️Control bird populations:
Plug small and large nesting holes and perches in your barn that are suitable for sparrows
Screen all openings in natural ventilation dairy barns
Seal off openings into silo roofs
Screen ledges used as nesting sites by pigeons
➡️Control rats and mice:
Construct rodent-proof buildings
Remove food and water supplies
Destroy existing populations by baiting, fumigating or trapping.
➡️Control people and pets
People spread contaminated material directly on footwear, hands and clothing. To decrease the spread of contaminants:
1. Inform farm workers, visitors and truckers of your farm protection methods and insist upon co-operation.
2. Discourage visitors from entering the housing and feeding areas.
3. Post "Do Not Enter" signs on livestock buildings and farm entrance gates.
4. Designate a specific visitor area to minimize contacts.
5. Insist visitors wash their boots before entering and leaving the farm.
6. Supply rubber boots or plastic disposable boots and clean coveralls for visitors.
7. Provide a footbath containing suitable disinfectant.
8. Insist workers wash their hands before milking cows and after working with sick animals.
9, Insist workers wear protective plastic or rubber gloves for calving cows.
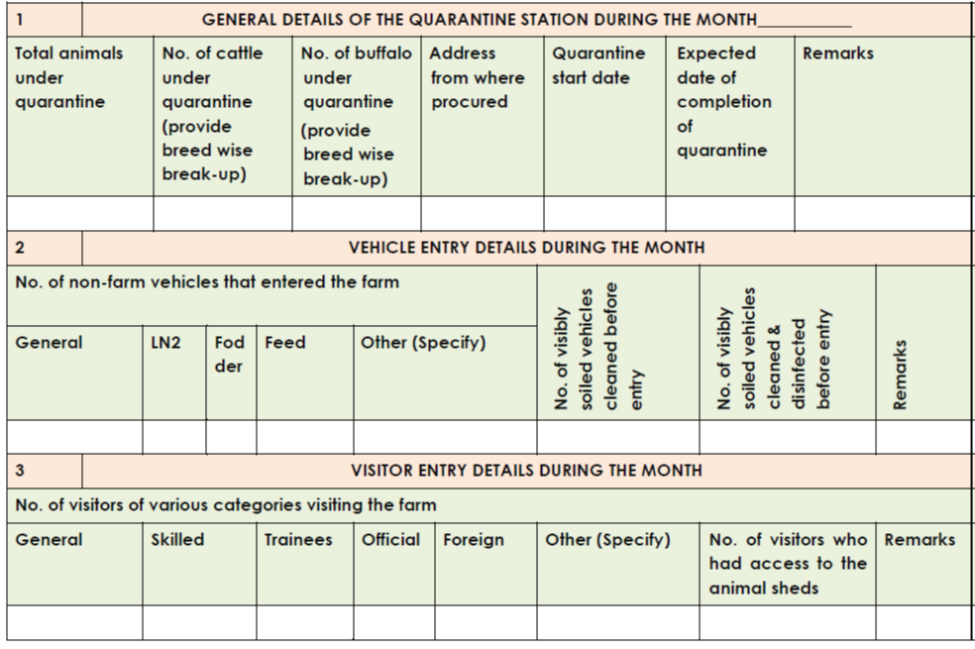
Consolidated monthly report of quarantine station