Part One
| Site: | EHC | Egyptian Health Council |
| Course: | Procedural work guide for the operations unit |
| Book: | Part One |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Monday, 23 December 2024, 4:35 PM |
Table of contents
- - Preparation
- - Organizational Chart
- - Job Descriptions
- - Introduction to the operations unit
- - Operations unit equipment
- - Charter of Patients and Nursing Rights
- - Ethics and ethics of the nursing profession
- - Communication skills
- - Quality and improving the work environment
- - International standards and goals for patient safety and security
- - Records and reports
- Preparation
Central Nursing Administration
Dr. Kawthar Mahmoud Mahmoud Head of the Central Administration for Nursing
Dr. Nevin Abd Rab Al-Nabi Muhammad Director General of Therapeutic Nursing Department
Prof. Amany Farouk Mohamed Senior Nursing Specialist at the Central Administration of Nursing
Prof. Azza Jalal Ahmed Nursing specialist at the Central Administration of Nursing
Prof. Hanan Amin Shousha Nursing specialist at the Central Administration of Nursing
Prof. Yasmine Sayed Abdel Basset Nursing specialist at the Central Administration of Nursing
Prof. Marwa Mohamed Hassan Nursing specialist at the Central Administration of Nursing
Prof. Ahmed Youssef Abdullah Nursing specialist at the Central Administration of Nursing
Prof. Angham Hamdy Abdel Khaleq Nursing specialist at the Central Administration of Nursing
Prof. Mohamed Abdel Ghani Youssef Nursing specialist at the Central Administration of Nursing
Prof. Taha Mohamed Ahmed Nursing specialist at the Central Administration of Nursing
Faculty of Nursing, Ain Shams University
Dr. Camellia Fouad Abdullah Professor in the Surgical Internal Medicine Department, Faculty of Nursing, Ain Shams University
Dr. Mona El-Shazly Mahmoud Head of the Department of Administration, Faculty of Nursing, Ain Shams University
Dr. Buthaina Nader Sadiq Lecturer in the Pediatrics Department, Faculty of Nursing, Ain Shams University
Dr. Samar Marzouk Lecturer in the Surgical Internal Medicine Department, Faculty of Nursing, Ain Shams University
Dr. Dina Mohamed Mohamed Lecturer in the Surgical Internal Medicine Department, Faculty of Nursing, Ain Shams University
Dr. Sarah Fathi Lecturer in the Surgical Internal Medicine Department, Faculty of Nursing, Ain Shams University
Review and supervision
Dr. Kawthar Mahmoud Mahmoud Head of the Central Administration for Nursing
Prof. Dr. Hisham Atta Youssef Assistant to His Excellency Prof. Minister of Health and Population
For human resources development and training
Prof. Dr. Sherif Wadih Advisor to His Excellency Prof. Dr. Minister of Health and Population for Emergencies
Dr. Nevin Abd Rab Al-Nabi Muhammad Director General of Therapeutic Nursing Department
Dr. Ali Abdel-Azeem Director General of Quality Management Ministry of Health and Population
- Organizational Chart
The Definition:-
The organizational structure is the formal framework through which management takes its place through an illustrative drawing that defines the relationships, through a description of the various centers that define the scope of responsibilities and authority, the scope of supervision, and the vertical and horizontal relationships between these divisions.
Types of organizational structure:-
◾ Formal organizational structure
◾ Informal organizational structure.
Formal organizational structure:-
The Definition:-
The formal organizational structure is defined by the executive authority as a result of planning. It draws and clarifies the relationship between people, their positions, responsibilities, and the relationship between them.
Informal organizational structure:-
It includes personal and social relationships that do not appear in the formal organizational structure drawing
Steps to prepare the organizational structure:-
◾ Determine the purpose of the hospital.
◾ Determine the sub-goals necessary to achieve the goal.
◾ Determine the necessary activities and implement sub-objectives. (Example: nursing / laboratory activities / nutrition...)
◾ Determine the work required to implement aspects of activities.
◾ Grouping work into positions such as doctors/nurses/technicians/heads of units/specialties/supervisory/technical categories).
◾ Grouping jobs into departments, for example (nursing jobs).
◾ Grouping departments into departments and sectors and then grouping them under one executive body, such as the Directorate of Health Affairs/Treatment Institution/Health Insurance
◾ Preparing an administrative organization guide that explains the rules, regulations, rules and instructions, the most important of which is the organizational structure.
NB :-
◾ -The number of department supervisors is determined according to the hospital’s organizational divisions, according to the location of the departments, the number of beds, and the type of specialties.
◾ -The number of department heads is determined according to the organizational divisions of the different departments in the hospital.
◾ -The number of supervisors, department heads, nurses, and assistants in shifts and evening hours is determined for each hospital, according to the workload in each hospital.
Organizational Chart

Organizational
Structure of the Operations Unit

- Job Descriptions
The Definition
It is a list that includes a group of elements specific to a specific job, such as [the name of the job, a summary of the job, the supervision of others over the job and the job’s supervision over others, duties and responsibilities, and the special qualifications to hold this job.
It is statements that explain the nature of the job and the responsibilities assigned to the job holder, as well as the relationship between the job and other jobs.
The job description of a health worker specifies:
◾ His powers, i.e. his right to make decisions
◾ His responsibilities, that is, the amount of work that he is expected to accomplish
Purpose of the job description:
It is to specify to the worker, the rest of the team members, and the supervisors:
◾ What the worker is expected to accomplish
◾ The level of performance expected from him
◾ Under whose authority he is.
◾ The people he supervises
Contents of the job description:
Job name :
It is the official name of the recognized job for the person who does the work or performs the job, for example, nursing technician or nursing specialist.
The date :
History is mentioned because the job description is not permanent. Workers and their duties change, and the job description must also be reviewed and changed when necessary.
Function :
Summarizes the main responsibilities of the job:
Duties: -
These are the most important elements of the job description, and even the most important part of it. Each unit duty should be fully defined as a recognized part of the job holder’s work.
Relations :-
This is simple data related to the following
The title of the person responsible for the job holder in performing his duties
Titles of the people whose work the incumbent supervises
Qualifications :-
Describes the qualifications, including basic training and experience, required of the job holder
Principles of organizing and writing job description information:
Arrange assignment descriptions in a logical manner
He mentions the separate duties clearly and concisely, and not going into detail becomes a motor analysis.
Sentences begin with kinetic, functional verbs such as: performed, used
Use quantitative words whenever possible, i.e. achieving the goal by 90%, for example
Using specific words whenever possible is better than unclear words
You start by mentioning the duties as duties and then delay the qualification data
Avoid generalization
If possible, determine the percentage of the total position that is spent on activities
Limits the use of the word “maybe” in relation to the performance of certain duties
Using the daily, periodic, and sometimes routine, if defined well, will make the meaning more specific and clear
Uses of job descriptions:
Job descriptions are used in career guidance for new employees
It is used as a basis for performance evaluation
Use job description items when making promotions
It can be used to identify weaknesses in performance
It is used to determine the numbers needed for the uncle
|
|
|
|
|
|
Organizational relations:
Under the supervision of: Director of Nursing at the hospital.
Supervises: Nursing staff members in the operations unit.
Work relations: patients, nurses, doctors, and other employees.
Primary purpose of the job:
Determine the tasks of all individuals.
Achieving the organization's goals.
Improving individuals' performance.
Improving the quality of nursing service.
Roles and responsibilities :
He plans, organizes, and distributes work to nursing staff members
With loneliness.
Estimating the unit's needs for nursing staff.
It trains nursing staff and on-the-job training personnel, especially new ones or transfers, while motivating them to continue acquiring information and skills and participating in their training.
Providing and completing the machines, tools and equipment necessary for nursing work.
Prepares schedules for shifts, nights, rest, and vacations, and distributes work among nursing staff members.
Supervising nursing staff members and following up on the implementation of nursing work by periodically visiting clinics.
Supervising attendance and departure and related records.
Evaluating the performance of the unit’s nursing staff.
Assessing patients' nursing needs and developing nursing plans for the unit.
Follow up on the implementation of treatment, observation, nutrition, and tests, and give directions to the nursing staff in the event of a deficiency or negligence in performance.
Reduced registration and recording of files, records and patient tickets.
Organizing meetings related to nursing work.
He prepares a daily report on the condition of patients and the problems that obstruct nursing work, submits it to his direct superior, and follows up on the implementation of comments thereon.
We suggest rewards and punishment.
Training new members of the nursing staff, nursing students, and lower categories.
Follow the rules and principles of infection control and ensure the quality of performance of various nursing tasks.
Follows professional etiquette and behavior in dealing with members of the health team, individuals, patients and their families.
Carrying out similar tasks assigned to it.
Minimum qualifications:
Bachelor of Nursing.
Preferably those who have additional qualifications (Master’s or Doctorate in Nursing Administration or Hospital Administration).
Practical experience :
Experience in nursing work in hospitals for a period of not less than 8 to 15 consecutive years, including at least three years in an administrative or supervisory position.
Knowledge and abilities:
Availability of leadership qualities and the ability to assume responsibility.
The availability of human qualities such as courtesy, respect for oneself and others, and trust in oneself and others.
Ability to apply management principles and functions and link them to nursing management.
Familiarity with the laws and rules regulating nursing administration.
Familiarity with the principles of leadership and effective communication.
To have an effective leadership personality.
Proficiency in English.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Organizational relations:
Under the supervision of: Nursing supervisors of the operating unit.
Supervises: all personnel in the operating room, including patients, nursing staff, and ancillary services.
Work relations: patients, nurses, doctors and ancillary services.
Primary purpose of the job:
Providing nursing services, including assistance during operations and assisting the surgical team as needed.
Adherence to the unit’s work standards, policies and procedures, the quality and safety assurance program, the principles of environmental preservation, and methods of controlling the spread of infection.
Roles and responsibilities :
Performing nursing handler or sterilizer duties skillfully and quickly.
Preparing the patient for the prescribed procedures and assisting in evaluating the patient’s condition.
Assisting the doctor in conducting examinations and any procedures related to direct patient care.
Providing nursing care to the patient in the operating room, evaluating the results, consulting with other specialists, and modifying procedures related to nursing care, as is necessary to provide the best care for the patient.
Observing the patient's health condition and informing him of any changes that occur to him.
Consider counting pieces of gauze, surgical needles, and instruments in accordance with established procedures to ensure that none of them are lost during operations, and record this in the prescribed form.
Ensure continuity of care for the patient during all stages of the process by submitting a report with the necessary information to the nurse responsible for the next stage of patient care.
Providing psychological support to the patient, showing interest in the patient’s comfort, and maintaining his privacy during all stages of surgical procedures.
Writing the initial nursing history, evaluating the patient’s condition, and developing a special nursing plan for each patient in the unit.
Ensuring the accuracy of information in patients’ medical admission records.
Carrying out the required administrative tasks and preparing all required reports, records and statistics.
Administrative and technical responsible for the inventory in the operating room, including materials, supplies, and equipment.
Ensuring the availability of appropriate quantities of used supplies, reporting and writing reports on any shortages, damages, or excess inventory, and following up on expiration dates.
Ensure the validity of all devices, follow up on their maintenance, and inform the supervisor of any malfunction.
Recording equipment used in surgical procedures in the patient’s record or where requested, and completing financial forms for patient accounts.
Assisting in preparation and development programs for operating room staff.
Participate in the urgent call system and be present in times of emergency when needed.
Carrying out any other tasks or responsibilities assigned to it in the field of work.
Minimum qualifications:
Diploma in Nursing/Nursing Technicians Division.
Practical experience :
One or more years of experience as an operating room nurse or completion of a training program for nursing staff in operating room skills is preferred.
Knowledge and abilities:
Completing specialized training courses for nursing technical and administrative skills in the Operations and Sterilization Unit.
Being able to perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation and breathing if necessary.
Working during different shifts according to the working hours schedule determined by the head of the unit’s nursing staff.
Effective communication skills in dealing with doctors and all the health team in the unit and outside it.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Organizational relations:-
Under the supervision of: Operating Unit Nursing Supervisor.
Supervises: Nursing staff and ancillary services in the recovery room.
Work relations: patients, nurses, doctors, and unit workers.
Primary purpose of the job:
Providing the necessary nursing care in the recovery room after surgical operations.
Commitment to the unit’s work policies and procedures, the quality and safety assurance program, environmental conservation principles, and methods of controlling the spread of infection.
Roles and responsibilities :
Implement the doctor's instructions and perform all required nursing tasks.
Use assessment skills to determine the patient's physical, psychological, social, and spiritual needs and prepare a nursing care plan that meets these needs.
Observing the patient's medical condition and informing the doctor of any significant and meaningful changes.
Maintaining a safe and clean environment for the patient by observing sterilization methods, observing and preventing dangerous situations, keeping dangerous machinery away from the patient, and ensuring that the recovery room is prepared and clean at all times.
Ensuring continuity of patient care in the post-operative period by obtaining the necessary information from the nurse responsible for the previous stage of patient care.
Assistant to the physician in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures as necessary.
Carrying out appropriate nursing procedures, carefully following the instructions for the recovery room, and accurately recording care steps and developments in the patient’s condition in the patient’s record (nursing notes).
Carrying out the required administrative tasks and preparing all required reports, records and statistics.
Selecting and preparing appropriate tools and equipment for use in post-surgical nursing care.
Administrative and technical responsible for all items inside the recovery room, including equipment, supplies, and materials.
Ensure the validity of all devices in the recovery room, follow up and maintain them, and report any malfunctions in the devices.
Recording equipment used in surgical procedures in the patient’s record, where requested, and completing financial forms for patients’ accounts.
Assisting in preparation and development programs for operating room staff.
Participate in the urgent call system and be present in times of emergency when needed.
Carrying out any other tasks or responsibilities assigned to it in the field of work.
Minimum qualifications:-
Diploma in Nursing/Nursing Technicians Division
Practical experiences :
Preferably more than one year of experience or completion of a training program for nursing personnel in the recovery room.
Knowledge and abilities:
Extensive knowledge and experience in post-operative care of surgical patients.
Knowledge of the principles of anesthesia and necessary care.
Being able to perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation and breathing if necessary.
Working in different shifts according to the schedule specified by the direct manager.
Good communication between doctors and nurses in the unit and outside it.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Organizational relations:
Under the supervision of: Surgical Nursing Services Supervisor.
Supervises: Central sterilization workers.
Work relations: nursing staff, doctors and other employees.
Primary purpose of the job:
Carrying out sterilization and eliminating pollution (disinfection) work and supervising workers in the central sterilization department.
Duties and responsibilities:
Developing the department’s mission and objectives and preparing and implementing the department’s regulations, procedures, quality control programs, safety and environmental levels, and infection control standards.
Ability and knowledge of sterilization and contamination elimination (disinfection) procedures.
Knowledge of infection control principles and the use of infection control policies and rules.
Operating equipment for sterilization and eliminating contamination (disinfection) in a safe manner.
Follow up on the necessary orders for the department.
Preparing monthly statistics for the department and monitoring consumption.
Follow up and evaluate the performance of the unit’s employees.
Using his abilities and manual skill at work, during breakdowns, performing simple repairs, and operating equipment and machines.
Work to reduce costs relative to business needs without posing a risk to patient care.
Manage all activities within the Sterilization and Supply Department and ensure that technicians follow sterilization principles in a constructive and productive manner.
Ensure the correct operation of all equipment and seek the assistance of a medical device maintenance engineer if necessary.
Request all important tasks weekly, routinely, and in emergency situations if necessary.
Preparing the annual evaluation of technicians working in sterilization and catering and recommending the measures that should be taken regarding them.
Developing improved methods, reviewing policies, and changing work levels within the Sterilization and Supply Department.
Participate in continuing education programs and staff meetings within the department.
Performing sterilization and catering technician work according to work needs and requirements.
Carrying out other similar work assigned to him.
Minimum qualifications:
Bachelor of Nursing.
Diploma in Nursing Technician from one of the recognized nursing institutes.
Practical experience :
Practical experience of not less than three years in central sterilization.
Previous supervisory experience.
Knowledge and abilities:
Training in sterilization operations.
Familiarity with the principles of public administration and supervision.
Master the basic principles of nursing care.
Master the principles of effective communication
The availability of human qualities such as courtesy, respect for oneself and others, and confidence in oneself and others.
- Introduction to the operations unit
The operations unit is one of the vital specialized departments in the hospital, so it must be dealt with with special skills. Because the nursing administration represents an important member of the health team, nursing must be familiar with all the skills specific to the field of operations.
Nursing service message for the Operations Unit Department
The hospital's nursing administration is committed to raising the health standard of patients and providing them with the best nursing services in line with the hospital's goals and procedures. It also works to raise the scientific and practical level of all members of the nursing staff in the operations unit and change their attitudes towards modern trends in nursing and medical sciences.
Operations suite
The operations wing is divided into four basic sections, each of which serves a specific purpose:
1) Geographical location:-
◾ The operating suite must be in a suitable location in all hospital departments so that it is easily accessible.
◾ Make sure it is far from places of pollution.
◾ Away from the heat of the sun and wind.
◾ It is on the first floor and is connected to the hospital via a private corridor.
◾ Centralization of equipment and devices. The presence of special devices and equipment in all operating rooms should be taken into account in order to avoid duplication of equipment and devices.
◾ The size of the hospital. The larger the hospital is in relation to the number of beds, the greater the number of operating rooms, i.e. (2 rooms for every 50 beds).
◾ Number of employees in the operations wing.
◾ Operating rooms should be spacious to facilitate movement of workers.
◾ Operations personnel must be particularly skilled and competent and receive continuous training.
Components of the operations wing units:-
Clean area includes:-
◾ Anesthesia room.
◾ Hand washing room.
◾ Recovery room.
2) The protective zone includes:
◾ Patient reception room.
◾ Office of the Chief Operating Officer.
◾ Doctors office.
◾ A room for storing surgical supplies.
◾ Doctors’ break.
◾ Plastering room.
◾ A room for endoscopes.
3) The sterile area includes:
◾ Operating rooms of all types.
◾ Sterile instrument storage rooms.
◾ Sterile package storage rooms.
◾ Sterile instrument store.
◾ The area for receiving used machines and tools has a special entrance other than operations.
Operating room contents:-
◾ A large electric flashlight with a number of special type bulbs for all lighting in one place, and it has a sterile arm so that the surgeon can move it in any direction suitable for him.
◾ Operations table: It moves in all directions according to the type of operation.
◾ Accessory holder: It has a leg and armrest, a leather belt to stabilize the patient, and a small armrest.
◾ For the head, a special support for brain operations, and shoulder supports.
◾ A large table to place sterile furnishings on.
◾ A large table to place the machines for the process.
◾ A table to place anesthesia medications.
◾ A table for placing laryngeal tubes for anesthesia.
◾ Monitor device (cardiogram).
◾ Mobile electric extractor device.
◾ Movable electrical cautery device (diaathermy).
◾ Round wheelchairs with and without backs.
◾ A scale and an electronic panel with a regular clock and a clock to determine the operation time.
◾ Pneumatic toricity.
◾ Gauze counting holder.
◾ Metal ladder.
◾ A holder with a plate on it to place the used gauze in.
◾ Holder with a plate of hot (sterile) solutions.
◾ 2 solution holders.
Special equipment:-
Ophthalmology operating room:
◾ Vitreous system (therectomy)
◾ Surgical microscope.
◾ An electric wheelchair for the microscope.
◾ Cooling device for cataract operations.
◾ Electric autoclave.
Orthopedic operating room:-
◾ A special table for orthopedic operations that is installed in the main table.
◾ A television X-ray device to photograph operations while they are being performed.
◾ C-Arm condenser X-ray machine.
Neurosurgery operating room:
◾ A special device to place the patient semi-sitting and hold the head steady.
◾ Electric saw for the bones of the skull.
Ear, nose and nose operations room:
◾ Surgical microscope device for ear operations.
◾ A chair for the microscope.
◾ Laryngoscope with light source.
Urology room:
◾ Complete cystoscope with light source and cables.
◾ A device for cutting prostate and bladder tumors.
◾ A device to break up stones
Obstetrics and Gynecology Room:-
◾ A baby bed equipped with suction and oxygen.
◾ Laparoscopy to perform tube clearing operations and diagnose cases.
◾ Microscope for gynecological operations.
Open heart operating room:-
◾ Heart lung machine.
◾ Electrical defibrillator (DC shock).
◾ Cell saver device
◾ Endoscopic device for extracting leg veins (Endoscopic vein harvest).
◾ Patient warming device (Bair hugger).
◾ Clotting time (ACT) device
◾ Intra aortic ballon pump.
◾ Cardiac ultrasound device + laryngoscope probe (transeosophygeal echo)
◾ Implanted arterial pressure measuring device.
Operating room equipment for human organ transplantation:
The operating room requires the following:
It applies to the operating room standards and descriptions issued by a decision of the Minister of Health, as well as the quality standards determined by the Supreme Committee for Human Organ Transplantation.
B- It must have the following minimum medical equipment:
◾ An efficiently working anesthesia machine equipped with a suitable ventilator.
◾ The presence of ampobags in reserve, the availability of oxygen cylinders and administration devices, and the availability of more than one source of oxygen.
◾ Electrical heart monitor.
◾ A device to measure the percentage of oxygen saturation in the blood.
◾ A device to measure the pressure of carbon dioxide in exhaled air.
◾ A device to measure non-invasive blood pressure regularly every five minutes.
◾ A device for treating ventricular fibrillation on a monitor screen, and the necessary medications for cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
◾ Suction device.
In the event of major surgeries or critical cases, the following must be available in addition to the previous equipment:
◾ A device to measure invasive blood pressure.
◾ A device to measure the percentage and type of drug in exhaled air.
◾ The anesthesia ventilator must have multiple warning methods when a malfunction occurs, and multiple modes of artificial respiration should be given.
Recovery room:-
The recovery room must be equipped with the following equipment:
◾ Devices that monitor EKG, blood oxygen saturation, and blood pressure.
◾ Ventricular fibrillation device on hand.
◾ Ambubag.
◾ Suction device.
The room must be supervised by an anesthesiologist.
Laboratory:
The facility's internal laboratory must have the ability to perform all the necessary analyzes for organ transplants, which include the following:
◾ Complete blood count.
◾ Blood chemistry analyses.
◾ Measuring the level of different immunosuppressive drugs in the blood according to the type of user and developing them as needed.
◾ Possibility of making tissue compatibility before implantation.
◾ The ability to perform all the tests necessary to diagnose infections, such as various viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites.
◾ The ability to perform all analyzes of aerobic and anaerobic cultures, blood cultures, body fluids, and so on.
Blood bank:
◾ The medical facility must have at least a storage blood bank, which has the following:
◾ Blood refrigerator with sufficient capacity.
◾ Chiller for plasma and cryo.
◾ Automated platelet shaking device.
◾ Availability of a system for compatibility of blood types.
◾ Records for receiving and deleting blood and blood products.
◾ A team consisting of a doctor who holds the Egyptian Blood Transfusion Fellowship or its equivalent, assisted by a team of technicians and secretaries.
Diagnostic Radiology Unit:-
The medical facility must have an advanced diagnostic radiology unit with the following devices:
◾ Regular X-rays, chest x-rays, and all areas of the body according to the case.
◾ The ultrasound device is capable of doing Doppler and echo, in addition to standard examination, with the possibility of using this in operating rooms, intensive care, and patient rooms, and the availability of different types with the required sensors with different frequencies as needed.
◾ Advanced Curved Arm Moving Arm (CARM) machine with a robotic monitor for use in interventional radiology in operating rooms and during surgery.
◾ X-ray devices for imaging arteries with dye, either by traditional methods or through digital devices.
◾ A spiral CT scan device, the possibility of studying organ imaging by triple examination, the possibility of taking samples, etc.
◾ The CT scan machine can be replaced by providing an advanced MRI machine.
◾ Digital records and medical statistics: The facility must have an advanced program to store, process, and retrieve medical information for all organ transplant patients, including all analyses, x-rays, photos, and reports, so that this information can be circulated between medical facilities and easily accessed, while preserving the patient’s privacy.
◾ The organ transplantation program must be linked electronically to the website of the Supreme Committee for Human Organ Transplantation for ease of performance and maximum benefit.
Requirements for organ transplantation:-
◾ For facilities that carry out kidney transplant operations: they must have a team of doctors with a high level of qualification, assisted by a team of trained nurses, and a number of dialysis machines of not less than three, with the possibility of performing the minimum number of urinary tract endoscopes, such as Cystoscopy, stent extraction, renal tube placement, and ureteroscopy when needed.
◾ For facilities that perform liver, pancreas, and intestine transplants: they must have an advanced endoscopy unit for the gastrointestinal tract, which includes upper and lower GI endoscopy, the possibility of treating varicose veins through endoscopy, and the ability to perform diagnostic, interventional, and therapeutic bile duct endoscopy (ERCP). .
It is not permissible to establish an intestinal transplant center except in facilities that have previously been licensed to perform liver transplant operations, and it is not permissible to establish a pancreas transplant center except in centers licensed to perform liver or kidney transplant operations.
- Operations unit equipment
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
- |
|
|
||
|
- |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
-
|
|
|
||
|
-
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
||
|
- |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
. |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
- |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
- Carbon. |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cpr board))
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Distributing the operating nursing staff to one operating room
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
النوع |
الصنـــــــــف |
الوحدة |
الكمية |
|
|
الأثاث |
- كشاف للسقف به 5 لمبة وله يد تحركه فى كل الإتجاهات |
|
|
|
|
- ترابيزة عمليات كاملة بها (2 ذراع – 2 حامل) لرفع الرجل مخدة إسفنج - حلقة للرأس. |
|
|
||
|
- ترابيزة تمساح. |
|
|
||
|
- ترابيزة مستطيلة. |
|
|
||
|
- ترابيزة مربعة. |
|
|
||
|
- كرسى مستدير بقاعدة جلد بدون ظهر. |
|
|
||
|
- حامل لشاش البطن. |
|
|
||
|
- حامل لإكسسوار ترابيزة العمليات. |
|
|
||
|
- سلم معدن. |
|
|
||
|
- سبورة بها :(لوحة إليكترونية – ساعة – فانوس أشعة ). |
|
|
||
|
الأدوات |
- طبق على حامل بعجل. |
|
|
|
|
- تروللى لنقل المرضى بمرتبة جلد. |
|
|
||
|
- حامل للمحاليل. |
|
|
||
|
- كشاف نور متنقل ومزود بالبطارية. |
|
|
||
|
- سماعة طبيب. |
|
|
||
|
الأجهزة
|
- شبكة غازات مركزية. |
|
|
|
|
- جهاز منظم للمحاليل بالنقطة. |
|
|
||
|
- جهاز دياثرمى بالكهرباء. |
|
|
||
|
- جهاز شفط بالكهرباء. |
|
|
||
|
- جهاز تنفس صناعى بالكهرباء. |
|
|
||
|
- جهاز تعقيم الالات الجراحيه (اوتوكلاف كهربائى) |
|
|
||
|
- جهاز مونيتور بالكهرباء. |
|
|
||
|
- جهاز ضغط الدم. |
|
|
||
|
- جهاز تخدير كامل بالفلوثك. |
|
|
||
|
- جهاز تسخين بالمحاليل. |
|
|
||
|
- ثلاجة صغيرة لحفظ الأدوية. |
|
|
||
|
- ميــــــــــزان. |
|
|
||
|
الأدوية |
- أنترفال |
|
|
|
|
- أتروبين |
|
|
||
|
- سكسينيل |
|
|
||
|
- فلاكسيديل |
|
|
||
|
- بافليون. |
|
|
||
|
- دورميكوم. |
|
|
||
|
- تراكيم. |
|
|
||
|
- تيوبارين. |
|
|
||
|
- بروستجمين. |
|
|
||
|
- فلوثان. |
|
|
||
|
- أدرينالين. |
|
|
||
|
-نورادرينالين. |
|
|
||
|
-فازوبريسين. |
|
|
||
|
-بروتامين. |
|
|
||
|
-بريماكور. |
|
|
||
|
ماغنيسيوم. |
|
|
||
|
ترايديل. |
|
|
||
|
- افدرين. |
|
|
||
|
- كالسيوم. |
|
|
||
|
- ديكادرون وفورتاكورتين. |
|
|
||
|
- مخدرات : - |
|
|
||
|
- بيترين. |
|
|
||
|
-فاليوم. |
|
|
||
|
- مورفين. |
|
|
||
|
- زيلوكايين بدون ادرينالين. |
|
|
||
|
- زيلوكايين مع ادرينالين. |
|
|
||
|
- مضادات حيوية : - جاراميسين. |
|
|
||
|
- فيلوسيف. |
|
|
||
|
تافانيك |
|
|
||
|
ميرونيم |
|
|
||
|
فانكوميسين |
|
|
||
|
- سيفوبيد. |
|
|
||
|
- زيلوكارد.
|
|
|
||
|
- محاليل للحقن : - جلوكوز 5% ، 25%.10% |
|
|
||
|
- محلول ملح + جلوكوز فى ملح |
|
|
||
|
- مانيتول 10% ،20% . |
|
|
||
|
- رينجرز . |
|
|
||
|
- لاكتات رينجرز. |
|
|
||
|
- اسيتات رينجرز. |
|
|
||
|
فولفين او هستيريل . |
|
|
||
|
- بيكربونات صوديوم |
|
|
||
|
مستلزمات طبية وجراحية |
- سرنجات بلاستيك20 مل |
|
|
|
|
- سرنجات بلاستيك 10 مل |
|
|
||
|
- سرنجات بلاستيك 5 مل |
|
|
||
|
- سرنجات بلاستيك 2 مل |
|
|
||
|
- سرنجات أنسولين. |
|
|
||
|
- فولى مقاسات. |
|
|
||
|
- قسطرة عادية نيلتون مقاسات مختلفة. |
|
|
||
|
- قسطرة سيلكون مقاسات. |
|
|
||
|
- قسطرة وريد مركزيه مقاسات. |
|
|
||
|
قسطرة شريانية مقاسات . |
|
|
||
|
- أنبوبة رايل مقاسات. |
|
|
||
|
- أنابيب شفط صدر. |
|
|
||
|
- أنابيب شفط دم ( للجروح ). |
|
|
||
|
- جهاز نقل دم. |
|
|
||
|
- جهاز نقل محاليل. |
|
|
||
|
- أنابيب حنجرية مقاسات. |
|
|
||
|
- جوانتيات معقمة مقاسات. |
|
|
||
|
- بتر فلاى ( فراشة ) مقاسات. |
|
|
||
|
- ممر هوائى مقاسات. |
|
|
||
|
- بلاستر. |
|
|
||
|
- باندايد ( مقاسات ). |
|
|
||
|
- أوبسايت مقاسات. |
|
|
||
|
استراباد للجروح . |
|
|
||
|
- إليكترودز ( كبسولة رسم القلب ). |
|
|
||
|
- كيس جمع بول . |
|
|
||
|
انابيب صدرية مقاسات مختلفة . |
|
|
||
|
- منظار حنجرى مع خافض لسان مقاسات. |
|
|
||
|
- بيتادين 10% لجلد مريض. |
|
|
||
|
- بيتادين 7.5 لغسيل الايدى. |
|
|
||
|
- كحول 70 – 90%. |
|
|
||
|
- سايدكس. |
|
|
||
|
- فورمالين لحفظ العينات حتى التسليم. |
|
|
||
|
أدوات نظافة |
- ليف. |
|
|
|
|
- كلوراكس وصابون . |
|
|
||
|
- فوط لتلميع الاثاث. |
|
|
||
|
- جلانس لتلميع الزجاج. |
|
|
||
|
- مساحة. |
|
|
||
|
- دفتر العمليات التى اجريت. |
|
|
||
|
- دفتر اذن صرف أدوية. |
|
|
||
|
السجلات التمريضية |
- دفتر لحجز العمليات ( مواعيد العملية ). |
|
|
|
|
- دفتر تحاليل الباثولوجى. |
|
|
||
|
-دفتر العينة المستأصلة. |
|
|
||
|
-دفتر تسليم وتسلم الحالات. |
|
|
||
|
-دفتر الغسيل. |
|
|
||
|
دفتر المنصرف اليومي 118 |
|
|
||
|
دفتر الاحداث الغير متوقعة |
|
|
||
|
دفتر تسليم وتسلم عربة الطوارئ |
|
|
||
|
-دفتر النفايات. |
|
|
||
|
دفتر الاحوال التمريضية . |
|
|
||
|
دفتر التقارير الطبية . |
|
|
||
|
دفتر الصيانة وابلاغ عن عطل . |
|
|
||
|
- دفتر أشعة. |
|
|
||
|
- دفتر اذن صرف مخازن. |
|
|
||
|
- ورق علاج. |
|
|
||
|
- ورق مسطر. |
|
|
||
|
- كشكول لتسليم الاخطارات. |
|
|
||
|
- دفتر اخطار عمليات. |
|
|
||
|
- كربون. |
|
|
||
|
- دبوس ابرة. |
|
|
||
|
|
||||
2) نموذج تجهيز غرفة الإفاقة إحتياجات ( 12 ) سرير
|
النوع |
الصنـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــف |
الوحدة |
الكمية |
|
الأثاث |
- أسرة مجهزة متحركة بها حواجز على الجانبين - شبكة غازات مركزية - مراتب مغطاه بالجلد. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- كرسى مستدير بقاعدة جلد بدون ظهر. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- عربة أدوية ( للطوارئ ). |
عدد |
|
|
|
- ترابيزة تمساح. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- دولاب للأدوية. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- خزنة للمخدرات. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- فانوس للأشعة. |
عدد |
|
|
|
|||
|
الأجهزة |
- جهاز لتسخين المحاليل. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- جهاز لتنظيم المحاليل بالنقطة. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- جهاز ضغط الدم. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- جهاز شفط متحرك. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- جهاز صدمات الفلب. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- جهاز تنفس صناعى. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- حامل مجهز للطوارئ بأسطوانات الأكسجين. |
عدد |
|
|
|
|||
|
الأدوات |
- سماعة طبيب. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- ترمومتر طبى. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- حامل للمحاليل. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- كشاف جانبى خاص. |
عدد |
|
|
|
|||
|
المهمات |
- ملاية كبيرة. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- كيس مخدة. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- مخدة. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- مرتبة جلد للتروللى. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- فوطة يـــد. |
عدد |
|
|
|
|||
|
أدوية |
- كورامين. |
امبول |
|
|
|
- ديكادرون. |
امبول |
|
|
|
- امينوفللين. |
امبول |
|
|
|
- افدرين. |
امبول |
|
|
|
- ادرينالين |
امبول |
|
|
|
- لازكس. |
امبول |
|
|
|
- أيزوتين. |
امبول |
|
|
|
- أيزوبتريل. |
امبول |
|
|
|
- زيلوكارد20%. |
امبول |
|
|
|
- كالسيوم. |
امبول |
|
|
|
- نوفالجين. |
امبول |
|
|
|
- ديبوتركس. |
امبول |
|
|
|
- اندرال. |
امبول |
|
|
|
- ريزمودان. |
امبول |
|
|
- المحاليل : |
|
|
|
|
|
- كلوريد بوتاسيوم. |
زجاجة |
|
|
|
- محلول ملح. |
زجاجة |
|
|
|
- جلوكوز 5% ، 25%. |
زجاجة |
|
|
|
- رينجرز. |
زجاجة |
|
|
|
- مانيتول 10% ،20% ، 25% |
عدد |
|
|
- مخدرات : |
|
|
|
|
|
- فاليوم. |
امبول |
|
|
|
- بيثيدين. |
امبول |
|
|
|
- مورفين. |
امبول |
|
|
|
- ستادول. |
سم |
|
|
|
- الفاكمفين. |
امبول |
|
|
مستلزمات طبية |
- جيل k.y. |
انبوبة |
|
|
|
- بلاستر. |
بكرة |
|
|
|
- كبسولة رسم قلب. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- ممر هوائى مقاسات. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- قساطر بلاستيك مقاسات. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- جهاز وريد. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- قسطرة وريد مقاسات. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- فراشة ( بترفلاى ) مقاسات. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- منظار حنجرى مع خافض لسان |
طقم |
|
|
|
- قسطرة تخدير حنجرية مقاسات. |
طقم |
|
|
|
- كانيولا للوريد مقاسات. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- قسطـــرة. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- سرنجات جميع المقاسات. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- إبر تخدير نصفى مقاس20 |
عدد |
|
نموذج تجهيز وإعداد غرفة مكتب العمليات
|
النوع |
الصنـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــف |
الوحدة |
الكمية |
|
الاثاث |
- مكتب استنلس ستيل معدن بأدراج. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- كرسى مكتب بظهر جلد. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- كرسى بلاستيك بظهر بلاستيك. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- لوحة استعلامات الوميتال. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- تليفــــــــون. |
عدد |
|
|
الأجهزة |
- جهاز استدعاء داخلى. |
عدد |
|
نموذج تجهيز وإعداد غرفة إستراحة بالعمليات
|
النوع |
الصنـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــف |
الوحدة |
الكمية |
|
الاثاث |
- كرسى فوتية مبطن بالبلاستيك. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- ترابيزة مستطيلة خشب. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- دولاب معدن. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- شماعة للحائط بلاستيك. |
عدد |
|
|
الأجهزة |
- ثلاجة 8 قدم. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- ثلاجة كولدير ( لتثليج المياه ). |
عدد |
|
|
أدوات |
- أكواب زجاج. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- صينية بلاستيك. |
عدد |
|
|
مهمات |
- فوط يد مستهلكة |
عدد |
|
|
|
- معطر |
عدد |
|
|
|
- جردل |
عدد |
|
|
أدوات نظافة |
- صابون سائل |
ك |
|
|
|
- فيم. |
علبه |
|
|
|
- سلك الومنيوم. |
ك |
|
|
|
- فوط صفراء. |
عدد |
|
|
|
- مساحة |
عدد |
|
عربة الطوارئ
|
الدرج الاول |
العدد |
الفترة الصباحية |
الفترة المسائية |
فترة السهر |
|
ادرينالين |
5 |
|
|
|
|
لازكس40.mg |
5 |
|
|
|
|
دوبامين |
5 |
|
|
|
|
ديبوتركس |
5 |
|
|
|
|
نورادرينالين |
5 |
|
|
|
|
امينوفلين |
5 |
|
|
|
|
ترايديل |
5 |
|
|
|
|
كالسيوم |
5 |
|
|
|
|
ماغنسيوم سلفيات |
5 |
|
|
|
|
صويوم بيكارب |
15 |
|
|
|
|
كلوريد بوتاسيوم |
10 |
|
|
|
|
كورادارون |
10 |
|
|
|
|
سوليو كورتيف |
5 |
|
|
|
|
ايزوبتن |
5 |
|
|
|
|
اندرال |
5 |
|
|
|
|
ايبانوتين |
5 |
|
|
|
|
زيلوكين فيال |
1 |
|
|
|
|
دورميكم |
5 |
|
|
|
|
الدرج الثاني |
العدد |
الفترة الصباحية |
الفترة المسائية |
فترة السهر |
|
سرنجة 10 مل |
10 |
|
|
|
|
سرنجة 5 مل |
10 |
|
|
|
|
سرنجة 3 مل |
10 |
|
|
|
|
كانولا مقاسات |
10 |
|
|
|
|
رباط شاش |
3 |
|
|
|
|
بلاستر |
1 |
|
|
|
|
جيل معقم |
1 |
|
|
|
|
خافض لسان |
1 |
|
|
|
|
جهاز وريد |
10 |
|
|
|
|
جهاز نقل دم |
10 |
|
|
|
|
سرنجة رايل |
5 |
|
|
|
|
علبة جوانتى لاتكس |
1 |
|
|
|
|
وصلة وريدية |
5 |
|
|
|
|
وصلة شريانية |
5 |
|
|
|
|
وصلة ثلاثية |
5 |
|
|
|
|
سرنجة 50 مل |
5 |
|
|
|
|
اسورة تعريف |
5 |
|
|
|
|
انابيب معامل (مختلفة) |
10 |
|
|
|
|
جوانتيات معقمة |
10 |
|
|
|
|
ورق رسم قلب |
1 |
|
|
|
|
كيس الكترود |
1 |
|
|
|
|
الدرج الثالث |
العدد |
الفترة الصباحية |
الفترة المسائية |
فترة السهر |
|
منظار حنجرى |
1 |
|
|
|
|
انابيب حنجرية(مقاسات) |
10 |
|
|
|
|
ممر هوائى (مقاسات) |
5 |
|
|
|
|
ماسك امبوباج (مقاسات) |
5 |
|
|
|
|
ماسك اكسجين(كبار-اطفال) |
5 |
|
|
|
|
ماسك نيبوليزر(كبار-اطفال) |
5 |
|
|
|
|
نيزل اكسجين |
5 |
|
|
|
|
بطاريات اضافية |
4 |
|
|
|
|
الدرج الرابع |
العدد |
الفترة الصباحية |
الفترة المسائية |
فترة السهر |
|
أنبوبة معدة(رايل)مقاسات |
5 |
|
|
|
|
قسطرة بولية(مقاسات) |
5 |
|
|
|
|
قسطرة تشفيط(مقاسات) |
5 |
|
|
|
|
كيس جمع بول |
5 |
|
|
|
|
أنبوبة صدرية+البرطمان |
1 |
|
|
|
|
ارترى معقم |
1 |
|
|
|
|
مقص معقم |
1 |
|
|
|
|
قسطرة cvp |
2 |
|
|
|
|
سلك مرشد لcvp |
1 |
|
|
|
|
غرز حرير |
5 |
|
|
|
|
مشرط جراحى |
10 |
|
|
|
|
بيتادين10%(زجاجة) |
1 |
|
|
|
|
علبة مسحات كحولية |
1 |
|
|
|
|
استرى باد |
1 |
|
|
|
|
كشاف |
1 |
|
|
|
|
الدرج الخامس |
العدد |
الفترة الصباحية |
الفترة المسائية |
فترة السهر |
|
محلول ملح..9% |
5 |
|
|
|
|
رينجر |
5 |
|
|
|
|
جلوكوز5% |
5 |
|
|
|
|
جلوكوز10% |
2 |
|
|
|
|
جلوكوز25% |
2 |
|
|
|
|
هستريل |
2 |
|
|
|
|
هيماجيل |
2 |
|
|
|
|
مانيتول20% |
2 |
|
|
|
|
على السطح |
العدد |
الفترة الصباحية |
الفترة المسائية |
فترة السهر |
|
جهاز الصدمات الكهربائية |
1 |
|
|
|
|
جهاز ضغط |
1 |
|
|
|
|
سماعة |
1 |
|
|
|
|
امبوباج كبير |
1 |
|
|
|
|
امبوباج صغير |
1 |
|
|
|
|
لوحة صلبةcpr board)) |
1 |
|
|
|
|
اسطوانة اكسجين |
1 |
|
|
|
|
حامل محاليل |
1 |
|
|
|
|
قائمه بأسماء الادويه عاليه الخطورة |
1 |
|
|
|
|
قائمه بأسماء الادويه المتشابهه فى الشكل والنطق |
1 |
|
|
|
|
التوقيع |
|
|
|
|
توزيع هيئة التمريض بالعمليات لغرفة واحدة بالعمليات
|
الوصف |
الفترة الصباحية |
نوبتجية |
سهرانة |
ملاحظات |
|
التمرض المعقم |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
التمرض المساعد |
1 |
1 |
1 |
يقوم التمريض السهران بعمل تمريض الإفاقة بعد العملية فى السهر |
توزيع هيئة التمريض بغرفة الإفاقــة
|
الوصف |
الفترة الصباحية |
نوبتجية |
سهرانة |
|
تمريض إفاقة |
1 |
1 |
فى فترة عدم وجود تمريض التخديريقوم تمريض الإفاقة بعملها وأيضاً فى حالات الحوادث |
نظام جرد العهده بوحدة العمليات
الهدف :
◾ التأكد من صلاحية وسلامة التجهيزات والأدوات الآلات.
◾ إستكمال النقص.
◾ مراجعة حسابات المريض وتحصيلها قبل خروج المريض من المستشفى.
◾ إستبعاد الغير صالح منها أو ما تحتاج إلى إصلاح أو تكهين.
◾ التأكد من القيام بتوفير إحتياجات العمل لليوم التالى ( ويشمل ذلك التعليمات أو الإستبدال أو التجهيزات الناقصة ).
الإجراءات
|
الجرد اليومى |
الجرد الإسبوعى |
الجرد السنوى |
|
لكل من الآلات والمهمات التى إستخدمت أثناء العمل وهى : - الأدوية - مستلزمات طبية مستهلكة - محاليل مطهرة - أدوات الصرف والبونات - الأجهزة الكهربائية - معدات التخدير |
- كشوف العهدالمستخدمة بجميع أصنافها وإستكمالها.
- البونات وأذونات الصرف والإستعاضة عن المنصرف. |
يتم الجرد السنوى على : جميع تجهيزات وحدة العمليات ويشمل ذلك : - العهد المستديمة من الآلات والأدوات والتجهيزات والمفروشات والأثاث... الخ. - المستلزمات الطبية. - الشرائح وأى أجزاء أخرى معدنية تم تركيبها. |
خط سير المريض بوحدة العمليات
◾ إستقبال المريض من القسم الداخلى فى المنطقة النظيفة.
◾ ينقل المريض على تروللى العمليات بعد تجهيزه إلى غرفة تحضير المريض (تخديره).
◾ ينقل المريض من غرفة تحضير المريض الى غرفة العمليات بعد تخديره.
◾ ينقل المريض بعد إنتهاء وإجراء العملية إلى غرفة الإفاقة حسب طلب طبيب التخدير.
◾ ينقل المريض إلى القسم فى حالة الإفاقة التامة بدون مضاعفات.
◾ فى حالة المضاعفات ينقل المريض الى وحدة الرعاية المركزة حسب طلب طبيب
{mlang}- Charter of Patients and Nursing Rights
The availability of policies and procedures that define at least the following patient rights:
◾ The right to obtain care if it is available in the hospital.
◾ The right to know the treating physician, the supervising physician and/or the responsible physician.
◾ The right to receive care that respects the patient’s personal values and beliefs.
◾ The right to know and participate in decisions regarding their care.
◾ The right to refuse care and not continue treatment.
◾ The right to security, personal privacy, confidentiality and dignity.
◾ The right to receive appropriate treatment for pain.
◾ The right to file a complaint or suggestion without fear of persecution.
◾ The right to know the prices of services and procedures.
◾ Patients’ rights must be clear and announced to patients and the staff.
The availability of policies and procedures that define the patient’s duties, which include at a minimum the following:
◾ Follow hospital policies and procedures.
◾ Financial commitment in accordance with the law, regulations and hospital policy.
◾ Show respect for other patients and healthcare workers.
◾ Follow the proposed treatment plan.
◾ Availability of policies and procedures that define patients and their families’ awareness of their rights and duties regarding refusing or not continuing treatment.
◾ Availability of policies and procedures that specify the process for patients to submit complaints or suggestions, verbally or in writing, anonymously.
◾ Availability of policies and procedures that define the process of obtaining consent based on patient identification, and specify the validity period of signed consent before obtaining new consent.
◾ The availability of a written form in the event that the patient’s belongings are delivered to a relative, containing the name of the person to whom it is delivered, the national number, the signature of the recipient, and the person responsible for the delivery.
The hospital has a list of procedures or types of treatment that require patient-identified consent, which includes the following:
◾ Surgical interventions.
◾ Anesthesia/kidney or hemiplegia.
◾ Blood transfusion.
◾ High-risk procedures or treatment (including but not limited to electrotherapy, radiotherapy, chemotherapy).
◾ Family planning interventions.
◾ Scientific research.
◾ The hospital has a system for informing patients and their families about available services and how to obtain them.
◾ The hospital has a system in place to inform patients and their families of any expected costs.
The availability of a policy that specifies the hospital’s responsibilities towards the patient’s belongings, including at least the following:
◾ Who is responsible?
◾ When does responsibility for these belongings begin?
◾ How to protect belongings.
◾ There is a specific process for informing patients and families of the results of care and treatment.
◾ The availability of policies and procedures that specify how the hospital informs patients and their families about how to donate organs and other tissues
◾ The availability of policies and procedures that define the autopsy process and document the results of this process.
Rights of nursing staff
The Purpose :-
Informing nursing staff of their rights and assisting in fulfilling them.
Steps:-
The hospital administration determines the general rights of nursing staff members in coordination with the Nursing Services Administration, which include the following:
◾ The worker’s right to feel that the hospital needs him.
◾ The right to feel part of the hospital.
◾ The right to feel that work relations are good.
◾ The right to feel respect and dignity
◾ Right to know (to understand the hospital’s goals and policies)
◾ The right to feel responsible.
◾ The right to file a grievance.
◾ The right to feel equal rights without favoritism or favoritism toward some at the expense of others.
◾ The right to an agreed upon written list of rewards and penalties.
◾ The right to continuous training during working hours.
◾ The right to a system of encouragement and motivation financially and morally.
◾ The right to free health care and proper nutrition.
◾ The right not to discriminate between categories of workers in the job treatment system.
◾ The right to a system of entertainment, psychological, social and cultural care.
◾ The right to a system to prevent and protect against disease.
Duties of nursing staff towards their patients
◾ To bear in mind that healing the patient and maintaining his health is its first goal, without other considerations such as religion, color, gender, or politics.
◾ To be the place of trust placed by the patient in terms of his recovery.
◾ To be kind-hearted in their treatment and to act wisely and accurately towards their patients.
◾ And to give the patient hope for recovery, whether physical or psychological, and to maintain absolute confidentiality of everything you know about the patient, and to participate with the patient in making some decisions related to his treatment.
◾ To be responsible for health education for the patient and providing him with complete information regarding his illness, how to cope with it, and what are the means of avoiding complications resulting from it, and not just giving him medication.
- Ethics and ethics of the nursing profession
First: Duties and responsibilities of the literary profession:
There are moral duties and responsibilities that govern and regulate the work of the nursing profession, in addition to the professional responsibilities and duties of nursing staff members. All organizations interested in the nursing profession, most notably the International Council of Nursing Staff, have paid attention to them, stressing the need for nursing staff members to adhere to the morals and ethics of the nursing profession. Therefore, it has drawn up a constitution and a code of ethics for the profession so that nursing staff members can be Nursing is aware to emulate and implement it, which will have an impact on the positive image of the nursing staff in society and their emergence as role models.
The most important provisions of this constitution are the following:
◾ Respecting life, alleviating suffering, and working to alleviate pain and raise the level of health.
◾ Providing the highest level of nursing service and professional behavior.
◾ To be prepared to practice the profession only and to work on acquiring information and skills.
◾ Respect the patient’s religious beliefs.
◾ Keep all information that she obtains through her work and do not disclose it except in accordance with the law.
◾ Do not prescribe or give medical treatment without a doctor’s orders except in emergency cases and notify the doctor immediately. Be intelligent and obedient and refuse to contribute to any unethical actions.
◾ Gain the trust of the doctor and members of the health team.
◾ Not allowing their names to be used in advertising products or in any form of personal advertising.
◾ Effective cooperation with other members of the health team.
◾ Adhering to the standards of personal etiquette in her private life.
◾ Citizens and members of other health professions participate in their efforts to meet the health needs of the local, national and international community. Thus, nursing staff members have many responsibilities and duties towards the patient, the workplace, society and towards the profession itself.
The following are the most important ethical responsibilities of nursing staff members:
The most important responsibilities of nursing staff towards their patients are:
◾ To keep in mind that healing the patient and maintaining his health is its first goal without any other considerations such as religion, color, gender, or politics.
◾ To be the place of trust placed by the patient in terms of his recovery.
◾ To be kind-hearted in their treatment, to act wisely and accurately towards their patients, to give the patient hope for recovery, whether physical or psychological, to maintain absolute confidentiality of everything you know about the patient, and to participate with the patient in making some decisions related to his treatment.
◾ To be responsible for health education for the patient and providing him with complete information regarding his illness, how to cope with it, and what are the means of avoiding complications resulting from it, and not just giving him medication.
Responsibility of nursing staff towards themselves:
◾ Nursing staff members must work to improve their scientific level by constantly being informed of everything new in the general natural sciences and special nursing sciences.
◾ Completing studies to obtain available academic degrees such as a specialized diploma, master’s and doctorate.
◾ Attending seminars, scientific conferences and seminars organized by medical and nursing societies and participating in scientific research that helps advance the nursing and health care profession.
◾ That they be completely convinced of the nursing profession and that they should bear in mind that this profession has its own respect, dignity and dignity, and that they should be of good conduct and behavior in their public and private lives.
Responsibilities of nursing staff towards colleagues at work:
◾ Sincere cooperation with members of the health team, which helps provide health care to citizens.
◾ They treat their co-workers as they would like to be treated and avoid talking badly about them and any comment or remark that would detract from the skill or opinion of any co-worker.
◾ Fully prepared to teach recent graduate colleagues all the foundations and concepts of modern nursing.
Responsibility of nursing staff towards the institution in which they work:-
◾ Respect the organization’s work laws and rules.
◾ Respect all employees of the organization and cooperate with their superiors.
◾ Respect the full uniform while working.
◾ Proper use and preservation of work tools, and reporting in the event of loss or damage to any of the devices and tools.
◾ Admitting the mistake and reporting it to those concerned.
Responsibility of nursing staff towards society:
◾ To be good citizens while respecting the traditions and customs of the community.
◾ Not participating in work that affects the honor and dignity of citizens.
To be sufficiently familiar with the laws and legislation of the state.
Responsibility of nursing staff towards the nursing profession:
◾ Paying attention to their appearance, adherence to dress, cleanliness and grooming.
◾ Stay away from any action that raises suspicions around her and be of good behavior.
◾ That they are convinced of the profession and that it is a humane work that is respected.
◾ Raising the level of the scientific profession through scientific research while delivering information to other groups
◾ Working to improve the material, economic and social conditions of workers in the profession.
◾ Improving the level of performance of nursing services in their workplace, as well as good selection of workers.
The following are the most important ethical responsibilities of nursing staff members:
The most important responsibilities of nursing staff towards their patients are:
◾ To keep in mind that healing the patient and maintaining his health is its first goal without any other considerations such as religion, color, gender, or politics.
◾ To be the place of trust placed by the patient in terms of his recovery.
◾ To be kind-hearted in their treatment, to act wisely and accurately towards their patients, to give the patient hope for recovery, whether physical or psychological, to maintain absolute confidentiality of everything you know about the patient, and to participate with the patient in making some decisions related to his treatment.
◾ To be responsible for health education for the patient and providing him with complete information regarding his illness, how to cope with it, and what are the means of avoiding complications resulting from it, and not just giving him medication.
Responsibility of nursing staff towards themselves:
◾ Nursing staff members must work to improve their scientific level by constantly being informed of everything new in the general natural sciences and special nursing sciences.
◾ Completing studies to obtain available academic degrees such as a specialized diploma, master’s and doctorate.
◾ Attending seminars, scientific conferences and seminars organized by medical and nursing societies and participating in scientific research that helps advance the nursing and health care profession.
◾ That they be completely convinced of the nursing profession and that they should bear in mind that this profession has its own respect, dignity and dignity, and that they should be of good conduct and behavior in their public and private lives.
Responsibilities of nursing staff towards colleagues at work:
◾ Sincere cooperation with members of the health team, which helps provide health care to citizens.
◾ They treat their co-workers as they would like to be treated and avoid talking badly about them and any comment or remark that would detract from the skill or opinion of any co-worker.
◾ Fully prepared to teach recent graduate colleagues all the foundations and concepts of modern nursing.
Responsibility of nursing staff towards the institution in which they work:-
◾ Respect the organization’s work laws and rules.
◾ Respect all employees of the organization and cooperate with their superiors.
◾ Respect the full uniform while working.
◾ Proper use and preservation of work tools, and reporting in the event of loss or damage to any of the devices and tools.
◾ Admitting the mistake and reporting it to those concerned.
Responsibility of nursing staff towards society:
◾ To be good citizens while respecting the traditions and customs of the community.
◾ Not participating in work that affects the honor and dignity of citizens.
To be sufficiently familiar with the laws and legislation of the state.
Responsibility of nursing staff towards the nursing profession:
◾ Paying attention to their appearance, adherence to dress, cleanliness and grooming.
◾ Stay away from any action that raises suspicions around her and be of good behavior.
◾ That they are convinced of the profession and that it is a humane work that is respected.
◾ Raising the level of the scientific profession through scientific research while delivering information to other groups
◾ Working to improve the material, economic and social conditions of workers in the profession.
◾ Improving the level of performance of nursing services in their workplace, as well as good selection of workers.
The following are the most important qualities necessary for nursing staff members: -
Nursing staff members must have the most beautiful qualities that qualify them to carry out their mission in the best way, such as:
◾ Healthy body and mind.
◾ Be mature in thinking and acting.
◾ They have basic information about the profession as well as general information.
◾ They have skills specific to the nursing profession.
◾ They have the ability to gain the trust of others and teach others.
◾ They have sound attitudes towards their profession.
◾ Role model of cleanliness and good appearance.
◾ Strong observation and smart.
◾ To be firm.
◾ Conscientious and cooperative.
◾ The ability to make decisions and have emotional stability, especially in crises and critical situations.
◾ Quickness of mind and quick action.
◾ Self-confidence.
- Communication skills
Definition of communication:-
Communication is the process of exchanging ideas, information, and trends verbally and non-verbally between individuals to achieve public or private purposes. Communication is a circular process and not a one-sided conversation. It means that the sender is at times a receiver and the receiver is at times a sender.
The importance of communication:-
Forming relationships between community members.
Exchange information, ideas and experiences.
Conviction to change positive knowledge, attitude and behavior among individuals and groups
Clarifying ideas, removing confusion, and correcting concepts.
Increase culture.
Influencing others through guidance and guidance.
Transferring information, data, statistics and concepts through various channels to contribute to decision-making.
A purposeful means of ensuring interaction and mutual exchange of the various activities of the organization.
A way to motivate employees.
Communication helps achieve goals.
Components of the communication process:-
Sender
The message
Communication channel
The future
Feedback
the environment
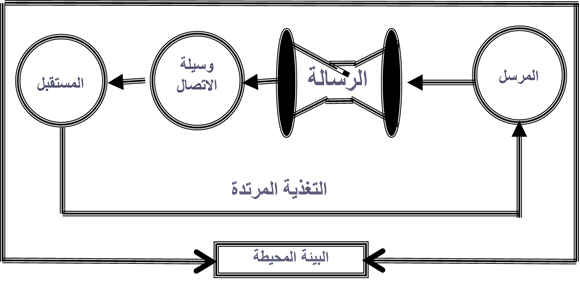
Sender:-
He is the person who starts the loop and sends the message
He is the initiator of the communication process
He must have sufficient correct information, a convincing method, and sufficient attention
The future :-
He is the person who receives the message
He must have sufficient preparation to receive the message
The message :-
It is the content or subject of communication
It must be easy, clear and understandable
Channel or means:-
It is the method used by the sender to transmit the message (communication).
The appropriate method must be chosen for the topic and the future.
Feedback:-
It is the reaction of the recipient of the message to what was stated in the message
Feedback is used to determine whether the message reached the recipient as the sender intended or not
Through feedback, the content of the message or how it is conveyed can be improved.
Types of communication:-
Verbal communication.
Non-verbal communication.
There are two types of communication:
First: Verbal communication:
(talk - printed material to read - watching a television or radio program)
Second: - Non-verbal communication:
(body and hand movement - sitting - facial expressions such as joy and sadness - eye movement...etc.)
Communication skill:
Listening skill.
Speaking skill.
Persuasion skill.
The skill of asking questions.
Dialogue management skill.
Skill in dealing with others.
The skill of using body language.
Listening skill
It is focusing attention on the opinions, thoughts, feelings, and linguistic and physical expressions of others. Not relying on the content of the words, but trying to reach the speaker's directions.
The difference between listening and listening
Listening: is limited to receiving the message organically through the ear.
Listening: It is the use of the mind with its full capacity in everything that has been received, by processing the received message mentally with interpretation.
Types of listening:
Good listening is often accompanied by good thinking
Why don't we listen?
Their inability to concentrate for any reason.
The intensity of their preoccupation with themselves.
They are so preoccupied with what they will say next.
Their lack of confidence in what they are listening to and the reasons why they are listening to it.
They do not have the ability to follow the points that the speaker is talking about.
They do not care about what is said to them.
We think seven times faster than we speak, and this makes us preoccupied with our judgments about the speaker’s speech?
Our desire to express ourselves instead of listening (I want the opportunity to talk).
Distraction due to side conversations or noise.
The importance of good listening
Good listening is the appropriate path for a leader or individual with strong relationships with others, as it saves a lot of time and effort in managing problems and conflicts, achieving goals, and negotiating with those around them, as listening leads to:-
◾ It affects the validity and accuracy of the decision.
◾ It makes the relationship mature and strong between individuals.
◾ Generates the ability to innovate and create.
◾ It makes the individual able to face problems and crises.
◾ Makes the criteria for evaluating others fairer.
◾ Listening means a permanent addition to a person’s ability to speak forcefully.
◾ It reduces error and represents the key to safety for the individual’s intellectual growth.
How to become an effective listener?
Look for the content of the topic and ignore the speaker's manner or mistakes in speaking.
Arrange the information you hear logically in your mind.
Do not rush to judge.... Rather, let the speaker finish his speech.
Do not turn your face away from your interlocutor (the eye sometimes listens).
Ask your interlocutor if the conversation is not clear.
Create an appropriate environment for yourself from the beginning that prevents you from focusing on things other than listening to the speaker.
Make your place in the session suitable for following the speaker with your eyes and ears, and try to eliminate factors that could obstruct this, such as sunlight falling on you or the presence of some devices in front of you.
2- Speaking skill
How do you prepare yourself before starting the conversation?
Determine the purpose and benefit of the communication
Tailor your message to your listeners
Good preparation of the topic of the conversation...it is the best source of trust.
Have an idea in advance about the person you will be speaking to.
Prepare supporting materials to support your talk.
Mental and muscle relaxation.
To be a good speaker
Avoid inexpressive faces - exaggerated expressions - distressed expressions.
Avoid sharp glances or direct, close-up looks.
Avoid repetitive movements as a result of excessive nervousness (movement such as a pendulum clock, for example).
Avoid inappropriate or excessive clothing.
Avoid stuttering - low voice - staying on one tone.
Expand your circle of thinking and fully understand the information
Use the recipient's language to convey the message clearly
Ask questions and then let the speaker confirm that what you have understood is in fact correct
Do not say lightly: I do not know: many of us know very little about the world in which we live, and pretending to answer or fabricating it only doubles the problems.
Pay your full attention to those you talk to: If you make time to communicate with someone, give them attention and care. Join the conversation and participate in it when you see that it is of interest to the communication process.
3- Persuasion skill:-
It is one of the skills necessary for the communication process, and it is used in personal interviews, group discussions, and talking with leaders. Definition: Enticement through reason, logic, and knowledge to make others accept changes in their opinions, attitudes, or behaviors.
Stages of the persuasion process:-
Attention stage: The individual is attracted to the new idea and shows enthusiasm for this idea.
Interest stage: A stage in which the individual wants to know details about the idea and has a desire to analyze facts and collect information.
Evaluation or mental comparison stage: In this journey, the individual performs a process of self-evaluation and comparison between the old and the new.
Experimentation stage: In this journey, the individual tries to get rid of tension and attraction, so he experiments and applies the pleasure of the idea on a small scale.
Adopting the idea/complete conviction: In this journey, the person is completely convinced of the idea and decides to continue implementing it.
Skill of asking questions:-
To keep the dialogue going, there must be a reaction from the other party that includes indicators that support that it received the message and helps the first party determine how to continue the dialogue. These indicators can be obtained through the optimal use of questions. The questions may be positive or negative. If they are positive, they explain the other party’s way of thinking and feeling, but if they are negative, they make him feel tense and embarrassed and push him to take a defensive position.
Therefore, the following must be taken into account:
◾ The goal of questions should be to reach agreement and not to get into personal matters.
◾ It is important not to ask questions that cause the other party to become anxious or stressed.
◾ Questions should help both parties, not be used as maneuvering.
◾ Questions should aim to establish an atmosphere of cooperation by motivating the other party to respond frankly.
◾ Ensure that the questions are not deceptive, contrived, evasive, shameful, or worthless.
◾ Questions should be appropriate to the situation.
◾ The questions should also be appropriate to the other party’s personality and general aptitudes.
◾ The purpose of questions should be to achieve a goal and not simply to elicit a response.
◾ The necessity of a connection between the questions.
◾ Finally, it is required and usual that questions be characterized by tact and respect for the other party.
Specifications of successful communication:-
◾ Both the sender and the receiver must believe and be interested in the message.
◾ Mutual respect between the sender and the receiver.
◾ The subject of the message is clear to both parties.
◾ Use appropriate means for the sender, the recipient, the subject of the message, and the place where it is presented.
◾ Communication is two-way, meaning there is interaction between the sender and the receiver.
◾ Use verbal and non-verbal communication equally efficiently as they complement each other.
◾ The more senses we use, the more efficient the communication process becomes.
◾ The message must be correct, accurate, clear, specific and short.
◾ Do not be a continuous sender or receiver.
◾ Set a clear goal for the communication process.
◾ Choose the appropriate circumstance from an environmental, social and psychological perspective.
◾ The language of communication must be appropriate for both parties.
Basic principles for communicating clearly
In order for people to hear, see and understand the message you want to deliver to them, you must:
Choose words that are easy and simple to understand.
To avoid scientific and medical terminology.
Make sure everyone present sees and hears what you say.
Display a message as short as possible without disturbing the content of the message.
Long messages lead to the attendees being distracted and not focusing on what you are saying and presenting. It also leads to them not remembering the message shortly after your speech.
You should talk to them about one topic at a time.
- Quality and improving the work environment
introduction:
There are multiple definitions of quality, and some or all of these definitions may apply to many topics or services. Each person’s expectations about the expected quality of the service or product depend on several factors such as his individual needs, personal experiences, and the influences of others on him. These factors help to form a set of characteristics that On the basis of which the quality of services provided to him is evaluated.
The perspective and judgment of quality may differ from the perspective of the patient, provider, hospital administration, and community.
Quality is the basis of providing health services, and to confirm the meaning of doing the right thing the right way the first time, we must ensure that things are done in a better way every day, ensure that we obtain the best clinical result for the patient, satisfy all our customers, maintain distinguished workers, and finally ensure the optimal use of available capabilities.
Definitions of quality
• Quality is conformity with needs and specifications.
• It is doing the right thing right the first time.
Quality and health services
• Making sure things are done better every day.
• Ensuring the best clinical result is obtained.
• Ensuring the satisfaction of all our customers.
• Ensuring we retain outstanding employees.
• Ensure optimal use of available capabilities.
Quality and cost
introduction:
The means and methods of providing high-quality health services vary, starting from working in a method of observation and discovering the problems that occur during the application of the system, then eliminating these problems and planning to develop systems that achieve high quality in the service provided, in a way that ensures reducing expenses and saving resources, and even increasing income and returns, through... Eliminate unnecessary and harmful procedures and improve efficiency.
The relationship between quality and cost
Methods and approaches to providing high-quality health services vary as follows:
1. The method of observing and discovering problems that occur during the implementation of the system and then eliminating these problems during work (leads to raising the level of service).
2. The method of taking preventive measures during the implementation of the system to identify the systems that lead to reduced quality and then work to develop these systems (leading to reducing service expenses).
3. The method of advance planning to establish systems that achieve high quality in the service provided, ensuring reduced expenses, saving resources, and even increasing income and returns. From the above it is clear that ensuring quality leads to:
• Eliminate unnecessary procedures.
• Eliminate harmful actions.
• Improving efficiency. (It achieves increased income and resources and reduced expenses).
Quality assurance
The four characteristics of quality assurance:
• Awareness of meeting the needs and expectations of the patient and society.
• Focus on systems and chains of procedures.
• Using data to analyze health service provision chains.
• Encouraging teamwork to solve problems and develop and improve quality.
Quality assurance
The quality assurance division consists of three stages that include ten steps:
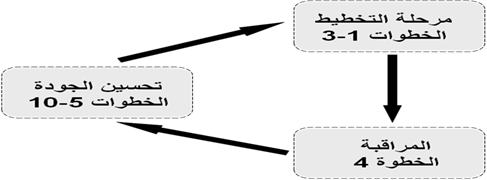
The ten steps to ensure quality
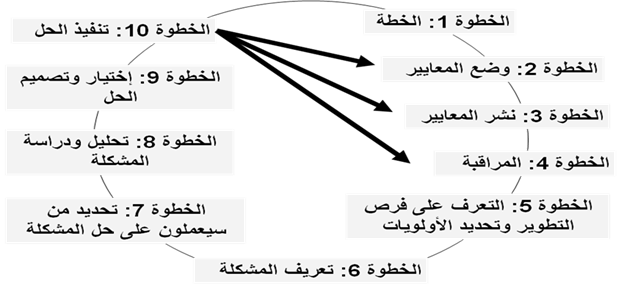
Characteristics based on which the starting point is determined:
Most frequent cases:
• These are activities that will affect a large number of people or their incidence will increase.
Conditions accompanied by problems:
• These are cases in which problems occur repeatedly, whether for workers or patients.
Cases most at risk:
• These are the activities that make the patient more exposed to danger:
1. Failure to provide health services.
2. Not providing the service when it is needed.
3. Providing an unnecessary service.
Standard
What is the standard:
A standard is a statement that defines expected quality.
Why standard standards:
Defining and defining quality “How are activities carried out?”
Quality assessment: “How well were the activities implemented?”
What is the standards section in determining quality?
◾ Identify important inputs.
◾ Identify the series of actions necessary to achieve the desired results.
◾ Describe the desired results.
Types of standards
◾ Clinical work guide.
◾ Administrative work rules.
◾ Specifications.
◾ Performance standards.
Standards sources
◾ Previously prepared standards.
◾ Local and internal standards.
◾ International standards.
◾ Educational bodies and institutions.
◾ Educational institutes and institutions.
Standards published by:
◾ Detailed explanation.
◾ A clear plan for implementation.
◾ Use of incentives.
Disseminate standards by:
◾ Written letters.
◾ Conferences and meetings.
◾ Friendly meetings.
◾ Work guide.
◾ Training.
◾ Monitoring and supervision.
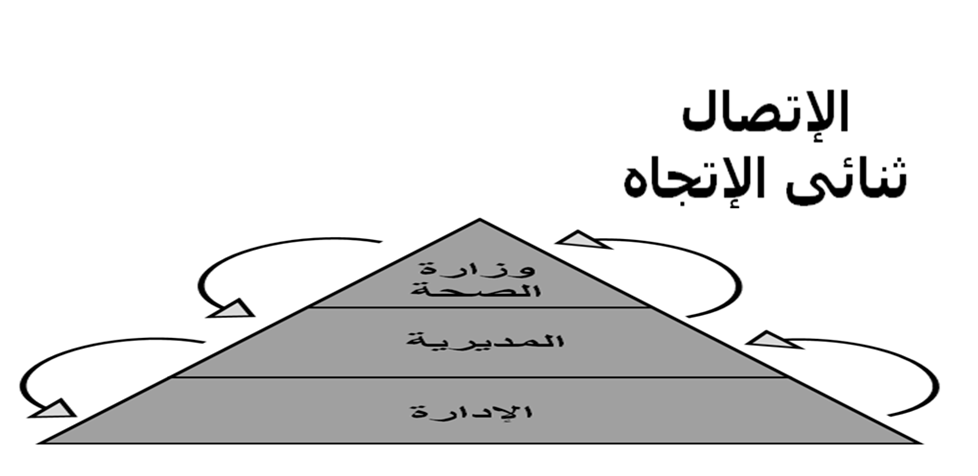
Monitoring
It is the departmental process of collecting and analyzing data on specific indicators to help managers determine the extent to which the main activities are implemented according to the plan and the extent of their impact on the targeted sector of service beneficiaries.
To design a good monitoring program you must:
• Focus on key indicators.
• Collect only the required data.
• Not exhausting workers.
• Collecting data that can be collected, studied and inferred.
• Feedback.
Division improves quality
Step five
Recognize the problem or improvement opportunity:
By knowing the types of data to be collected.
There are two types of data:
Quantitative data:
- Surveillance system.
- Surveys.
- Evaluation results and situation assessment in special cases.
Qualitative data:
Step six
Definition of the problem in practice:
It expresses the difference and gap between the desired performance
And the current situation
Step seven
Determine who will work to solve the problem:
By choosing a team that has the following characteristics:
◾ Who understand the problem.
◾ Who can help.
◾ Those who have technical experience.
Step eight
Analyze the problem to find out the root causes:
By using tools to analyze problems:
Step nine
Design and develop solutions:
By setting specifications for the solution and identifying the obstacles:
Choose the best solution based on criteria such as:
• Ability to implement the solution.
• The solution is free of negative impact on other activities.
• Implementation of the solution.
• Management support for the solution.
• Community support.
• ---------etc
Step ten
Apply solutions
Follow up on solution implementation:
• Did the solution achieve the desired results?
• Did the steps go correctly?
• Are there steps that were difficult?
• Did any problems arise during implementation?
• Is there opposition from other parties and what is the reason for it?
Building a quality assurance program
• Strengthening connection and loyalty to quality.
• Implement an initial review process for quality-related activities.
• Establishing a future vision and program objectives.
• Determine the level and areas of activities.
• Defining the responsibilities.
• Resource allocation.
• Strengthening important administrative skills and systems related to quality.
• Prepare a written plan.
Common errors when implementing the program
• Leaders’ lack of belonging.
• Lack of patience among senior management.
• Lack of specific strategy or methods.
• Rushing into action before fully understanding.
Quality improvement story:
• Telling the story of quality improvement is characterized by simplicity, clarity, and the use of sentences and diagrams. It helps to:
• Visual documentation.
• Strengthening the use of statistical methods.
• Strengthening communications and reducing duplication.
• Preparing presentations and reports.
• Strengthening the use of the surveillance system.
• Help the team understand the differences between procedures and tools.
• Providing a unified approach.
• Report on quality improvement activities

Monthly report on quality activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
Definition of Kaizen philosophy:
It is a compound word of two parts that means “change for the better.” It is a primary means of achieving continuous improvement. It includes many improvement tools used in management, and one of these tools is 5S.
Five S?
5S is the philosophy of taking care of the workplace by organizing and cleaning it. It consists of five basic steps, and each step is called in Japanese with a word that begins with the letter S, hence the name 5S. This philosophy became known worldwide by this name, so much so that these five Japanese words were translated into English words starting with the letter S in order for the name to be valid. We can translate these five words into Arabic words that begin with the letter T, which are classification, organization, cleaning, standardization, and stabilization.
The five elements of this philosophy:
Five T consists of five elements:
1- Sorting classification, which is in Japanese: Seiri:
Taking care of the workplace begins with classifying everything in it.
Meaning of classification: Classification here means that we classify things into things that are necessary for work at the present time and things that are not necessary for work. After that, we get rid of the things that are not needed for work and keep those that are necessary for work. Such as: tools, files, materials, waste, papers, and equipment.
The classification process is the first step in this process
2- Set in Order, which is in Japanese: Seiton:
After that comes the organization process, which aims to preserve the things that we decided to keep in an organized way that helps us perform the work efficiently. The organization process does not only include arranging tools or files on the shelves, but it also leads to reconsidering the general plan of the workplace itself. We have to think about the most appropriate way to organize the workplace based on our current work.
3- Cleaning or polishing (Shining) in Japanese: Seiso:
The goal is a very clean work environment. This process is a process that is carried out in sections every shift or every day. There are things that must be cleaned by the person who uses them or handles them, such as work tools, including keys, tools, and supplies that he uses.
4-Standardization, which is called Seiketsu in Japanese:
After all this effort and experience in organizing and cleaning, specific rules should be set for what the workplace should be like. This includes defining the responsibilities of each individual, setting standard methods for the cleaning process, and announcing all of this so that each individual knows what duty he has in his department and how to perform it. This ensures that the situation will continue in this good manner and we will not return to old habits again.
5- Install Sustain, which is Shitsuke in Japanese:
We come to the final step, which is establishing systems to ensure the continuity of this entire process. For example, systems are put in place to review the cleanliness of places. An effective method is for one party to inspect another party, and a representative from one department inspects the process of filing files in another department or the cleanliness of the work site.
Five s benefits:
There are many benefits from it
1- Reducing time wasted searching for documents or tools
2- Reducing injuries due to the cleanliness of the floors, the absence of anything lying here and there, and the clarity of safe passage places
3- Reducing equipment malfunctions due to their early detection
4- Eliminate excess effort and unnecessary movements through a serious process of organization
5- Feeling a beautiful work environment as a result of the cleanliness and organization
6- Replace damaged tools as soon as they are damaged, instead of discovering it late and disrupting work
7- Easily discover lost things
8- Reducing the malfunctions that occurred after maintenance operations as a result of some dust entering the delicate components (and this has been mentioned in other fields)
9- Reducing quality problems that occurred due to pollution and dust.
- International standards and goals for patient safety and security
The Definition
A common goal that requires the process of coordinating the efforts of the health staff with the patient to protect him from injuries. A process provided by the institution to make the health care provided more advanced, safe and secure. The process of preventing unexpected patient injuries.
Principles and standards of patient safety and security:
Risk assessment: environment - patient.
Identifying risks: - developing a plan to protect the patient - how to act when an error occurs - recording and analyzing the incident: - determining the cause - developing solutions to reduce the recurrence of the occurrence.
Who is responsible for the patient's security and safety?
Patient safety and security standards are the right of every patient and the responsibility of all employees of the medical institution.
No employee is excluded, regardless of their administrative responsibilities.
Senior management: department managers working.
Patient safety and security standards:
◾ Introducing the patient in the correct way.
◾ Improving good and effective communication methods.
◾ The safety of using high-risk medications.
◾ Ensure the operation, the correct procedure, and the correct patient.
◾ Reduce the risk of infection by washing hands.
◾ Reduce patient falls to prevent injuries.
◾ Preventing disconnection or misconnection of catheters or tubes.
◾ Preventing bed sores.
◾ Risk management and patient safety.
◾ Delivery and pickup policy.
◾ Isolation and restriction policy.
The first criterion:
1. Introducing the patient in the correct way:
The patient's name in four letters along with the patient's medical number inside the hospital.
Failure to introduce the patient in the correct manner leads to:
◾ Giving the medicine to another patient.
◾ Performing a procedure on another patient.
◾ Delaying giving treatment or performing a procedure.
◾ Giving an incorrect diagnosis.
◾ Connecting an incorrect patient to operations.
◾ Cancel an operation.
Why does an error occur in the definition?
◾ Multiple interventions.
◾ Multiple places to provide the service.
◾ Multiple dealing individuals.
◾ Some patients are unable to identify themselves.
◾ Lack of a clear identification system.
How do we avoid identification errors?
◾ Do not rest assured - take enough time.
◾ Do not depend entirely on the patient.
◾ Make sure that the information, stickers, and identification bracelet are correct.
Do the following:-
◾ Introduce the patient in the correct manner upon admission.
◾ Make sure the patient’s name is as it appears on the ID card.
◾ Make sure that the identification bracelet data is correct before putting it on.
◾ Put on a new bracelet if you lose the old one.
◾ Ensure that the patient complies with the required procedure.
◾ Ensure that the patient is properly matched before transferring him.
◾ Apply the sample identification label immediately after taking the sample and before leaving the patient.
Do not do the following:
◾ Do not tell the patient his name, but let him tell you his name.
◾ Do not take any sample before matching the patient’s data to the sample request form.
◾ Do not label the sample identification on the container before taking the sample.
◾ Do not complete the work of the procedure remotely.
Understand and adhere to hospital policy:
◾ The hospital’s commitment to international goals for patient safety and security
◾ Patients are identified by their admission site.
◾ The hospital’s commitment to at least two definitions:
◾ Patient’s name is quadruple.
◾ His medical code.
Both definitions are verified each time when:
◾ Giving medication.
◾ Collection of samples.
◾ Giving blood or its derivatives.
◾ Do any tests.
◾ Perform any other procedure.
Second criterion:
Improving effective communication methods.
The means of communication that most lead to errors:
◾ Verbal orders.
◾ Telephone orders.
◾ Receiving test results verbally or by telephone.
Verbal orders: administered face to face between the sender and the receiver.
Telephone orders: They are administered through the telephone between the sender and the receiver.
Responsibility of the recipient of the message or order:
◾ Writing the order or message while dictating orally or by telephone.
◾ Read the matter to the sender and wait for a response with a comment.
◾ If the matter is related to giving medicine, it must include the five basics.
◾ After reading the order, the receiver completes the order data by writing the date and time, the recipient’s name and position, the sender’s name and position, and then signing.
◾ In emergency situations, such as “cardiac arrest,” it is sufficient to repeat the matter to the sender and wait for a response with a comment.
Responsibility of the sender or giver of the order:
◾ Sign the order promptly.
◾ Spell the name of the medication if necessary.
◾ The numbers are dictated as they are pronounced, then each number is mentioned separately.
◾ Gives the command without using the abbreviation.
Understanding and adhering to hospital policy:
The hospital accepts verbal and telephone orders within very limited limits when it is impossible to write them by the person responsible for them and if delaying them may affect the patient.
The sender and receiver must abide by their responsibility in this regard.
The sender's signature on the given order shall be made no later than 24 hours.
Third criterion
Safety of using high-risk medications.
Definition of high-risk medications:
These are medications that, if used in an inaccurate and improper manner, may lead to serious injury or death to the patient.
The most important of these medications:
Insulin.
Narcotic medications.
Anticoagulants.
Potassium chloride KCl and potassium phosphate.
Sodium chloride solution more than 0.9.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
General instructions to reduce the risks of giving medications in general:
◾ Passing the “drug review” test, conditional on allowing treatment to be given.
◾ The presence of a pharmacological reference for some medications.
◾ Develop a bilateral review policy by two members of the nursing staff and circulate it.
◾ Linking the administration of some medications to laboratory results.
◾ Link the administration of analgesics to pain assessment.
◾ Eliminate the presence of high-risk medications from the sections.
◾ Lack of medicines with similar packages and similar taste in one place.
◾ Place a clear label with the name in the place where each medication is kept and stored.
◾ Review the use of a solution pump using a dual method.
◾ When the treatment is given for the first time, the drug label is matched - according to the medical order - to the drug administration record sheet. When repeated administration, the drug label is matched to the drug administration record sheet.
◾ Identifying, recording, analyzing errors and finding out the reason is the way to improvement.
Keys that help avoid errors when giving treatment:
◾ Information about the patient.
◾ Information about the medication.
◾ Effective communication.
◾ Labeling of drug packages: When preparing their packages, each package must be distinct so that they are not confused (the presence of a single dose system is useful in solving this problem).
◾ Inventory: Providing the appropriate inventory in quantity and quality.
◾ Environmental factors: Having a system designed to administer medication contributes to reducing errors, for example, “good lighting - distance from noise and interruptions.”
Giving the patient appropriate instructions regarding treatment
Understanding and adhering to hospital policy:
◾ Medicines are substances whose misuse may pose risks to patients.
◾ There is a group of medications that have been agreed upon as high-risk medications.
◾ These medications are not placed in regular nursing departments.
◾ When used, a double review is done before giving it.
Fourth criterion
Verifying the operation - the correct procedure - the correct patient”
The problems of the wrong patient - the wrong procedure and the destination of the operation occur as a result of:
◾ Ineffective or incomplete communications between health team members.
◾ Not involving the patient.
◾ Lack of policy.
◾ Failure to evaluate the patient.
◾ Not reviewing the patient’s file.
Understanding and adhering to hospital policy:
The policy is consistent with international standards to prevent an error on the part of the operation, procedure, or patient, as follows
◾ Determine the location of the operation
◾ The mark is placed before the patient is anesthetized.
◾ The mark is visible throughout the procedure
◾ Maryam’s name in triple and the medical number
◾ The process and its destination
◾ Signatures and dates completed.
Verification process before the operation:
◾ Verify (the operator - the patient - the name of the operation...).
◾ Verification is carried out by the floor nurse - the surgeon - the recovery nurse - the anesthesiologist separately.
◾ Verification is recorded in a special form and signature.
◾ Marked by the doctor or his assistant.
◾ Ensure the availability of supplies.
◾ The surgeon must ensure with the operating nurse that...
◾ Supplies - Safety of the equipment used - Providing machines
◾ Final verification Time Out: It takes place immediately before the procedure begins. - It depends on team work and effective communication.
The team consists of (the surgeon - the anesthesiologist - the nurse) whose purpose is to make sure that the correct procedure is performed on the correct patient in the correct direction.
Time out sheet
Fifth standard:
Reducing the risk of infection in hospitals
◾ The institution must establish a system that reduces the incidence of infection as a result of being in the hospital.
◾ The institution must adopt instructions and directives for hand hygiene.
◾ The organization must implement an effective hand care program.
◾ Taking care of hand hygiene.
◾ A simple, low-cost process that reduces hospital infection rates. Hand washing remains the best way to reduce the transmission of infection
◾ In hospitals, the obligation to wash hands is not implemented effectively in all countries of the world, with variations.
Reasons for not adhering to hand cleaning:
◾ The number of employees is less than the usual ratios.
◾ Allergy to the materials used in cleaning.
◾ Insufficient information available to workers about the importance or method of cleaning and individuals’ behaviors towards protecting patients.
The following was observed regarding the commitment to clean hands:
◾ Doctors are less interested in cleaning hands.
◾ Nursing assistants are the least concerned about cleaning hands
◾ Males are less observant.
◾ Intensive care workers are less committed.
◾ Workers wearing gloves are less observant.
◾ From the employees’ questions, the following was learned: “Their statements.”
◾ The materials used cause allergies.
◾ Lack of sufficient sinks for washing hands.
◾ Unavailability of soap.
◾ Always busy.
◾ Patients’ needs are more important.
◾ We wear gloves.
◾ There are no clear instructions.
◾ The possibility of transmitting infection is small.
◾ We don’t remember.
◾ We did not see female trainers or supervisors doing this.
Reducing the risk of infection in hospitals
What lives on the skin of the hands?
Colonial microbes: They live continuously on the skin and are not usually affected by regular washing, but they are usually removed when washed with disinfectants.
Temporary microbes: They stick to hands when dealing with patients, contaminated tools and devices, or the surrounding environment. They are often responsible for transmitting infections in hospitals and are usually removed by routine hand washing.
Ways to take care of hand hygiene
◾ Routine hand washing with soap and water.
◾ Removing dirt - any organic materials - getting rid of temporary microbes.
Hands should be washed before and after:
◾ Performing any interventional procedure on the patient.
◾ Dealing with any wounds.
◾ Direct contact with the patient - routine hand washing with soap and water.
◾ Removing dirt - any organic materials - getting rid of temporary microbes.
◾ Hands must be washed before: - Serving any meal - Leaving work - Caring for patients with weak immunity.
How to wash hands?
◾ Remove any jewelry. Turn on the faucet with your elbow or hand.
◾ Wet hands with water, apply soap and distribute it on both hands.
Follow the picture instructions. Rinse hands. Dry hands well with a single-use towel. Close the tap with the same towel
Sixth standard: Reducing the risk of falling
A fall is a sudden and unexpected downward fall that may or may not result in injury.
How can patients who are at risk of falling be identified?
◾ Evaluation is a process carried out by nursing staff to collect data that helps identify the patient’s problems.
◾ Evaluation is a procedure that involves several aspects, one of which is assessing the possibility of falling.
◾ The purpose is to identify patients at risk of falling so that the necessary precautions can be taken.
◾ The policy stipulates that all patients (departments - clinics) are evaluated for the possibility of falling.
◾ You will use an evaluation form within an hour for department patients and within 10 minutes for clinic patients.
◾ The evaluation is repeated once every 24 hours. Those who scored from zero to 44 are classified from simple to moderate and are applied to them.
The following precautions:
◾ Familiarizing the patient with his surroundings - the suitability of what he wears on his feet - the bed in a low position.
◾ Fix everything that is moving - good lighting - the patient’s personal needs are at his fingertips.
◾ The nurse call machine and telephone are working and in proper condition - the room is tidy and the floors are dry.
Know the patient:
How to call the nurse when needed - Notify the nurse when feeling “dizziness - fainting...”.
Use any aids used.
Those who obtained 45 or more must follow the following:
◾ Familiarize the patient with his surroundings several times.
◾ The nurse is there to help every time the patient is moved.
◾ The patient’s room is close to the nursing station.
◾ The bed is in the low position and good lighting stabilizes everything that moves.
◾ The patient’s needs are at his fingertips.
◾ The nurse pager and telephone are working and within easy reach
◾ The room is tidy, the floors are dry, and there are no obstacles in the patient’s way.
◾ The patient should not be left alone on the commode or wheelchair.
◾ What is worn on the foot to prevent slipping.
◾ The patient is asked every two hours during the day about his requests.
◾ He is followed quietly while working.
◾ The possibility of falling is communicated verbally among members of the nursing staff when changing shifts.
◾ This is written in the nursing notes.
◾ The importance of these precautions is discussed with the patient’s family.
◾ The patient is asked every two hours during the day about his requests.
◾ He is followed quietly while working.
◾ The possibility of falls among nursing staff members is made verbally known when shifts are changed.
◾ This is written in the nursing notes.
◾ The importance of these precautions is discussed with the patient’s family.
The seventh standard is to prevent separation or misconnection of catheters or tubes
◾ All connections are connected to the patient in the correct place.
◾ The name of the connection or catheter and the date of installation are written on it.
◾ The leads, catheters, and the insertion site are taken care of for signs of infection and other signs.
The responsible nurse places an adhesive tape on which she writes:
◾ The date the catheter or tube was installed.
◾ Type of catheter or tube.
◾ The size of the catheter or tube.
◾ The person who installs the catheter or tube.
◾ Assessing the placement and connection of the catheter or tube according to its type and the purpose of its installation or at the beginning of work shifts and during the delivery and receipt process.
Eighth standard: Preventing bed sores
◾ Bed sores are one of the nursing problems that may occur to patients when they are not taken care of.
◾ When the patient receives a new admission at the time of admission to the department and has bed sores, a declaration is written and signed by the patient or whoever accompanies him stating that the patient has bed sores and of what degree they are.
◾ The nurse responsible for the patient examines the patient at risk of developing bed sores and determines his degree of exposure to bed sores.
◾ The treating physician and the responsible nurse determine the degree of the pressure ulcer in order to know the medical care plan required for the patient. The doctor records the result of the evaluation in the patient’s medical record.
The patient exposed to bed sores is evaluated as follows
First degree :
Redness in the area prone to ulcers compared to normal skin color. Cover and protect the exposed area.
Second degree :
Loss of the surface layer of the skin and the presence of a scarlet-red ulcer with the presence of white or yellow fluid sometimes.
Covering/protecting the skin/moisturizing and healing the area.
Third degree:
The presence of a deep ulcer that includes the superficial layer of the skin and what lies beneath it. There is a white, gray, or yellow fluid. There is an edge to the ulcer. There is a purulent discharge.
Covering the skin/protecting it/moisturizing and healing ulcers/removing dead tissue/cleaning and treating infections/aiding healing.
Fourth degree
There is a deep ulcer that reaches from the surface layer of the skin to the muscles and bones. There is a foul odor. There is a brown or black secretion. There is a purulent discharge.
Covering the skin / protecting it / moisturizing and healing ulcers / removing dead tissue / cleaning and treating infections / helping healing / filling the gap.
Precautions to be taken to prevent bed sores:
◾ If the patient is bedridden, he must use an air-filled mattress (air mattress).
◾ Use pillows between the joints (knees, elbows).
◾ Use soft, clean and dry furniture.
◾ Avoid creating folds in the bedding under the patient.
◾ Constantly monitor the skin (dryness, wetness, redness).
◾ Dry the body well after washing.
◾ Eat a balanced diet.
◾ Consult a physical therapist regarding appropriate exercises to improve blood circulation.
Ninth standard: Risk management and patient safety:
◾ Risk management is the other side of the patient’s safety and security. The risks that the patient may be exposed to in the hospital are identified, an analysis is made of them, and a method is developed for how to deal with them, solve them, and prevent them from occurring again.
◾ There are risks that occur from people.
◾ Risks resulting from interventions to which patients are exposed.
◾ Risks from hospital infrastructure.
◾ Risks arising from incorrect work system
The tenth standard: Delivery and receipt policy:
The Purpose:
Communicating important information about patient care from one doctor to another or from one nurse to another during the patient’s medical service shift.
Politics:
The obligation of the medical service providers during the work shift to provide and exchange general information about the patient while providing medical care to him. The head of the department develops a handover and receipt form that contains the important information that is exchanged between the medical service providers in his department. The medical service providers deliver and exchange medical information among themselves. During the work shift, according to the relevant guides and forms, information is exchanged between service providers during the exchange of work sessions, with sufficient time to discuss information about the patient and provide answers to inquiries about the care or service required to be provided to the patient. The head of the department ensures the continuous implementation of the handover and receipt process in the event of a transfer. The Patient Medical service providers exchange important information about the patient and provide answers to inquiries about the patient’s condition during the handover and handover process. The information that must be conveyed orally or through handover and handover forms is: the patient’s name, age, date of birth and address Diagnosis History Patients Allergies Medications/Food/Liquids Tests/ Tests, previous and planned operations, health care plan for the patient within 24 hours, tests and analyzes required to be performed, procedures required before the patient is discharged.
Standard Eleven: Isolation and restriction policy
The Patient Care Law guarantees the patient his right to enjoy his freedom and not be restricted or isolated in accordance with Article (36) of the law unless the emergency situation requires it. Isolation or restriction is an exceptional situation that the treatment team does not resort to as part of the treatment plan because the principle is to avoid them and use them after Exhausting the means that least restrict the patient's freedom.
The patient's emergency situation is represented by the emergence of aggressive behavior or disturbed behavior that threatens his safety or the safety of others around him and constitutes an imminent danger that cannot be controlled or contained by means that are less restrictive of his freedom (such as reassuring the patient, using positive reinforcement, or modifying the environment surrounding him).
Isolation and restriction procedures shall not be applied except by direct order from the responsible physician or his representative within the facility who has experience in applying these procedures.
The therapeutic team performing the isolation or restraint must be professionally trained in both procedures and possess the skills that qualify it to carry out them, taking into account the application of internationally approved standards.
Isolation or restriction procedures must be carried out according to methods that are psychologically and physically safe and preserve the patient’s dignity.
Isolation or restriction measures must not be a means of coercion, discipline, comfort or retaliation by the treatment team.
Isolation or restraint procedures shall be carried out for a specific time and must be ended immediately upon the expiration of the reasons that necessitated their application. The period of isolation or restraint for adults shall not exceed 8 continuous hours in accordance with the provisions of Article (36) of the executive regulations of the law. It is renewable, but only after another debate and a new examination of the patient. By the responsible physician or his representative. Renewal requires the continuation of the emergency situation, and it is preferable that the time specified for the isolation or restriction procedure be in accordance with international standards as follows: -
4 hours for adults (18 years or older)
2 hours for teenagers (9-17 years old)
One hour for children under 9 years old
A patient subject to restraint or isolation reserves the right to see an official of the Patient Rights Committee and also has the right to file a complaint.
Isolation: is detaining the patient against his will in a room or area designated for that purpose, isolated from others, so that he cannot leave it, provided that the place conforms to all internationally approved specifications for isolation rooms.
Restriction: It is the restriction of the patient’s movement and its types:
Manual restraint: - Manually or physically, the patient is contained with the least amount of force by immobilizing his arms and legs, avoiding pressure on his back and neck, and keeping his position lying on his back as much as possible.
Mechanical restraint: - What is meant is the use of tools or devices to limit the patient’s movement so that they are close to his body to the extent that he cannot easily escape from them, and also allow him little freedom of movement. It is safe and provides the patient with physical and psychological protection. It keeps the patient from falling. It is easy to adjust and does not waste dignity. For the patient, it does not require surgical intervention to install it. It allows for quick termination when an emergency occurs in the patient’s surroundings.
When restraining, one person is required on each limb and another for the patient's head. The patient is placed lying on his back in the bed, and each ankle and wrist are restrained so that he is tied to the bed from four sides. Soft restraints are used, such as gauze, leather restraints, or medical belts, according to the desired degree of fixation and the patient's condition, and are not applied. Restraints on the chest, neck and head.
To apply isolation or restriction measures, the following steps must be followed:
◾ Observation of the patient by the therapeutic team present with him in terms of behavior and actions and the speed of predicting the presence of an imminent danger as a result of his behavior.
◾ The therapeutic team (often the department’s nursing staff) monitors any aggressive behavior in the patient or severe agitation that threatens his safety or the safety of others around him and evaluates it professionally, not personally, towards the patient.
◾ Trying to use the means that are least restrictive of the patient’s freedom, and after exhausting them and being unable to control the emergency situation, the treatment team resorts to containing the patient and trying to control his movement with physical restraint only. It is not permissible to isolate the patient or restrain him chemically or mechanically except by direct order from the responsible physician or his representative. about him.
◾ Fill out the paragraph related to the nursing staff member’s report on the emergency case in the isolation and restraint form
◾ Call the responsible doctor or his representative immediately to discuss the case and do the following:
◾ Examine the patient clinically (psychologically and physically)
◾ Evaluate the extent of the risk and whether it requires the application of isolation or restraint measures, and attempts to control it by means that least restrict the patient’s freedom.
◾ Informing the patient of the reasons that necessitated isolation or restriction measures, the danger of his behavior to himself and others, and quickly ending the procedure if the reasons necessitating it do not exist.
◾ The responsible physician or his representative must complete the form for isolation and restraint, which includes:
◾ Clinical examination of the patient, psychological and physical
◾ Risk aspects and severity
◾ Less restrictive means that have been exhausted
◾ The specified period of isolation or restriction
◾ The type of procedure that will be decided for the patient
◾ Description of the prescribed method of isolation or restraint, for example (the place of isolation is the patient’s room or another room - the mechanical restraint, the nature of the tools used in the procedure and how they are used and distributed among the parts of the body)
◾ Determine the start and end times of the procedure in isolation or restraint
◾ Pointing out the necessity of observing critically ill patients such that their condition requires special care, for example: patients with respiratory system diseases, heart diseases, and obese and overweight patients.
◾ The responsible physician or his representative must state his name, signature, and the date of the procedure
◾ The procedure is carried out under the direct supervision of the responsible or on-duty physician and in the presence of one of them
◾ Identifying the cases and circumstances that require the treatment team to terminate the procedure
◾ The responsible physician or his representative must review the patient’s treatment plan and update it according to the patient’s clinical condition and the circumstances surrounding him to avoid a recurrence of the emergency.
◾ A member of the treatment team is assigned to observe the patient face to face around the clock throughout the specified period of isolation or restriction, and to follow up on him every 15 minutes and record the following:
◾ Injuries that the patient may have suffered during the procedure
◾ Vital signs, respiratory rate, nutrition, skin color, behavior, and general condition
◾ The state of blood circulation in the places of restriction (pulse, skin color)
◾ Frequency of movement, provided that restrictions are lifted every two hours for 10 minutes
◾ Provide him with fluids for two hours and record his intake
◾ The patient is given two hours of opportunity to excrete (urine, stool) when needed
◾ It allows the patient to sleep and provides him with protection and comfort during sleep
◾ Ensure that restrictions are placed in their correct places and amended when necessary
◾ Protecting the patient from harm by others (verbal and physical) during the procedure
◾ Observing the patient’s ability to understand the procedure, his ability to adapt to it, and the form of his behavioral response
◾ The name of the nursing staff member performing the procedure and observation must be recorded on the isolation and restraint form
◾ The hospital is committed to creating a special record of isolation and restraint procedures, which records:
◾ Patient’s name, registration number, admission date
◾ Type of procedure, date, and duration
◾ Name of the responsible physician and nursing staff member performing the procedure and observation
◾ The record is presented to the medical director daily, and the hospital administration is notified of this action as soon as it is taken during working hours or immediately the next morning when it is applied in the shift.
Reasons for ending isolation or restriction measures:
◾ The signs of danger that necessitated applying the procedure disappear and the emergency situation disappears
◾ The success of one of the least restrictive means of the patient’s freedom to control and modify the patient’s behavior
◾ The appearance of signs of deterioration in the patient’s organic condition requires terminating the procedure
◾ The occurrence of an emergency in the vicinity of the procedure that prevents its completion, such as a fire
- Records and reports
The work of the various types of nursing staff, including the head of nursing - inspectors - supervisors and nursing staff members, includes writing many reports and recording health and nursing data.
The process of measuring performance and planning health nursing services depends on the accuracy of registration and the efficiency of records and reports. Therefore, attention must be paid to records and reports so that the information is correct, complete, accurate, recorded in a clear manner, and kept in a safe place so that it is not damaged or lost.
The importance of records and reports:-
Records and reports have many important benefits that can be summarized as follows:
◾ A record of the unit’s work and nursing work in terms of quantity and type so that it can be referred to when necessary.
◾ One of the means used to evaluate the performance of the unit and workers
◾ Means of communication between the employee and the authorities.
◾ A tool for guidance when planning health and nursing services
◾ A tool for guidance when organizing educational programs and training courses
◾ A way to learn about the situation in society, common problems and diseases, and methods of treating them.
◾ A tool for conducting comparative research in the fields of health and nursing
◾ A document that can be relied upon in legal problems to protect health workers and institutions.
Characteristics of good recording and reporting:
◾ Accuracy, clarity and honesty in recording
◾ The data must be complete, correct, neatly arranged and objective
◾ Accuracy of timing when reporting certain important information, incidents, or disasters that cannot be postponed, as the reporting must occur immediately and at the specified time. The report must end with the signature of the informant or writer, the date, and sometimes also the hour.
Reports:-
A report is an oral or written message, the purpose of which is to convey information about a specific topic or incident for recording, reporting, or to take a specific action. Usually, reports are submitted from the subordinate to the superior on a regular basis and at specific times, with the exception of accidents and disasters, which are reported immediately upon their occurrence.
A good report is one that conveys information in a clear and precise manner, using simple sentences and without repetition - using clear words that do not have ambiguity or carry more than one meaning - avoiding the use of the passive voice - choosing appropriate words that clarify the purpose - while ensuring accuracy in writing.
Taking into account that there is sufficient time for drafting and review before signing, a copy of the report must be kept for reference when necessary.
The report usually consists of the following parts:
Name of the person or entity to whom the report is sent
Report title - It must be brief, clear, and indicative of the subject of the report
A simplified summary of the topic
The introduction includes a quick presentation of the history of the topic, its development, and the special circumstances surrounding it in terms of time, place, and people
The body of the report - or the main part of the report, which includes a complete presentation of the topic based on observations, interviews, and documents
The conclusion reached by the report writer and his personal opinion for treatment or solutions
Conclusion and recommendations
Signature and date
There are many types of reports:
Including printed and unified forms in all hospitals and units, such as statistical reports, reports attached to samples for laboratories, or a request to perform x-rays...etc.
There are also verbal reports, such as what the nursing staff informs her colleague in the next shift, such as the condition of a specific patient or a special treatment that is required to be performed. It is preferable to record this information in a written report as well for reference when necessary.
Methods of communication from the boss to the subordinate (from top to bottom) are in the form of administrative orders or instructions - work manuals - bulletin board patrols - and sometimes they are in the form of verbal instructions.
Most written communications that go down from management to workers are issued in the form of administrative orders, work manuals, bulletin board periodicals.
As for written data and information that come from workers to the top, they may include statistical data and information about the quantity and type of services, and written reports from subordinates to superiors may affect service planning and decision-making to solve problems, resulting in the achievement of goals. Good management gives instructions and directions to workers about the quality of data. The statistical information that must be included in the report for each nursing department or unit
As for the reports prepared by supervisors or head nurses and inspectors, they are usually related to solving problems, what has been done and what should be done, as well as an evaluation of current production and quality of care, along with presenting suggestions to solve problems that are outside their control and authority. Written reports can be kept as documents and a source that can be referred to if they contain Provides correct, accurate and real information.
Reports related to nursing services management:-
1- Report of receipt and delivery of the shift:-
Necessary as a means of communication to transfer and follow up information from one group of nursing staff members to another group during daily work 24 hours a day. These written reports provide nurses with notes about patients and what happened to them during the period preceding their work. The importance of this report is that a large number of nursing staff members and members The health team meets with the head nurse to give the necessary data before writing the report, raise any questions, and reach clarifications and solutions to the problems.
2- Daily report:
This report is written by the hospital’s head nurse to the director to inform him about:
◾ The general condition of the hospital.
◾ Statistics of patients who had changes or complications.
◾ Cases of patients that have undergone changes or complications.
◾ Cases of patients following specific treatment or research.
◾ Entry, exit, transfer and death cases.
◾ Critical cases.
◾ The plan to be followed in the event of an emergency
◾ All cases with high fever, especially after childbirth
◾ Complaint by patients or service users.
◾ There are many forms of this type of daily general report
3- Patient census report:
It is the official number of patients in the inpatient department or hospital departments at a specific time, usually at midnight. Nursing during the night is responsible for writing this report, and its purpose is to know the number of patients in the inpatient department at any time, the bed occupancy rate, and the number of empty beds.
4- Reports on work problems and the extent of progress in following the proposed solutions:
◾ Writing reports on work problems, along with giving recommendations for solving them, is an effective tool for obtaining facts and helping to direct the discussion of a particular problem in meetings, as well as providing guidance for the follow-up system.
◾ These reports also help other nurses and all members of the health team and superiors know the real reasons behind these problems, so that they can confront similar problems that occur in the future and when evaluating progress in solving these problems and in achieving the desired goals of the work.
The following must be followed when writing reports on work problems:
◾ Definition of the problem and its size.
◾ Give an accurate statement of the errors and what needs to be fixed.
◾ Analyze the reasons that led to these errors.
◾ Remember the roots of the problem as the report writer sees it.
◾ Proposed solutions to eliminate the causes of the problem, along with clarifying the people who will implement the solutions.
5- Reports on accidents and emergency situations:
It is the responsibility of the nursing staff to maintain the safety and well-being of patients and users of health services in hospitals and health units
They are responsible for implementing and following up on the treatment and nursing plans for these patients, as well as for avoiding accidents and dangers that may occur in hospitals and health units. In order to provide insight and determine the duties of nursing staff members in the event of disasters or an emergency, they must be introduced to the hospital or unit system and how to inform their superiors. Work when internal disasters occur, as well as how to carry out their duties in response to them
Therefore, one of the most important duties of the nursing services department in hospitals and health units is to follow a special system for reporting the occurrence of such errors and accidents as soon as they occur, and to alert and train nursing personnel when they take up work on the necessity of reporting these errors and accidents to those responsible. One of the most effective methods of reporting is writing reports on accidents and emergencies.
Reports of medication administration errors:
Such errors may occur from members of bodies that deal with issuing, preserving, or administering treatment to the patient, such as nursing staff, pharmacists, and technicians. This may indicate that they did not follow the necessary procedures of the hospital in giving and dispensing treatment. This may also be an indication that the doctor’s orders are necessary. It must be written accurately and clearly, and the pharmacy instructions written on the packaging must also be written accurately and clearly
Analysis of reports on accidents that occur to patients during their stay in the hospital or their visit to health units shows a lack of accuracy on the part of those responsible for caring for the patients. For example, negligence in not following the instructions issued by the head nurse regarding the operating room, which must be followed by the nursing staff and doctors, such as counting the technician’s towels before closing the wound. During the operation, until the shortage of these pads is discovered before the opportunity is too late, so that the hospital bears this responsibility alongside the doctors and nursing staff.
Likewise, accidents may occur for workers due to failure to follow the appropriate method and methods at work. For example, when linens are not checked before putting them in their container to be sent to the laundry, the laundry workers may be exposed to injury from quickly leaving scalpels or sharp tools in them.
For each of these examples, it appears that nursing staff members have an important effective role in preventing accidents and mistakes that may result to patients and workers that may happen to the patient while he is in the hospital. Therefore, reports on the patient’s physical and mental condition must be recorded in the patient’s file and notified to the head nurse and the doctor. What is responsible at the time, such as the appearance of bed sores or lice infestation, as well as an undesirable reaction to a treatment, such as the occurrence of chills (shivers) when giving solutions intravenously or by injection, must be recorded and reported to the specialist as incidents and recorded in writing in a report..
The report of emergency incidents and treatment errors includes the following:
◾ Patient’s name and diagnosis
◾ Date of entry, frequency or visit
◾ Time to notice and report the situation
◾ What was done to prevent the condition from occurring
◾ The circumstances of the situation, its dimensions, and the unusual factors that affected the environment at the time the situation occurred
◾ Steps taken to correct the situation and remedy the error
◾ Date, signature of the individuals writing the report
◾ Suggestions from the head nurse to prevent such an error from occurring and are sent to the director of the hospital or health unit.
6- Reports on patient complaints:
The patient's complaint must be reported immediately to the head nurse. It is important for both the nursing team leader and its members to become aware of the patients' complaint and their relatives from the beginning of the complaint so that it does not escalate and so that it facilitates the study and analysis of nursing plans to find appropriate solutions at the right time.
It is possible that complaints submitted by patients and their relatives regarding the quality of services provided constitute a kind of effective participation in directing these services in the interest of patients, workers, and the institution alike, by involving the patient in implementing the plan drawn up to care for him. Therefore, nursing staff members must consider the complaint objectively. The patient is assisted in accepting the necessary adaptation while he stays in the hospital, implementing his treatment, and accepting health instructions.
Such a report includes the following:
◾ The content of the complaint and its justifications as stated by the patient.
◾ Actions taken to resolve the complaint.
◾ Result.
◾ Date and signature.
7- Administrative reports:
Sometimes the executive authority and directors of hospitals and health units request writing and submitting monthly, quarterly, or annual reports from each department or unit of the institution or hospital. The Nursing Services Department may request written and periodic reports from the heads of nurses and nursing units in the hospital. Likewise, nursing inspectors often request monthly reports from Head nurses of health units
Such a report includes the following:
A brief account of the unit’s activities, the type of nursing staff, the number of working hours and shifts, and statistics on births, admissions, discharges, deaths, and home visits.
Current capabilities of machines, tools and maintenance status
Problems affecting nursing care regarding manpower, environment, machines and tools
A narration of the reasons for bringing about a change in the work pattern in terms of labor or resources and the result of this change, giving evidence and indicators that prove these changes and their results.
These reports must be taken seriously by the superiors and their results must be followed up until the required changes are made to raise the level of services in health units. If they are not taken seriously, these reports are considered a waste of time and energy and become unproductive...
Records:
Records are an administrative tool used to preserve and arrange information and prevent its repetition. They contribute to achieving the goals of administration, the educational process, and conducting scientific research.
The following are the different types of records used in hospitals and nursing units:
1- Patient file:
◾ It is the document that indicates the quality of health care given to patients or beneficiaries of health services. It includes information pertaining to the patient since his admission to the hospital or his first visit to the health unit, as well as his laboratory tests, observations and details of therapeutic procedures, as well as the patient’s reaction to the treatment and services provided to him.
◾ It also contains records of consultations for treatment and surgical operations.
◾ It also has separate papers to record treatment and medications.
◾ They are not only records to collect information about the patient, but they are also considered a legal document used when necessary in judicial cases, and therefore the data contained in the patient’s file has a privacy character.
◾ There are many efforts being made to raise the level of efficiency of using records as an administrative tool at all levels of health services.
The patient's record (file) is used for the following purposes:
◾ Help to reach diagnosis and treatment.
◾ Recording the services provided to the patient.
◾ Contributing to education and conducting research.
◾ It is used as an important legal document in cases brought before the judiciary.
◾ It is used in quantitative and qualitative analysis when evaluating services.
Nursing responsibility for patient files:
Organizing and arranging the records of new patients and patients, provided that these files include the following: -
◾ Personal data of patients and attendings, complete forms for vital signs and nursing notes.
◾ Laboratory forms, x-rays, and other records for specialized departments
◾ Treatment papers.
Responsibility of the unit head nurse towards keeping patient records:
◾ Records must be kept in a safe place away from tampering and loss.
◾ Do not give records to others unless the patient is referred for study or to the treating physician.
◾ Do not remove any paper from the patient’s or patient’s file for any reason
◾ No one, including relatives, friends or families of patients, is allowed to read the records except with written permission from the director of the hospital or unit.
◾ Providing instructions and training to new nursing staff members on how to take complete and correct notes.
◾ When the patient is discharged, you must ensure that the record is organized, correct, and complete before sending it to the office responsible for its preservation.
◾ Patient records and reports must contain the patient’s progress from his admission until his exit from the unit, and the details must be sufficient so that it is easy to use in following up on the patient’s condition whenever necessary, as well as when conducting scientific research.
2- Records for taking nursing notes:
This includes recording accurate observations about the patients’ condition and the nursing care given to them. It also includes special information related to medications, treatment, food, and health instructions, as well as recording notes about the patient’s physical and psychological condition, the patient’s reaction to treatment, the extent of his adaptation to the disease, and any change that may occur in his condition.
The purpose of this record:
◾ There should be a unified and agreed-upon record for all employees in one hospital to write notes by the nursing staff to facilitate the transfer of responsibility from members of the nursing staff to others during working hours.
◾ Facilitating the rapid review of the patient’s condition and the performance of nursing care.
◾ Emphasize the importance of taking nursing notes.
3- Records of distribution of duties to members of the nursing team:-
It includes the names of the nursing staff members working in the unit and the names of the patients assigned to their care, as well as the special duties assigned to each of them. There must be a unified form that is filled out daily by the head of the unit’s nursing staff, and this record must be placed in a clear and known place for everyone.
The record of assignment distribution includes the following:
◾ Name of the responsible nurse
◾ Patient’s name
◾ Diagnosis
◾ Needed nursing care or special treatment and research
◾ The type of duties that nurses are responsible for, such as assisting the doctor in examining or giving treatment to patients who are in need
◾ As well as special duties such as preparing to give injections or preparing a dressing cart for wounds
The purpose of this record:
◾ Informing members of the nursing team working in nursing units in hospitals and health units in writing about their daily responsibilities.
◾ Determine nursing responsibility for each patient.
◾ A basis for evaluating the nursing care given to patients.
4- shift tables:-
It is a record that is prepared weekly and daily and specifies the plan drawn up to cover the nursing and health unit with nursing staff over a 24-hour period and includes the following:
◾ Names of the unit’s nursing staff.
◾ Different levels of nursing staff in groups over a week. Detailed has 24 hours on the number of shifts.
◾ Name of the head nurse in each shift.
◾ Rest days, sick leave, excuses, and absences.
◾ Meeting times, rest hours, and lunch.
The purpose of this record:-
◾ It explains the coverage of the units with the nursing workforce and the extent of its adequacy
◾ The presence and absence of nursing staff in the unit is recorded daily
◾ Information is given about all nursing services in relation to the numbers and levels of the workforce
◾ It also shows the number of working hours for each nursing staff member.
5- Custody inventory records:
◾ Labeled records for all devices, furniture, tools and machines, specifying the quantity, specifications and condition of each.
The purpose of this record:
◾ Providing the head nurse with information about tools that are missing, broken, or need to be repaired
◾ Return the excess to its appropriate place, as well as the borrowed tools, before counting or inventorying the item.
6- Employee performance evaluation records:
These are records used to evaluate the performance of employees annually or every six months
The purpose :
An objective basis on which employees are promoted and given rewards and incentives
An incentive for employees' professional advancement.
It explains the reasons for poor performance and gives recommendations for good work.
7- Time tables:
For routine and non-routine work
The purpose :
It shows the time when activities occur, which are daily, weekly and monthly
Daily schedules show when the unit's routine activities occur
Monthly time sheets such as when monthly reports and orders are submitted
Models used in operations
Operating Room Count Sheet Nursing Form
A form for counting the number of surgical machines and supplies
Surgeon: …………………….. Assistant Surgeon: .................. .................. Type of operation : ....................................
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A form for counting the number of surgical machines and supplies
Surgeon: …………………….. Assistant Surgeon: .................. ..................
Type of operation : ....................................