Chapter Five
| Site: | EHC | Egyptian Health Council |
| Course: | Developing the administrative skills of nursing leaders |
| Book: | Chapter Five |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Monday, 23 December 2024, 4:12 AM |
- Orientation
. identification
- ***The third element of the administrative process is direction.
It means "issuing instructions and directions from superiors to subordinates to begin work and how to complete it."
Guidance is the process of guiding subordinates in carrying out tasks and raising their morale. It includes directing subordinates towards:
- The plan
- Organization
- Coordinating the work of subordinates
- The new circumstance.
- ***The third element of the administrative process is direction.
- It means "issuing instructions and directions from superiors to subordinates to begin work and how to complete it."
- Since the guidance process is related to the boss’s interaction with subordinates, the boss must know the personality of his workers and know how to treat them in the appropriate way. This comes through the communication process that must be developed by managers so that they can make individuals achieve the organization’s goals.
Guidance is not the implementation of actions, but rather directing others in their implementation of actions .
Guidance is defined as working during implementation, in order to confront any problems, This is in order to ensure that work proceeds in the required manner and level, which ensures that workers are directed towards achieving goals with the highest degree of efficiency And effectiveness
Tips for the Mentoring Process : The following suggestions are adapted from “What Every Supervisor Should Know”
* Don’t make it a power struggle . Try to focus your attention - and the attention of employees - on the goals that must be achieved. The idea is to imagine that this is what the orders require, as it is not based on the whims of the manager.
* Avoid rough methods . If you want your employees to take instructions seriously, do this.
* Watch your words . Words can become an unreliable messenger for your thoughts. You should also monitor your tone of voice. Most people accept the fact that a supervisor's job is to issue orders and instructions. Their opposition to these orders is based on the manner in which these orders were issued.
* Assume that employees understand everything . Give employees a chance to ask questions and discuss goals. Support them to confirm their understanding by having them repeat what you said.
* Make sure you get “feedback ” the right way. Give employees who want to object to tasks the opportunity to do so at the time you delegate the tasks to them. It is better to know and control opposition and misunderstandings before starting work than to wait until later.
* Do not give a lot of commands . Excessive information is considered discouraging for employees. Keep your instructions short and direct. Wait until workers finish the first job before asking them to start a second job.
* Give them only important details . For old aides, there is nothing more boring than hearing about known details.
*
try not distinguish anyone
. It is inappropriate to punish the person instructed to foul the task. Try to decrease doing this as much as possible.
**What does the guidance function depend on?
The directing function depends on the manner and administrative method through which the president can push his subordinates to work to the best of their abilities. Within a framework through which satisfaction is achieved Their desires and achieving their personal goals, the president uses subjective methods of motivation and encouragement, which are considered conditions of leadership.
Conditions that must be met for good guidance:
- Guidance and training
- Clarity
- Unify the source of guidance
- That it be complete
- The directive must be enforceable
- The order must be in writing
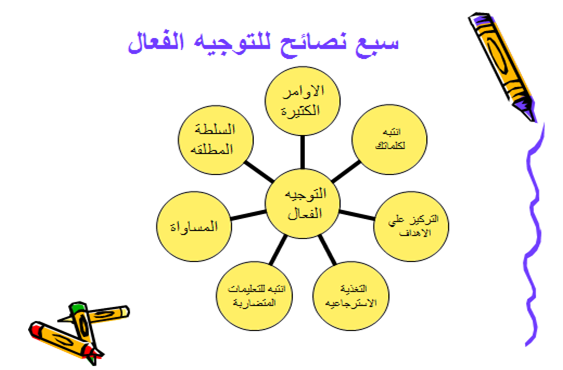
Importance of the guidance function:
- The importance of the directing function comes from the fact that good plans and effective organization alone are not sufficient to ensure that individuals accomplish the tasks assigned to them automatically or inspired by their will.
- Management must direct individuals towards completing work in appropriate ways, and management must bear responsibility for monitoring the results of these work afterwards.
- In the absence of a guidance function, the project is like a car in a stationary state. It needs a leader to start operating it and drive it toward the goal and on the route specified for it, with the stage of control, control, and supervision coming after that, successively.
- Effective supervision
Supervision concept:
- In its simplest sense, supervision means getting work done through others.
- It is also reassured that individuals carry out their duties and responsibilities in the required manner
- It is the effort made by the person in charge of the team to help its members perform their duties fully, push them to achieve all the desired goals, and direct them on how to overcome the problems and obstacles that may encounter them while performing their work, in addition to coordinating the efforts of the employees, transferring experiences among them, and helping them develop .
- Supervision is the process of monitoring work and giving directions, and it is an important part of the effective follow-up process. Therefore, supervision helps improve performance and achieve goals, and supervisors They are responsible for helping other workers to improve the performance of their work and achieve the goals of the organization in which they work. A successful supervisor is one who provides support and assistance without domineering and has skill, understanding and patience.
- ** What is effective supervision?
- It is the implementation of work and achieving goals through subordinates.
- It is dealing with people, accomplishing work, and achieving results through others.
- The ability to motivate employees and achieve consistency and integration in performance to complete work and achieve common goals.
- The practical technical element.
- Administrative element.
***Administrative supervision is the ceiling of the administrative process, which consists of planning, organizing, implementing, and evaluating. The administrative supervisor understands the strategic goals of the organization that it seeks, accurately determines its actual reality, identifies the performance gap between reality and what is hoped for, and seeks to train, qualify, and motivate the workers he supervises and prepare the environment for them to achieve. The strategic objectives are according to a carefully studied plan. He periodically evaluates the extent of his achievement and seeks continuous improvement of the administrative system. Therefore, he has diverse knowledge, high capabilities, and precise specialized skills that contribute to his success in his mission.
Who is an effective supervisor?
The supervisor is the one who applies the principles of management only, while the effective supervisor is the manager or official who applies the principles of management in his daily work and directs the available resources towards success. He does not achieve the required effectiveness except by taking into account interests and good dealing and behavior.
Characteristics of good supervision:
Commitment achieves the following goals:
- The relationship of participation between the superior and the subordinate on goals and methods of work
- Work in a team style and encourage holding periodic meetings and reaching agreement on what is being discussed
- Fair distribution of agreed upon tasks
- Reward and punishment for those who deserve or further training
- Discuss progress and problems that arise
- Not to be biased or discriminate between employees, while avoiding favoring some employees at the expense of others
- Listening and paying attention to different points of view, especially patience when conflicts arise between employees
- Avoid group criticism
- Advice within the limits of capabilities, with clarification and possibility of implementation
- Planning based on needs, priorities and available resources
- Awareness of the responsibilities and personal problems of all employees
- Teaching new skills and exchanging information and experiences among employees
- Provide possibilities
- Managing meetings successfully and effectively
- Create an appropriate environment to encourage employees to perform well
- Evaluating the performance of employees while monitoring their approach to work
- The ability to introduce variables and present them to others, as well as prepare and deal with these variables
Supervisory skills:
Good supervision requires mastering the following skills:
- Professional technical skills: the ability to use experience, methods, and methods to complete work.
- communication skills
- Mental skills
Human relations skill :
- No discrimination in treatment.
- Mutual trust between supervisor and employee.
- Stand firm.
- Appear calm in front of others.
- Establishing a personal relationship with subordinates.
- The relationship with employees shall be on a fair and legal basis.
. Methods of supervision methods.
1 . the traffic :
In this method, nurses' work is observed by:
- Note the capabilities, machines, and tasks
- Note the cleanliness and tidiness of the place
2. personal interview :
This method is used between the head nurse and the nurses in the following cases:
- Personal interview for the new nurse
- Personal interview for nursing staff members
3. Reports
4. Meetings with bosses
5. On-the-job training
6. Stimulus
7. Leadership
Supervision plan for the nursing staff:
The nursing staff supervision plan is divided into two types:
· First: a long-term plan:
o For new nursing staff
o For those who are not new to nursing
· Second: Short-term plan:
o Weekly
o Daily
Principles of supervision :
• Giving the employee information about his work and the entity for which he works.
• Discussing work problems.
• Praise for good work.
• Use constructive criticism to improve poor performance.
• Giving interns an opportunity to demonstrate their competence in assuming responsibility
• Do not condescend to your subordinates.
• self-control.
• no You make promises you cannot keep.
• no Attribute your subordinates' ideas to yourself.
• Admit your mistakes.
• Be loyal to your group members.
• Justice.
• Encouraging employees to develop themselves
• Good manners.
• How to issue orders
• How to make decisions
The manager functions as a supervisor: - Planning -Organizing -Recruiting - Evaluating -Reviewing -Problem solving and decision making
Providing work requirements . Coordination Create a healthy work environment .- Learning and consulting . training and development . Stimulus
Tasks Supervisor duties:
First: General duties :
• Giving general directions and clear instructions necessary to perform the work.
• Monitoring and supervising subordinates.
• Training subordinates on the job.
• Forming a human relationship with subordinates based on mutual trust and common understanding.
• Leading the work team to achieve the facility’s goals.
Second: Work-related duties
• Planning work in the units he supervises and for the individuals working under his supervision.
• Distributing work to subordinates in a fair manner.
• Coordination with other departments.
• Ensure that the work is completed on time according to the plan and according to the specified standards.
• Ensuring the quality and quantity of performance.
• Innovating new ways and methods of performing work.
Third: Duties related to subordinates
• Developing the skills and abilities of subordinates.
• Delegate responsibilities to subordinates.
• Solve problems arising between subordinates.
• Motivating subordinates to develop and improve performance.
• Taking care of subordinates’ affairs, including vacations and promotions.
• Maintaining order while working in accordance with the behavioral controls in force in the facility.
• Evaluating employees' performance.
Fourth: Duties related to superiors and colleagues
• Implementing the facility's general policies.
• Bear responsibility for the work in the department he supervises.
• Collaborate with colleagues in other departments.
• Flexibility in accepting the transfer and replacement of subordinates.
• Responsibilities towards oneself:
- Paying attention to developing personal qualities (self-confidence, patience, firmness).
- Paying attention to developing skills and methods (delegation, team development).
Basic requirements for effective supervision:
• Driving ability. Ability to motivate
- The ability to organize and evaluate work.
• Ability to review and evaluate employee performance .
• Ability to create a healthy work environment .
• Ability to solve problems and make decisions .
• Ability to train subordinates.
• The ability to plan. - Ability to communicate effectively .
- Ability to manage knowledge. - The ability to self-management- Delegation
Definition of delegation
Delegation is the assignment of authority and responsibility to another person to carry out specific activities, while the person who delegates the work remains responsible for the results of the delegated work. Delegation is a means to increase productivity, and it also strengthens the skill of the delegated subordinate in making decisions.
- The word “delegate” means that a person entrusts something to another, appoints him as his representative, or entrusts him with responsibility or authority.
- Accordingly, delegation is the process of enabling another person to carry out a task that is originally one of the tasks of the delegated person
- As it is known, delegation is the transfer of authority to a competent person to perform a specific task in a specific situation, while remaining accountable for the results of the delegation on the delegated person .
The importance of delegation :
• The manager is given more time for effective planning .
• The manager is given more time to complete his other administrative tasks.
• Helps reach effective decisions .
• Encourages subordinates to take initiative and exploit their skills
• Develops the skills of subordinates .
• Subordinates gain confidence in themselves and their skills
Proper delegation
Proper delegation in the nursing profession is characterized by five characteristics:
- appropriate task
- Proper posture
- The right person
- Proper communication and guidance
- Appropriate supervision and evaluation.
Delegation steps
- Define the task you will delegate
- Choose the person to whom authorization will be made
- Define tasks
- Reaching an agreement
- Performance monitoring
- Provide feedback.
Effective delegation strategy:
- Advance planning
- Determine the necessary skills and levels
- Choose the person who is the most role model
- Communicate the goal clearly to the authorized person
- Enable the authorized person
- Setting deadlines and monitoring progress
- Provide guidance
- Performance evaluation
- Completion reward
Successful delegation results:
- Facilitating work
- Improve efficiency
- Increase employee effectiveness
- Developing employees' skills
- Ensuring that the work is done by the right person.
Common mistakes in delegation
- Lack of delegation
- Over-delegation
- Inappropriate delegation
Obstacles to delegation:
- A person's belief that no one else can do the work
- Lack of trust in employees
- Lack of self-confidence and lack of sense of security
- Lack of clarity in job description
- Inadequate training
- Lack of adequate recruitment and selection of workers
- The time spent explaining the task
- Unwillingness to bear the risks involved in relying on others
- Fear of losing power
- Subordinates' resistance to delegation
- The delegate does not know the views of subordinates
- The amount of delegated work is very challenging both physically and mentally
- Subordinates’ belief that they are unable to complete the delegated task
- Natural resistance to authority
- Over-delegation
Tasks that should not be delegated :
• Orienting new nurses . - Calendar
• Imposing penalties .
• Authorization of the president’s signature .
Why don't more people delegate?
• Bosses' lack of confidence in decisions made by others on their behalf.
• Lack of efficiency of managers and their lack of awareness of the advantages of delegation.
• Lack of competence of subordinates such that the boss is unable to rely on them.
• Lack of trust in those working with him. - Fear of employee competition.
• The manager's lack of understanding of his true responsibilities and powers.
· Fear of appearing lazy .
- Nursing records
*Nursing records
* identification Records
Importance Records
Points The task of keeping records
adjectives Featured for registration
Species Records
identification Records:
1- is a tool It is used to arrange and record information and data, and it is one of the important management methods that... It is used in planning and evaluating work, developing plans, and following up on their implementation In education and research.
2- Records It is a tool Administrative: It is used to preserve and arrange information and prevent its repetition. It contributes to achieving goals Administration and the educational process.
3- They are models or administrative tools that are designed by the administration To collect important data to achieve the goal of the unit or facility.
NB :
- considered as Records are the source of cumulative or important information that is used in care Patient, research and also making sound decisions.
- The importance of records:
- It is considered A record of the unit or department’s work and the nurse’s work in terms of type and quantity that can be referred to when necessary.
- It is one of the important management methods that are used In planning and evaluating businesses and developing operational plans, it is also used in research And education.
- A tool for guidance When organizing educational programs and training courses for nurses and staff.
- Do not repeat the tests that have been previously performed.
- A tool for conducting Comparative research in the fields of the health Nursing.
- Helps the patient Follow up on his condition in case the disease recurs.
* Helps in overcoming On the time problem.
- A reliable document in legal problems To protect workers In the hospital and institutions Health.
- A means of identifying the situation in society, common problems and diseases, and methods Her treatment.
- Means of communication between the employee and superiors.
- One of the methods used to evaluate the performance of the unit and workers.
- Helps the doctor And nursing in Research and education Medical, diagnosis.
- tracking Nursing care provided to the patient .
**Important points for record keeping:
- It must be Records are accurate and current.
- It must be Records are clear and concise.
- You must provide Records important facts for evaluation and study.
- He should Save forms at all times.
- He should Keep confidential records and write them confidential in color red or printed.
- You must save Records in a clean, dry place .
Distinctive features of registration:
- Accuracy and clarity And honesty in registration.
- All inclusive.
- The data must be complete, correct and organized Sequentially and objectively.
- Nothing with it Scraping or scratching, and in the case of scratching- It must be
signed next to it, and the crossing out must be in handwriting One italic on the word and the signature next to it and the name is clear.
- Accuracy of timing when reporting certain important information Or accidents or disasters
that cannot be postponed.
• The registration must be reviewed before signing it in terms of accuracy of information and clarity of handwriting.
The registration must be printed on paper Of good quality so it can be kept with it And refer to it when necessary .
Types of records: There are types of Records
* Private records With the patient : It
is composed
From the contents of a file The patient's condition is summarized from the time of admission to the hospital until the time of discharge or death- * Contains the patient file On the following records :
- Evaluation newspaper Nursing care of the patient upon admission.
- Marks sheet Vitality
- newspaper Implementation of treatment.
- Intake fluid balance sheet And the outside.
- Insulin Method Sheet.
- A newspaper for six preparations Processes.
- Notes sheet Nurses.
- Patient turning newspaper.
responsible Head of department.
Toward conservation Records.
Organizing and arranging new patient records, including:: Patients’ personal data, for example upon admission (age - name - diagnosis).
- The form for monitoring vital signs the nurse.
- Private papers With treatment.
- Laboratory and x-ray forms And other records.
- Records must be kept somewhere Amin, far from
futility and loss.
Do not give records to others except in the case of transfer The patient, the study, or the treating physician.
- Not separating Any paper from the patient's file for any reason
- Not allowed To read the records of any patient’s relatives or any other person or persons except with written permission From the hospital
director, the doctor responsible for the patient’s condition, or the head of the department- when Patient Discharge You must ensure that the record is organized, correct, and complete before sending it to the office Responsible for
its preservation
- Giving instructions and training For new nurses on how to take correct complete notes or how to deal with... Papers.
- ought to Patient records and reports contain the patient’s progress from his admission until his discharge from the department The details are sufficient to make it easy to use to follow up on the patient's condition whenever necessary As well as carrying out scientific research.
The nurse's responsibility for records and reports.
- Because the nurse is legally responsible
If any records or reports in its possession are lost, it must be reported following the following.
- Keep it in a safe place and do not Allowing those other than those responsible for caring for and treating the patient to view it.
- Consider all data recorded in Reports and records are confidential.
- Give instructions Training
for new nurses on how to record and take complete and correct notes.
- All information is kept in the patient’s record Patient treatment tickets and papers related to the research or operations performed on him during He stays in the hospital until he is handed over to the discharge office upon his discharge from the hospital
- Upon delivery Neoptia Or receive it with complete tracking accuracy Receiving patient treatment tickets
- Records or reports are yet to be received It is enforceable by officials according to the instructions specified by the hospital
- Be careful not to scratch, scratch or scratch Removing papers from records
The nursing role of records and reports :
- Taking into account the distinctive qualities of good recording and reporting
- Take into account the completeness of the file contents:
- Patient data
- Special forms for nursing registration
- Test and laboratory forms
- Using specialized departments
- Treatment papers etc...
Keeping records in a safe place away from tampering and loss
Maintaining confidentiality and patient rights
Follow regulations and laws in submitting any information
Do not give records to others except in the case of transfer according to regulations and instructions
Explaining proper registration methods for new nurses
Make sure to complete the register before arriving at the exit office
The record contains everything that happened to a patient, developments, and discharge status.
**Types of records found in the office of the Chief Nursing Officer .
• Record shifts at the level of all hospital departments for nurses.
• Attendance Record.
• Appointment records for nursing team members.
• Calendar records.
• Custody inventory records.
• Employee performance evaluation records .
• Time tables.
- Nursing reports
Objectives :
1- Definition of what is meant by reports.
2-Discuss the importance of the report.
3-Identify the different types of report.
4- Mention the specifications of a good report.
*the introduction:
The work of the nursing staff, in its various types, includes writing many reports and recording health and nursing data. The process of measuring performance and planning nursing services depends on the accuracy and efficiency of the reports. Therefore, the importance of nursing reports must be understood so that the information is correct, complete, accurate, and written in a clear manner, so that nursing staff members understand the extent of its importance and providing nursing care. At a high level.
*Definition of reports :
1- Exchanging information from one person to another or from one person to others.
2- Rapid delivery of information to ensure the provision of up-to-date information that is important to all members of the health team, which helps them make appropriate decisions for nursing care.
3- It is one of the means of communication and its purpose is to deliver real and realistic information to the right person at the right time.
4- Reports are verbal, written and also computer-mediated communication that aims to convey information to others.
*Nursing reports are:
A method of communicating specialized or specific information to a person or group of nurses, verbally and in writing, in order to identify significant changes in a patient's condition and communicate these findings to the relevant health team members. Reports are also not only a collection of information about the patient, but they are a document used when necessary.
*The importance of reports:
1- A complete report gives a sense of security resulting from knowing all the factors related to the situation.
2- It is considered one of the methods used or being used to evaluate nursing staff.
3- It is considered one of the means of communication and its purpose is to deliver real and factual information.
4- It is considered a document that can be relied upon in legal problems or a document used when necessary.
Types of reports:
* There are two types of reports:
*External reports:
They are exchanged between the nursing administration and other departments, such as radiology or analysis, or they are reports that are exchanged between two different departments, such as the report that is exchanged between members of the nursing staff and the admission office (statistical report).
*Internal reports:
These are reports exchanged between different members of the nursing administration, or they are reports exchanged within a single department between its members, or between members of a single department that are exchanged between members of the nursing staff, such as (department conditions report - hospital conditions report - accident report).
*Characteristics of a good report:
1- Reports, whether verbal or written, must contain current, accurate and concise information.
2- Legitimate communication channels must be followed when exchanging reports.
3- I must pay attention to accuracy and clarity while writing reports.
4- The data must be complete, correct, sequential and objective.
5- Accuracy of timing must be taken into account when reporting certain important information or incidents that cannot be postponed, as reporting must occur immediately.
6- Reports must be written in ink.
7- There are no shortcuts.
8- There are no scientific terms in it.
9- There is no abrasion.
10- A date must be specified.
11- The contents of reports must be correct and reflective
Indeed, it contains all the data in a concise manner.
12- It must be signed by the person responsible fo writing reports and writing the date of its editing .
Department status report
1- Definition of what is meant by a department status report.
2- Determine the purpose of using the adverbs of the section.
3- Explain the importance of the department’s conditions report.
4- Mention the qualities that must be present in the department’s report.
5- Description of the content of the department's condition report.
6- Use the department status report in different situations.
7- Description of the procedures that must be followed when writing a department condition report.
Department status report
*Introduction: This type of report is :
The oldest report in nursing management, and its longevity is considered due to its importance in moving work goals forward, but despite the introduction of many changes in the way it is written, it is still necessary as a means of communication to transfer and follow up information from one group of people to another group during daily work, 24 hours a day. This type of report provides the department's head nurses with observations about patients and what happened to them during the period prior to their work. Reporting on the department’s conditions keeps the department head informed of what is happening. Hence, the nursing team that will be given will be constructive, continuous, and based on a specific and thoughtful goal, and this report has educational potential at the time of changing or exchanging shifts.
*Definition :It is a verbal and written report that is exchanged by the head nurse of the department or her caretaker at the beginning of the next shift or at the end of one work shift and the beginning of another. This is to inform the nursing staff members of the upcoming shift of changes in patients’ condition, different treatment regimens, and nursing needs.
*The importance of reporting the department’s conditions:
1- A complete report gives a sense of security resulting from knowing all the factors related to the situation.
2- It is considered one of the methods used or being used to evaluate the nursing staff in the department.
3- When the condition report provides complete and consistent data, this leads to better service for the patient.
*The purpose of the department’s conditions report:
1- Transferring information or data based on actual, documented facts.
2- Securing or ensuring continuity of nursing care for patients.
3- Improving the nursing care provided to patients.
4- Preparing workers to carry out their daily work according to the patient’s condition.
*Qualities that must be present in the department’s status report:
¯ It must be written in ink.
¯ It has no shortcuts.
¯ There is no abrasion.
¯ It contains no scientific terms.
¯ It must be accurate.
¯ Must be organized.
¯ It must be written in clear handwriting and in understandable language.
¯ To be comprehensive. To be brief.
¯ The date and time must be specified.
¯ It must be signed by the person responsible for writing the report.
*Content of the department’s condition report:
*The report consists of three parts:
1- The department head must begin with the introduction and include :
⬅️ Total number of patients in the department.
⬅️ Number of admissions.
⬅️ Number of exits.
⬅️ Number of conversion cases.
⬅️ Number of deaths.
⬅️ Number of critical cases.
⬅️ Number of cases of preparation for operations.
⬅️ Number of recent operations cases.
2- Report content: via
Information is collected about the condition of each patient, and a brief report is written in front of each patient, such as [high temperature 39 degrees] and remembers what was done in case of high temperature, such as applying ice water compresses and informing the doctor. The temperature was measured after an hour and it was 38.5 degrees, and the temperature is taken into account. Every two hours.
3- Critical cases and operations report:
A brief report must be written about critically ill patients and operations. It includes:
⬅️ Degree of awareness.
⬅️ Nursing notes.
⬅️ Vital Signs.
⬅️ Patient complaint.
⬅️ Intravenous fluids required.
⬅️ Required tests.
⬅️ Incoming and outgoing fluids.
⬅️ The condition of the wound, if any, and its replacement.
⬅️ The tuber, if any.
⬅️ Rail, if any.
⬅️ Catheter, if present.
⬅️ Bowel movement after operations.
*Remember each patient individually by describing his condition as it is. If there is no change in his condition, write [his condition is stable]. If changes occur in the patient’s condition, you must mention the changes and what was done in a brief form.
Hospital conditions report
· Defining what is meant by a hospital conditions report.
· Determine the purpose of using the hospital conditions report.
· Mention the qualities that must be present in the hospital conditions report.
· Description of the components of the hospital conditions report.
· Description of the procedures that must be followed when writing a hospital conditions report.
· Explaining the instructions for reporting hospital conditions in its form.
Hospital conditions report
*The definition of the hospital conditions report is:
1- A report is exchanged from the unit to the head nurse's office. It is a summary of the cases and treatment plans for a specific group of patients and is written by the department head or her caretaker at the end of the shift.
2- It is the exchange of information between the hospital's head nurse and her caretaker during the evening or evening shifts.
*Usage objectives:
1- Exchanging information about the presentation of critical cases in the hospital.
2- It can be used to demonstrate the performance of nursing care for the patient.
*Characteristics that must be present in a hospital condition report :
⬅️ Hospital conditions must be written in ink.
⬅️ It has no shortcuts.
⬅️ It has no abrasion.
⬅️ It contains no scientific terms.
⬅️ Specific to the section and type of section.
⬅️ Specified by date.
⬅️ Brief.
⬅️ precise.
⬅️ Organizer.
⬅️ It has no spelling errors.
⬅️ Signed by the person responsible for writing it.
*Components or content of the hospital conditions report :
This report is written in the special form by going to the different departments in the hospital at the end of the shift and asking about the number of patients in the department.
⬅️ Section type.
⬅️ Number of patients in each department.
⬅️ Total number of patients in the whole hospital at the time of delivery 2am, 8pm, 8am.
*Type of patients included in the report:
⬅️ All patients before operations.
⬅️ All patients after operations.
⬅️ All admissions.
⬅️ All cases exit.
⬅️ All cases of death.
⬅️ All transfer cases.
⬅️ All critically ill patients.
⬅️ All patients with changes in vital parameters.
⬅️ All patients who require careful medical intervention.
⬅️ All emergency cases (diabetic coma - bleeding - convulsions).
⬅️ Depression cases.
⬅️ Burn cases over 75% .
⬅️ Cases at risk of suicide attempts.
⬅️ The report does not include those with stable conditions.
* The patient's name and a simple summary of his condition are written in front of the shift in which the conditions are collected, and this report is exchanged from the head nurse of the hospital, who is responsible for supervising the hospital in the evening shift, and also from the one responsible for supervising the evening shift, who is responsible for supervising the hospital in the night shift. It is then exchanged between the person in charge on the evening shift and the head nurse at the hospital in the morning.
Incident report
1-Definition of what is meant by an accident report.
2- Determine the purpose of using the incident report.
3- Enumerate the types of accidents that can occur.
4- Mention the characteristics that must be present in the accident report.
5- Describe the procedures that must be followed during the incident.
6- Explanation of the instructions for the accident report form.
Incident report
*the introduction:
It is the responsibility of the nursing staff to maintain the safety and well-being of patients and to implement and follow up on treatment and nursing plans. As well as avoiding accidents and errors that may occur in the hospital. In order to determine the duties of nursing staff in the event of accidents, they must be taught how to report the accident during or immediately after it occurs, as well as how to carry out their duties regarding it or towards it.
To ensure a safe environment within the hospital, the nursing staff must be careful to perform their duties in a way that reduces and prevents errors and the occurrence of accidents. This is to protect patients and protect themselves and those working with them. The nursing staff must follow the proper methods for reporting incidents and dangers as soon as they occur, by writing an accident report. Writing such a report ensures the security, safety and comfort of patients, the nursing staff and those working with them, and protection from their exposure to legal accountability .
*The definition of an accident report is:
An accurate and comprehensive report on unexpected incidents that could affect the patient, his family members, or members of the nursing staff.
In addition, the incident report is considered an internal system for the health organization. It is necessary for internal use in the Quality Assurance Program and is made confidential to the Committee through Quality Assurance Committee meetings.
*Purpose of use:
1- An inventory of incidents that occur in the nursing unit.
2- To ensure a safe and secure atmosphere for patients, their families, and individuals working in the hospital.
3- To determine how to prevent dangerous incidents that could affect any individual within the hospital.
4- To investigate errors that occur within the nursing unit and find out their causes so that they do not occur.
5- It is used to document any abnormal event in the hospital system and patient care.
6- This report is used as a reference until any special or specific incident occurs regarding the quality of nursing care given in the unit, in which the nursing staff members are accused of negligence and are subject to legal accountability.
* Types of accidents that can occur:
- The patient falls from the chair, in the bathroom, or from the bed.
- Treatment error.
- Error in using machines.
- Error in nursing procedures.
- Error related to patient behavior.
- An error related to the behavior of (visitors).
- Error related to theft.
- Diagnostic error.
- Error related to missing items.
- An error related to the transfusion of blood or solutions.
- A fire occurs.
- An injury occurs.
*Qualities that must be present in an accident report :
1- An accident report must be written in ink.
2- It has no shortcuts.
3- It contains no scientific terms.
4- It has no abrasion.
5- Specifies the date of the incident.
6- Specifies the time the incident occurred.
7- Specified by the type of incident.
8- Specifies the location of the incident.
9- To be precise.
10- Brief.
11- Write a description or comment from the department head.
12- Signed by the person who witnessed the incident.
Incident report form
the hospital :
the date :
the time :
Section :
· Please tick ( √ ) in front of the type of incident
1- Patient falls ( )
2- Treatment error ( )
3- Error related to the use of machines ( )
4- Error related to nursing procedures ( )
5- Error related to patient behavior ( )
6- An error related to visitor behavior
7- Error related to theft
8- Error related to missing items ( )
9- Another mention
Summary or description of the incident:
The doctor has been informed Yes ( ) No ( )
The patient was examined Yes ( ) No ( )
The direct manager has been informed Yes ( ) No ( )
Damage resulting from the accident:
1- There are no damages ( ) 2- There are serious damages ( )
2- There are damages related to the accident ( ) 4- Death occurred ( )
Signature of the department head
Signature of the person in front of whom the incident occurred
Reports related to nursing services management.
· Shift receipt and delivery report
· Daily Report
· Patient statistics report
· Reports on work problems and progress in following the proposed solutions
· Reports on accidents, emergency situations, and reports of treatment errors
· Reports of patient complaints
· Administrative reports
These reports must be taken seriously by superiors and their results must be followed up until the required changes are made to raise the level of services in health service delivery units. If they are not taken seriously, these reports are considered a waste of time and energy and become unproductive.
- Effective leadership
**Meeting concept:
It is the meeting of a number of individuals, in one place or in several places, and at a specific time, to discuss a specific topic or topics, in order to achieve a specific goal or goals.
**Definition of meeting management :
• It is an exchange of information and ideas between two or more people who have active roles in order to achieve specific results.
**The importance of meetings:
1. Provides important information to those in charge of business.
2. Give these people the opportunity to express their opinions.
3. Through it, ideas can be explored and evaluated and experiences learned.
4. Consensus agreement is reached .
5. Decisions made through meetings are more legitimate than individual ones.
6. The meeting creates an atmosphere of commitment so that each individual takes upon himself the task of implementing what was agreed upon.
7 . Effective meetings reduce paperwork and cut through red tape.

**The seven obstacles to meetings:
- Lack of necessary funding.
- Lack of financial capabilities.
- Lack of necessary information.
- Absence of people with expertise in the subject of the meeting.
- Not having enough time to hold the meeting.
- The official’s unwillingness to hold the meeting.
- Members not wanting to attend the meeting.
**Stages of the meeting:
**The first stage: pre-meeting
- Decide if a meeting is necessary.
* Is it possible to achieve goals more effectively than...
Through a means other than the means of meetings.
- Determine the objectives of the meeting:
- What you intend to achieve from the meeting.
- Decisions that must be made.
- Executive steps that must be taken.
- 3--Prepare the agenda:
- Include topics that are directly related to the objectives of the meeting.
- Try to reduce the number of important topics that you cover
It is included in each meeting so that it can be addressed comprehensively
And sufficient depth.
• Arrange agenda items according to their importance so that the most important topics come first.
• Group related agenda items into one topic.
• Determine the time allowed to discuss each agenda item.
- Collect all available information and data related to the agenda items and identify the important points .
- Distribute in advance the agenda and documents related to the topics that will be presented for discussion.
2- During the meeting:
- Start the session at the specified time.
- The meeting opened with praise and praise to God and blessings and peace be upon His Messenger.
- Welcome attendees, especially new ones, and make them feel wanted and welcome.
- Reward those who showed up on time, even with a nice word.
- Review the agenda and have it approved by the members.
- Follow up on the decisions of the previous minutes.
- Explain the objectives of the meeting.
- Explain the powers available to the president and members.
- Agree with the members on the method of managing the meeting, and on the procedures that will be followed (such as: how much time is allocated for each item, will voting take place or will directives be sufficient, how many people will be for each item, how will we close the discussion,... )
- Prevent interruptions (phone, visits, etc.).
- Remind yourself of the importance of time and its proper investment.
- Summarize the important points you heard, if the discussion took on the aspect of complexity and differing points of view, in order to review your understanding and the understanding of others of what was said.
- Commit to the time specified for each item on the meeting agenda.
-When you finish discussing each meeting item, summarize the decisions or results reached.
-Summarize what was reached at the end of the meeting, and if there are specific implementation steps that must be taken, specify who will take them, and the sufficient time to complete them.
- Determine the date and purpose of the next meeting.
**After the meeting:
- Prepare the minutes of the meeting and distribute them to those who attended and those who did not attend. The minutes must be an accurate record of what took place at the meeting, and must include the decisions and recommendations issued by the meeting, specifying work assignments, the names of the people entrusted with these assignments, and the deadlines for their completion. Also record the date and time set for the next meeting.
- Follow up and monitor the work that has been accomplished
**End of the meeting and recommendations:
• Make sure the minutes are accurate.
• Ensure the quality of decisions (implementation body, appointments, follow-up body, cost, etc.).
• Remind the goals.
• Summarize the results achieved by the meeting.
• Thank you for the interaction, participation, and good listening.
• Determine the date, place, and purpose of the next meeting.
• Determine when they will receive the report and its annexes.
• Make sure everyone knows what they are assigned to do.
• Clean the meeting table and do not leave papers behind.
• Evaluate the meeting.
• Follow the implementation of decisions.
• Repair the relationships the meeting spoiled.
**Meeting documentation stage:
• The meeting is documented in the secretariat’s book (minutes of meetings). This task is undertaken by the secretary or designated secretary. The minutes must contain the following:
o Meeting serial number
o
Meeting place and meeting date (day, date and hour)
o
Names of attendees
oNames of absence and
reason for absence (excused or unexcused)
oThe most important discussions on the topics raised
oDecisions issued by and for/against/abstaining
o
Tasks for each member (assignments) specifying the member and the duration
o
o. Date and place of the next meeting and topics to be discussed
Signature of the session chair, secretary, and possible attendees as well.
- Team building
**What is the team :
- It is a group of people who share the responsibility of working to achieve a known and unified goal.
- Small number of people , integrated skills
- There are performance goals
- Participation in accounting
- If a team member fails to perform his assigned duty, he is considered an obstacle to achieving the goal.
**What is the team :
• A small number of people
• Integrated skills
• Loyalty to a known goal
• There are performance goals
• There are directions for action
• Participation in accounting .
**Definition of the team:
A team is a group of individuals who participate in performing a unified work, and each of them bears certain responsibilities and partial tasks in this work, and the team members have empathy and belonging that help them easily perform and be satisfied with this work.
**Definition of the work team:
- It is a number of individuals cooperating to carry out a common task, but what is most important in their work is the success of the goal that the members set together and unanimously. They also support each other, cooperate freely, and communicate openly and clearly.
**Work team members :
Leader - Goal - Members
** Why the work team?
- Taking advantage of the multiple talents of individuals.
· Increase communication between members.
· Develop a sense of unity and friendship.
· Creating an atmosphere of cooperation to increase production.
· Reaching collective solutions.
· Reducing burdens and distributing roles.
· Exchange information and experiences.
- Effectiveness in solving problems due to the availability of experience.
- Achieving a balance between individual productivity and members’ needs.
- Providing the latest and most accurate information.
- Providing everyone with the opportunity to participate in decision-making and bear responsibility for its implementation.
**The importance of work teams:
- Coordination between different work teams.
* Cognitive increase.
* Developing individuals’ performance.
* Exchange of experiences.
* Saving time and effort.
* Producing new leaders.
**Definition of team building :
o It is a planned process aimed at forming an integrated group capable of performing specific tasks and achieving specific goals through cooperative activities .
**Goals for building work teams:
The goals of building work teams are as follows:
• Building a spirit of trust and cooperation among individuals.
• Developing individuals’ skills and increasing their awareness.
• Developing managers’ skills in improving relationships within the organization between superiors and subordinates.
• Developing conflict resolution skills and disputes between individuals and groups
• Providing open communication between parts of the organization, leading to greater transparency and clarity in confronting issues and problems.
• Giving more time for managers to focus on planning and setting goals.
• Optimal use of available resources and capabilities to achieve efficient performance
**Why we build a team:
• Unifying and pooling integrated skills and experiences
• Create communication channels that help solve real problems and also use creativity in the process.
• The need for development and innovation
• The presence of special goals that require collective thinking and creativity.
• There are problems that require different skills and experiences to solve .
**Conditions for forming a work team :
1 - Team building must stem from the employees’ satisfaction, conviction, and desire, and not from a decision imposed by management.
2. There must be a strong reason for forming the team.
3. The relationship between team members must be mutually dependent.
4. That the members have equal importance within the team.
5. That members understand their roles and the roles of others.
6. The leader and individuals must have a strong desire to make the team’s tasks successful.
7. Availability of a reasonable level of trust, connection, respect, desire for cooperation, ability to tolerate others, and acceptance of different points of view.
**Specifications for building an effective team:
- Fellowship
- Respect
- Good climate
- cooperation
- Consistency
- Interconnectedness
- The initiative
- Clear goals
- Roles are defined
- Mistakes are identified without pinning them on others
- The ability to be creative .
**Team building problems:
• Lack of leadership and driving skills
• Bad planning
• Bad training
• Bad behavior
• Having conflicts
• There are no motivation and encouragement programmes.
**Communication problems :
• There is no understanding between team members
• They don't listen to each other
• They waste time in useless meetings
• The dates are incompatible and conflicting
• There is others and competition between members
• There are personal conflicts .
**Team types .
There are 3 types of team: .
**work team .
- It consists of achieving a specific goal, through a clear plan, and specific and well-known roles for the members.
- The team's success depends on the members' commitment and desire to work, the extent of their response to work requirements, and the extent to which each member is aware of the roles expected of him.
**Problem solving team .
It is formed to solve a specific problem. Each member puts his experience into solving it, and his efforts are integrated with the efforts of others.
- The success of this type of team depends on the members’ conviction about the problem and their desire to solve it, mutual trust, and the team’s belief in the possibility of solving the problem by pooling and coordinating their efforts.
**Development team “Innovation”
- It is formed to discover new horizons and opportunities, and its mission is improvement, renewal and development.
- Its success depends on the members’ innovative capabilities and unconventional thinking, the desire to develop and aspire for the best, the belief that there is always something better, and the presence of competitiveness and enthusiasm among the members.
**Types of individuals in the group:
1. The quarrel-loving type:
Be calm, don't let them get you into trouble.
2 . Positive type:
They are very helpful in discussions.
Accept their contributions and ideas and use these contributions often.
3. The type who knows everything:
Let group members address that person's theories.
4. The talkative type:
Intervene and interrupt them politely. Set a time for them when they start talking.
5. The shy type:
Ask them questions, try to increase their self-confidence and give them encouragement as much as possible.
6. The rejecting type:
• Recognize their ambitions, appreciate and use their knowledge and experiences.
7. The indifferent type:
• Ask them about their work, and let them give you examples of their experiences or things they find interesting
8. The transcendent type:
• Don't criticize them, say yes to them as a way to get rid of them .
9. The one who asks and insists on getting answers to his questions:
• This type tries to catch the session leader's mistakes. Try to return their questions to the group to think about and answer.
**team leader:
He is responsible for achieving coordination, integration, and interaction among team members.
- There is a great deal of trust, respect and cooperation between him and the members.
- He is convinced of the team’s goals, is sincere in achieving them, and is serious about leading members to reach them.
- He must have a mature personality and appropriate practical experience.
- The leader acts as an advisor to the team, facilitating the members' tasks, guiding and teaching the members, and providing advice and advice.
**Team Leader Responsibilities :
• Transfers information and skills to other team members
• Interpret policies and work orders.
• How to manage work effectively and evaluate results.
• Encouraging members to perform work in innovative ways.
• Behaviorally, be a role model.
• Transferring the team’s achievements to management.
• Plays the role of mediator when conflicts arise.
**Driving skills :
Skilled team leader:
1. Suggests tasks.
2. Suggests actions.
3. Supports employees.
4. Manages conflicts.
5. Avoids defense and attack.
6. Makes sure the team understands.
7. Summarizes progress.
8. Looking for information.
9. Gives information.
10- He avoids interrupting.
11-Encourages the participation of others.
12-He uses silence.
13- He is good at listening.
**An effective leader is:
1 - The person who has the ability to gather individuals around him to make a collective decision
2- The person who can bring the team the strength of unity by:
- Gathering them based on unity of purpose.
- Grouping them into a work unit.
- Convince them that responsibility is shared
3-The person who makes good use of the resources (material and human) that he has
4- The leader is not just a coordinator among the team members, but he works to achieve the goal by directing the efforts of others who cooperate and cooperate.
** Specifications of an effective team:
*Overall effective team specifications:
• trust
• cooperation _
• Outstanding performance
• A sense of responsibility.
• A common interest in work
** Reasons for the failure of work teams:
• The team structure is not compatible with the organization structure.
• - Senior management abandoning support for the team.
• - Focusing on work and neglecting relationships between members.
• - Members’ lack of discipline and their evasion of responsibility for what they do.
• - Increasing the size of the team and disorganizing the relationships between members.
• - Lack of understanding of the stages of team development.
• - Weak internal or external leadership.
• - The organization’s failure to exploit the team’s efforts.
• - Members do not receive sufficient training.
**Obstacles to activating and forming the team:
. Lack of belief in evolution.
- The job burden for administrators and teaching staff
. Lack of belonging.
- Lack of experience.
- Refrain from not following up on the work of the teams.
- Not following up on the work of the teams.
- Emergency matters.
**Barriers that hinder team performance:
• Disruption of team member cohesion
• Conflict
• Lack of time
• Lack of coordination and follow-up
• Absence of an element of information sharing
• Defensiveness and making excuses
• Traditional thinking
• Intertwining and mixing of communication channels .
• Task load
• Lack of a clear and accurate understanding of the member’s role
• Misunderstanding of basic issues
• Lack of clear definition of each person's role
• Laziness and lethargy .
**Problems in team meetings :
- Starting meetings later than scheduled.
· Not setting goals for the meeting before the session.
· Absence of an agenda.
· Some members attempt to dominate the meeting and monopolize the conversation and monopolize the conversation and discussion.
- Limit the meeting to exchanging information and solving problems.
· Members constantly interrupting each other.
· Lack of results, lack of follow-up, and dispersion of members’ responsibilities.
- Stimulus
Motivation concept:
“Motivation is the basic drive that drives individuals to achieve and satisfy their desires. Motivation is also defined as “an internal feeling to start a certain behavior, stop it, or change its course.”
Work Motives
These are the driving factors that come from within a person and arouse in him the desire to work and achieve.
It is, therefore, a state or internal force inherent in the individual that activates and moves his behavior towards certain goals.
Need
It is an internal state that makes certain results seem attractive to the individual, meaning that a need is a desire to satisfy a certain deficiency or want of the individual
incentive
An environmental influence whose purpose is to arouse motivations and achieve a response to them, and thus it stems from the work environment.
Motivation
It is an administrative practice for the manager to influence employees by stimulating motivations, desires and needs for the purpose of satisfying them and making them more prepared to give their best in order to achieve high levels of performance and achievement in the organization.
The importance of motivation:
- So that workers love their work, and feel satisfied with what they do.
- To achieve the goals of the educational process to which your school contributes.
- Let effective, loving and active people help you in your management.
Important factors in motivating the worker:
Officials should pay particular attention to three factors:
Cooperation with the institution: Workers feel more motivated to work when they realize the importance of cooperation with the institution they deal with.
Contentment: When employees realize that the work they are doing constitutes a qualitative addition to the organization’s work, they are motivated to continue with the same seriousness and diligence.
Choice: Workers feel motivated to work more and harder when you give them the authority to make decisions during work. However, try to find other appropriate ways of encouragement: such as giving them bonuses and
so on. But in all cases, you must focus on the factors that affect employees’ enthusiasm at work. Especially the factors hidden within each of them.
Objectives of the incentive policy:
The goal of developing a good incentive system leads to achieving beneficial results, the most important of which are:
1) Increasing work outcomes in the form of quantities, production quality, sales and profits.
2) Reducing the surplus of workers, for example, reducing costs and the quality of raw materials, as well as reducing the loss of human resources.
3) Satisfying the needs of workers of all kinds, especially the highest levels of appreciation and respect.
4) Allowing workers to increase their income while increasing their effort according to the established equations, which leads to encouraging skills to exert more effort.
5) The employees feel the spirit of justice within the organization, developing the spirit of cooperation among employees, and raising the spirit of loyalty and belonging.
6) Contributing to devising the best methods for workers’ performance with the least amount of effort and at the same time achieving the best results.
7) Improving the organization’s image before society.
Benefits of stimulation:
A good incentive system achieves many benefits, including:
1. An increase in labor productivity, sales and profits.
2. Reducing labor waste in material and human aspects.
3. Increasing employees’ incomes and making them feel a sense of justice within the organization.
4. Attracting hard workers to the organization and developing their spirit of loyalty, belonging and stability.
5. Avoid many employee problems such as absences, negative employee turnover, and employee decline.
6. Morale and conflicts
Motivation obstacles:
1) Fear or dread of the institution.
2) Lack of clarity of goals among the organization’s management.
3) Lack of follow-up with workers, so one does not know who is doing good from who is doing wrong.
4) Lack of training on the job and lack of guidance to correct mistakes.
5) There are no channels of communication between managers and workers, so everyone is at a loss.
6) Administrative errors such as multiple and conflicting decisions.
7) Multiple leaders and conflicting orders.
8) Frequent change in leadership, especially if each of them has a style of work that is different from the previous one.
Useful ways to gain employee cooperation:
• Work to build a sense of respect and appreciation for employees by flattering them and praising them for the good work they have accomplished.
• Try to be patient, and make workers feel that you care about them.
• Make room for workers to participate in taking responsibility for improving work, and train them in this.
• Try to make both quiet and noisy workers, or extroverts, feel satisfied.
• Involve your workers in your perceptions, and ask them for more ideas.
• Teach others how to do things themselves, and encourage them to do so.
• Link bonuses to good work performance, not to job standards and seniority at work.
• Allow and even encourage side initiatives.
• Encourage employees to solve their problems on their own.
• Evaluate the employees’ achievements, and explain the values that these achievements added to the organization.
• Remind them of the sacrifices others have made for this work.
• Remove the fear from their hearts and chests about the effects of that work on them if it has negative effects.
• Give them immunity from rumors and slander.
• Always and never repeat to them the necessity of pairing work with sincerity. Always repeat to them.
• Try to make the work groups proportionate in distribution and tasks.
• Try to interact and communicate with employees.
• Try to provide employees with what stimulates their desires for many things.
- Conflict management
introduction
Conflict is not a modern matter. It has been and continues to be of interest to those interested in management sciences, and the interest of administrators in the skills of managing various conflicts between employees has increased, as organizations suffer from many types of conflicts that occupy attention and time, in addition to their negative impact on the organization’s ability.
What is the conflict???
Conflict is a disagreement or incompatibility between two or more people whose interests, goals, or interests appear to be incompatible
What is conflict:
— It is the process that begins when a specific individual or (group) feels a kind of frustration as a result of one of the other individuals or groups violating the rights of the first.
What is the conflict???
Conflict occurs when there is a conflict of interests that turns into a conflict over goals, and at the same time there is a difference in values that turns into a conflict between the different methods used by each individual.
Negative aspects of the conflict :
- Some employees feel defeated and dissatisfied
- Distances between employees and the organization
- The prevalence of a spirit of suspicion and mistrust among employees
- Individuals focus on individual achievements more than group achievements
- Decreased team spirit and deterioration of organization performance
- High labor turnover rate.
Positive aspects of the conflict :
- Developing ideas
- The tendency towards searching for new ideas
- Giving opportunities to express opinions
- Search and solve permanent problems
- Drive the creativity and development process

Perceived or (perceived) conflict
— This stage begins when the parties to the conflict realize that there is an expected conflict that will occur, and the conflict begins with the party that feels a contradiction in its interests or goals.
Felt conflict :
- It is the stage in which the parties to the conflict feel the phenomena and indicators indicating the start of the actual conflict between the different parties
Realistic conflict
- This is the stage of using behavior to show the actions and reactions resulting from the existence of a conflict, examples of which include attack or withdrawal .
Types of conflict :
Internal conflict (psychological conflict within the individual)
√ Intra-group conflict (conflict between members of the same group)
√ Organizational conflict (conflict within the organization)
Factors affecting conflict:
Characteristics of the parties to the conflict
Causes of conflict
The interests of individuals and groups
The social environment
Causes of conflict
* Time * Experience * Administrative leadership
* Lack of resources * Excessive sensitivity
* Conflict of goals and interests * Lack of clarity of roles
Conflict with oneself
The difference between an individual's own values and the values surrounding him
Factors that increase conflict with oneself
√ Failure to coordinate between the individual’s personal abilities and capabilities and his ambitions
√ Failure to prioritize
√ Self-hypocrisy
Causes of conflict within the group
* Fear * Insecurity * Lack of information about the group
* Group values * Group requirements
Factors that increase conflict within the group
* Attack * Obstruction and placing obstacles * Love of appearing and attracting attention
* Love of control * Searching for personal interests
Factors that reduce conflict between the individual and the group
* Encouragement * Reconciliation * Setting standards
* Monitoring * Opening communication channels
Organizational conflict
When conflicts appear in the organization, management must intervene so that the conflict does not go beyond the acceptable limit
Ways to confront conflict
* Competition * Compatibility * Avoidance
* Cooperation and participation * Reconciliation and negotiation
Competition
Uncooperative behavior that is embodied in individuals seeking their interests at the expense of others. This behavior is often used by individuals who are oriented towards power and strength.
When is it used????
- This method is used in situations characterized by a high degree of force variation.
- Or in the case of unwillingness to respond to the demands of others
- Situations that require a quick decision (emergency situations)
Compatibility
Compatibility is the opposite of competition, and consists of non-cooperative behaviors. The individual tries to be compatible with the circumstances surrounding him or others, and neglects his interests and interests.
When is it used????
- When an individual feels that he made a mistake
- When other issues are more important than personal issues
- To strengthen social relationships with others
- To reduce the amount of losses in the event that you are unsuccessful in the conflict
Cooperation and participation
Behavior that is the opposite of avoidance, as it involves cooperation and seeking to work with others to find a solution that satisfies both conflicting parties
When to use???
- When an individual wants a solution, all parties respond
- When you want all individuals to commit to implementation
- When you want to know the points of view of others
Reconciliation and negotiation
Agreement means striving and making some concessions to reach a point of meeting and understanding with the other party
When to use????
- In the case of equal strength
- To achieve a temporary settlement of the matter
- In the case of reaching a quick solution under time pressure
Avoidance
Uncooperative behavior. The person who uses this method of dealing with conflict does not look out for his own interests or the interests of others, but avoids conflict in any form.
avoidance (avoidance)
- The individual withdraws from the conflict because he does not want to help himself or because his belief in his goals is not strong. One of the most important situations in which the individual uses this method is:
- If the conflict is trivial
- In the event of an inability to satisfy personal desires
- Ensure that the problems resulting from the solution are greater than the return of the solution itself
- If others are more capable of solving the problem.
Types of conflicts within work environments
1. Conflict according to its level: (conflict within the individual, between two individuals, within the group, between groups, at the organization level, between organizations )
2. Conflict according to its directions: vertical conflict and horizontal conflict .
3. Conflict according to its results: positive conflict and negative conflict .
4. Conflict in terms of organization :( Organized conflict: This shows the expression of actions that require action and social solidarity, unorganized conflict : This is how behavioral forms such as complaints, complaining, and leaving work are used )
5. Conflict in terms of planning: strategic conflict and unplanned conflict .
- Stages of the conflict process:
- Latent conflict stage: Here, no awareness, understanding, or feeling results from the emergence of conflict, but some situations appear that affect the relationship of some parties, such as competition for limited resources or the need for independence and multiplicity of goals.
- The stage of realizing the conflict: Here the conflict is realized without there being any previous situations, such as one party misunderstanding or misunderstanding the other party .
- The stage of feeling the conflict: Here there may be an awareness of the conflict, but without the manager feeling that there are situations of anxiety and tension .
- The conflict manifestation stage: Here it can be noted that the behavior issued by each party indicates the emergence of a conflicting problem .
- Post-conflict stage: If there are solutions that satisfy both parties, it is expected that there will be cooperation and affection between the parties, but if there are no solutions, feelings will remain dormant and increase and will explode at any moment. .
Conflict management in work environments:
One of the reasons that called for organizations to manage conflict is the increasing interest in globalization and the decreased reliance on local authorities or governments to do some work. Harrigel presented a method for resolving and managing conflict that relies on two elements: :
1. Distribution: That is, one of the parties to the conflict is aware that the amount of what one of them will gain will be at the expense of the other party’s loss .
2. Integration : The result of the parties’ calculation is that each will achieve a gain, and this element leads to greater satisfaction .
- In the event of a conflict, the administration resorts to using one of the following methods :
1. WithdrawalIt is the manager abandoning some work duties for a short period, such as postponing the answer to a memo or absenting himself from a meeting. It is used in the event that the problem is minor and does not require a lot of time, or the manager does not have a great personality or presence, or there is someone who can develop solutions. In the absence of the director .
2. Calm downIt is the intervention of the administration, led by the director, by following a behavioral strategy, which is that the conflict will gradually disappear while calling for the necessity of cooperation between the parties. .
3. Compromise solutions: that is, the manager's choice of an alternative that satisfies both parties and does not result in loss for either party .
4. Coercion: This is the administration's resort to using legal force to resolve the dispute, and it is preferable to use it in emergency situations .
5. Confrontation: Acknowledging the existence of a conflict, then the administration resorting to using the scientific method, evaluation, and studying alternatives to reach acceptable solutions .
The role of the head nurse in conflicts:
Disagreements often occur when people work in groups or work teams, and the supervisor must prevent this from happening or work to resolve them as head of the team. An efficient supervisor is one who listens to problems and tries as much as possible to help solve them. Therefore, the head nurse has an important and fundamental role in preventing conflicts and also in resolving them in a way that is acceptable to the parties to the conflict and in a way that benefits the workplace .
Preventing conflicts:
The most important causes of disagreements between team members are lack of clarity of vision and chaos in the work, that is, when opinions differ about what work should be performed and how team members should perform it. Conflicts can be prevented and their impact reduced by:
- Regular meetings of team members
- Giving people the freedom to express their ideas openly and then make a collective statement about them
- Participation in achieving goals after agreeing on them
- Develop a clear and detailed job description
- Establish clear instructions and procedures for work
- Justice in the distribution of tasks and duties
- Preparing schedules according to which tasks and duties are distributed
- Equipment management
Types of equipment
Equipment is divided into two types: the consumable type and the non-consumable type, and equipment management includes both types.
- Expendable equipment: It is the equipment that is used in a short time, such as medical cotton, single-use syringes, etc
- Non-expendable equipment: It is the equipment that lasts for several years and needs care and maintenance. This equipment is divided into two types, fixed and non-fixed:
o Fixed non-expendable equipment: This is the equipment installed in the wall or floor of the hospital, such as sinks, sterilization devices, etc.
o Non-expendable equipment that is mobile or fixed: includes tools that have been used for more than five years, such as wheelchairs, trolleys, etc.
. Equipment management procedures:
There are four main procedures in equipment management:
- the demand
- Storage
- Exchange
- Monitoring and maintenance
– 1. Equipment Request:
Requesting equipment includes the following skills:
- Prepare a list of needs and resources based on knowledge of previous use and an estimate of the current rate of use
- Balancing needs, available resources, and estimating costs
- Fill out the application form.
-2. Equipment storage:
- Equipment can be stored in one of two places:
o A main or reserve store where quantities are kept and not used
o Where the equipment is used after it is released from the warehouse
o Storing equipment requires the following skills:
o Recording the receipt of new items and recording what is disbursed
o Keeping daily records or cards for inventory
– 3. Equipment disbursement:
o The nurse is responsible for some equipment. For example, the nurse in the maternity ward is responsible for scales, syringes, serums, birth equipment, and other devices.
o After requesting and receiving the equipment and then recording it in the inventory book or register, it can be disbursed whenever needed
o There are three written procedures that are followed when disbursing equipment and are recorded in the records designated for this purpose:
o Disbursement record: that is, writing the disbursement in the inventory book
o Issuing an exchange permit for signature
o A record of the assets of the department that receives and uses the equipment
– 4. Equipment monitoring and maintenance:
o Expendable equipment needs to be monitored to avoid wastage, while non-expendable equipment needs maintenance to maintain it in a usable condition.
o Monitoring and maintaining equipment requires the following skills:
o Convince workers of the need to clean equipment and keep it in good condition
o Use an inspection checklist
o Discover any differences in the equipment and find out its cause.
. The importance of equipment records and their benefits:
o Referring to records of previous orders facilitates the preparation of subsequent orders, whether after a month or a year, as the supplier’s address, item number, and quantities required can be identified under normal circumstances.
o Knowing the quantity in the inventory register is a good indicator of when it is time to order more supplies, avoiding long periods without essential equipment.
o Exchange permits specify the party responsible for caring for, breaking or damaging equipment, and they also encourage workers to bear responsibility.
o Inventory lists help quickly inspect equipment and discover discrepancies, waste, extravagance and theft.