Chapter Three
| Site: | EHC | Egyptian Health Council |
| Course: | Developing the administrative skills of nursing leaders |
| Book: | Chapter Three |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Monday, 23 December 2024, 12:47 PM |
- Planning
Definition of planning
*Planning is setting the necessary plans to achieve goals, and it is the primary function on which the rest of the other management functions depend.
*Planning is an intellectual process that relies on logic and arrangement, in which an effort is made to clarify the goals that management wants and to search for the best means to achieve them, as well as an attempt to predict or predict the obstacles that may be encountered and how to overcome them.
Therefore, planning is essential for time management and thus facilitates the application process. The planning function also requires arriving in a systematic manner at answers to the following questions:
· What ? where ? when ? how much ? how ?
Since the planning function represents a complex and complex function, it is advisable for all team members to participate in it by answering these questions:
The importance of planning
The importance of planning is represented in the following points:
· Focuses efforts on achieving the desired goals
· Allows optimal use of human and material capabilities
· It helps workers cooperate, coordinate their efforts, and achieve productive efficiency
· It is considered the basis of oversight to monitor implementation and evaluate performance and the extent of achieving goals
· It helps to discover problems before they occur and provides the opportunity to correct the course if necessary for the mother.
Steps to make the plan
Making the plan includes the following steps:
· Setting the goal and collecting data on:
o current situation
o Available possibilities
o Statistics and reports
· Create a set of plans and alternatives to achieve the goal, specifying the cost and implementation period
· Study the steps, compare them, and choose the best one
· Setting priorities and putting the plan into effect.
Prepare a work plan, which is summarized in the following table
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Characteristics of a sound plan
A sound plan has the following characteristics:
· Exploiting the capabilities available in implementation, which will lead to cost reduction
· Choose a plan that achieves more than one goal
· Flexibility to allow the necessary adjustments to be made in the event of difficulties or unexpected changes during implementation
· It must be written and known to those implementing it
· It must be integrated and consistent in its components, and there should be no conflict in its parts
· Involvement of those who will implement it in the planning process, which helps to implement it efficiently
· It must be based on realistic data and statistics
Planning obstacles
The most important obstacles facing developing a sound plan are the following:
· One person (senior management) makes plans
· Freezing the planning process into formal templates that make them lose flexibility and simplicity
· Lack of interest in reviewing plans periodically to determine the level of the leader/according to the goals, making sudden decisions outside the scope of the plan
· Management undertakes daily executive matters and allocates less time to strategic planning
· Lack of interest in defining the organization’s objectives
· Lack of participation of executive managers in the planning process
· Not relying on plans as criteria for measuring and evaluating managers’ performance.
Characteristics of successful planners :
· Curiosity
· creativity
· Competitiveness
· Self confidence
· perseverance
· wisdom
· Process (practical person)
Why don't we plan :
· Lack of consistency and lack of patience
· Lack of conviction in the feasibility of planning
· Ignorance of planning and lack of knowledge of its importance
· Lack of familiarity with planning skills .
· Fear of the unknown
· Not knowing priorities and arranging them according to importance
Types of planning :
Strategic planning : It defines the general objectives of the organization. It is also called
Long- term planning : which takes 5-10 years to achieve
2. Tactical planning : It is primarily concerned with implementing strategic plans at the middle management level.
It is called medium - term planning : which takes 1-5 years to achieve
3. Executive planning : It focuses on planning the needs to accomplish the specific responsibilities of managers, departments, or departments . It is called short-range planning Which takes from one day to 12 months to achieve .
- Strategic Planning
The concept of strategic planning :
Predicting the future and preparing for it based on analysis of the present and expectations of future trends to determine the goals desired to be achieved, and determining the appropriate methods and means to achieve these goals efficiently and effectively in accordance with priorities and a timetable .
Benefits of strategic planning :
O Focus on achieving our dreams and goals.
O define the priorities .
O Helps focus efforts and resources.
O Identifying opportunities and investing in them.
Strategic planning steps :
• Analyze the current situation
• Predicting future direction
• Design and formulate the strategy
• Implementing the strategy
• Evaluating and monitoring the implementation of the strategy .
Steps in the strategic planning process :
SWOT Analysis
This means identifying the strengths and weaknesses of the organization's internal environment, over which it has control. And opportunities and threats in
the external environment, which constitutes a pivotal element in the process of preparing the strategic plan, by providing a general framework for thinking about the organization’s internal and external environment .
• It is an analytical framework within the process of planning an analysis :
• Internal environment: strengths and weaknesses
• External environment: opportunities and threats
Why do we use the SWOT approach? In the analysis?
Analysis points help in preparing a plan that takes into account many internal and external factors, increases the possibility of benefiting from the available strengths and opportunities, and reduces the impact of weaknesses and threats.
Necessary requirements before starting to conduct a SWOT analysis ):
• Clearly define the roles and tasks that you must perform
• Evaluation of internal or personal resources
• Analyze and understand the external conditions associated with the organization
The internal environment of the organization:
• The internal environment is all the practical areas that exist within the organization (financial management, human resources, programming, activities, etc.).
• The organization must identify the strengths and weaknesses in implementing its functional and administrative performance ( since no organization will have equal relative powers in all its practical (functional) areas ).
• This helps the organization prepare alternative strategies to take advantage of opportunities and avoid threats.
A Basics of analyzing the internal environment :
The process of analyzing the organization's internal environment helps identify strengths and weaknesses.
This process is based on the use of specific criteria that help in making comparisons, the most important of which are:
• Analysis of past performance
• Compare rates and ratios
• An analysis of the work indicators of this non-governmental organization compared to other organizations
• Comparing the performance of this non-governmental organization with the ideal performance of other organizations.
strength point:
Strengths are actually internal capabilities that exist in the organization and help them take advantage of available opportunities and combat threats.
Questions:
• What are the things you are good at doing ?
• How are our competitors ?
• What are our sources?
Weaknesses:
The presence of any weak factors or conditions that prevent the organization from meeting its needs and taking advantage of the available opportunities.
َQuestions :
What are our weaknesses ?
What is the most annoying thing for those who benefit from our services?
Opportunities :
• It is any external circumstances or specific situations that facilitate the achievement of general goals.
Questions
• What external changes or conditions help implement the program ?
Threats:
Any conditions or situations that affect the efficiency of the organization.
Questions
What changes or external conditions could affect the organization or program?
- Time circuit
What time is it?
o Time is an element of life. It is unlimited and is also considered a valuable resource.
Therefore, it requires special skills to benefit from it and make optimal use of it.
o Time management means the optimal use of available time.
· * Time management: It means self-management and that an effective manager is the one who begins to consider his time Before embarking on his tasks and work, and that time is one of the most important resources if it is not managed Nothing else will be managed.” We said before that time is stagnant and cannot be managed Saving it, compensating it, or postponing it, and thus we realize its difference from the rest of human resources Natural and material. So it is possible to summarize the definition of time management in other words: Good and correct use of the specified and permitted time to achieve a goal
· The optimal use of time to achieve specific goals, through effective planning, organizing, directing, following up and evaluating activities and duties within a specific period of time.
**Time management strategies:
1- Planning :
· Setting priorities to determine the work that should be started .
· Scheduling activities: which determines how much time is required for each activity .
· Work for six important tasks and this can be done through a pocket agenda .
· Give planning the time and effort it deserves
· Have your plan written down and at hand
· Survey the opinions of those around you and those who share with you
· Make your plan at three levels (monthly, weekly, and annual plan)
2- Organizing time :
· Preparing a daily to-do list .
· Effective delegation .
Business organization:
Organization of work is the identification of tasks according to the importance of their completion. The work can be divided as follows:
o Work performed urgently: These are tasks related to daily problems, such as those related to the inability to prepare nursing staff and machines, emergency work, or important meetings.
o Tasks that lead to a deadline : These are problems that are less important or have a specific deadline
o Works that are not performed: that is, they are not completed, and these are problems that are solved by themselves without intervention or can be solved by another person through delegation.
*Control working time:
Controlling working time aims to avoid overcrowding of work, as this leads to an increase in errors as most administrators have a lot of work, so it is important for the nurse manager to learn the steps to control time, which include:
* Steps to control time:
o Define the priorities
o Completing the work you started and not starting other work before finishing what you started
o Rearranging work and setting priorities again according to what has been accomplished
o Controlling time consumption includes:
o Telephone interruptions
o Meetings
o Lack of sufficient information on any subject
o Excessive written work
o Failure to follow up
o Inability to say the word “no”
o Act only in times of emergency
o Speed in making decisions without studying
o Frequency
o Open door policy
o Neglecting to organize files
o Incompetence of assistants
** Reasons for not managing time well
o Laziness and the tendency to rest and procrastinate
o Lack of punctuality (accuracy)
o Not writing goals
o Overlapping appointments. (poor organization)
o Not setting priorities
o Lack of planning
o Sudden (mishandling of emergency)
Time planning tips
· The nurse, especially the administrator, must realize how to waste time and also recognize the time-consumers and try to overcome them. So:---
o Do not always be within reach of everyone so that they may interrupt you at work. When you sit down to do something, it must be away from noise and interruptions, and it is preferable for it to be in a separate room. If that is not available, you must sit with your back to the door or the people in the place in order to reduce interruptions.
o Avoid pleasantries at work
o If you notice that the guest continues talking at length when he finishes speaking, this indicates that the conversation has ended
o Scheduling a long conversation with different excuses for anyone who wants to chat, and setting a time for that during rest
- Decision making and problem solving
introduction:
Some management scholars believe that decision making is the basis
Management and its heart, and often managers see it as a process
Making decisions is their primary job because they have to
Continuously choosing what should be done, and who will do this work
When, where and how, therefore, the decision-making process is inherently
A continuous and cross-functional process of planning, organising, directing and controlling.
Definition of the word decision: It is the most appropriate alternative presented and the one that contributes most to achieving the goal or solving the problem.
The word decision means: the final decision and specific will of the decision maker regarding what should and should not be done to reach a specific situation and a specific and final result.
• Decision-making process : Choosing the best alternative to solve the problem after making a comparison between the available and possible alternatives.
•Decision making: It means all the steps required for the decision to come into existence, and it includes the steps of identifying and defining the problem, analyzing and evaluating the problem, collecting data, proposing appropriate solutions, evaluating each solution separately, and then choosing the best solution .
• Decision making : It is the process of thinking, analyzing, and comparing alternatives to form a specific decision formula on a specific issue.
• Decision making: It is the process of choosing a specific alternative, announcing it to those concerned, and documenting it in a formal and transparent manner
**Decision making steps:
· Determine the problem (diagnose the problem
· Data collection
· Present alternatives and choose the appropriate alternative
· Implementing the solution
· Follow up on the implementation of the solution
Types of decisions :
1. Programmed/non-programmed decisions .
a. Programmed decisions . These are the decisions that are characterized as repetitive, routine, and well-defined, and there are prior procedures to solve them. Usually, they are related to simple, repetitive, uncomplicated problems, and the manager has previous experience in dealing with them, so they do not require new information, and they can be programmed through the organization’s information systems. It is easy to identify alternatives. Such as decisions regarding appointment, promotion, disbursing incentives, training employees, and decisions to purchase the organization’s needs.
B- Non-programmed decisions. These are decisions that are characterized as infrequent, non-routine, and not well-defined, and there are no previously known procedures for solving them, and the manager does not have sufficient prior experience with them. These decisions cannot be predicted in their effects or outcomes. They are related to complex and difficult problems, and require new information. They also require... To study, analyze, develop and evaluate alternatives, and requires a good information system and high skill from managers. Example, producing and marketing a new product, merging with another organization, facing new economic, political or strategic conditions in the market . In this type of decision, there are no specific patterns for solving this type of problem, and therefore a state of uncertainty prevails .
2- Expected/unexpected decisions Anticipated and Non -anticipated Decisions
a. Unexpected decisions . These decisions are characterized by the fact that they do not give the decision maker enough time to carry out the stages of the decision-making process, and put the decision maker under the influence of pressure. Example of sudden decisions to face a sudden crisis with some clients .
B. Expected decisions . These are the decisions that are derived from the plan or as a result of converting the plan into a specific executive program. The decision maker is usually exposed to less pressure. .
-3 Short-term/long-term decisions :
a. Short-term decisions . These are decisions that are based on a high degree of certainty and certainty, where sufficient detailed information is available, and are linked to variables that can be controlled and controlled. They are usually taken by managers at lower levels (middle, lower), as they take a short period of time in the future (week - year). Example decisions on training programs, employee compensation, purchasing needs of the organization .
B. Long-term decisions .
These are decisions that are based on high degrees of uncertainty about the future and its variables (prediction of the future), where there is difficulty in providing sufficient accurate information. It is considered
Strategic decisions at the senior management level. Example choosing a new branch location, changing business rules, expansion or merger .
Factors influencing decision making :
1- Personal factors : including the individual’s experience in dealing with this situation and previous situations, the educational level and the amount of information one has. Courage in making a decision, his relationship with others, his ability to make a decision and implement it through them, as well as convincing them of this decision.
2- Professional factors: The administrative level occupied by the decision maker in the unit, where the individual’s ability to make a decision and implement it is affected by the administrative position he occupies as well as the powers available to him.
3- Factors specific to the institution’s policies: such as the philosophy of this institution in involving nurses in decision-making, that is, making it collectively, as well as the presence of clear and available regulations that help the head nurse to make the decision in an easy and sound manner, as well as the position of senior management in the same place to accept and support the implementation of the decision taken and methods of communication. .
4- Available resources: The presence of the necessary resources, including individuals, equipment, tools, money, and sufficient time, can contribute effectively to selecting and implementing the necessary decision or solution.
5- The quality of the decision: Is this decision vital and urgent, or is it one of the routine decisions that are taken on an ongoing basis and can be dealt with in a simple way?
6- Every decision must lead to a result that contributes to achieving the goal.
7-It is not possible to please every person.
8- The process of making effective decisions requires sufficient time.
9- Recognizing the inevitability of change.
10- Establish a system to follow up on every decision.
11- Recognizing that the decision will entail a series of actions.
Decision making qualities:
· The decision is the result of a process through choosing the available alternatives in order to achieve the goal
· Decision making is an intellectual process that includes innovation, receiving and using information
· Decision making is used in all institutions, whether healthy or unhealthy
· Decision-making is carried out in approved stages that are perpendicular to each other, and the result of any stage is considered an input for the next stage.
Mistakes in decision making:
• Inefficiency in obtaining information
• Determine by time
• Bad communication
• Other obstacles such as:
• A) Personal qualities
• b) Lack of experience
• c) Lack of adaptation
• D) Being influenced by an idea
• e) Firmness of opinion
• Not realizing the problem
• Bad diagnosis of the problem of lack of knowledge of the optimal situation .
• Failure to generate new alternatives and simply accepting well-known traditional solutions
• Failure to accurately evaluate alternatives and failure to determine criteria for selecting the optimal alternative ..
• The weak ability of the decision maker to recognize social pressures, customs and traditions, and misconduct in creating a balanced situation between what the decision requires and the pressures, customs and traditions imposed by society. .
• Failure to involve responsible decision makers associated with the problem with those who will be affected by the expected solutions to the problems .
• Failure to develop an action plan to implement the decision or to follow up on the implementation of the decision
. Decision making styles:
· The first type, “making decisions based on experience” : The supervisor here relies on her intelligence, previous experience, and what is called “feeling.” She usually makes the decision quickly and is often unable to explain how or why this decision was made.
The second type: “Decision making through study and analysis” : The supervisor searches for facts by collecting information and organizing ideas to reach from causes to results, and finding relationships that explain phenomena (problems), and she reaches the decision after balancing and reviewing the results.
· Alternatives.
· The third style: “Decision making with a mixture of experience and study ”: The supervisor combines the two previous styles. She does not cling to study for the sake of studying, nor does she ignore real experience. She mixes study with the outcome of practical experience.
. Some behavioral concepts that influence decisions:
There may be many behavioral concepts that affect the stages of decision-making or the effectiveness of sound decision-making. The most important of these influential behavioral concepts are:
· Perception
· The ability to study information
· Value
Problems that affect administrative decision-making .
• Job dissatisfaction.
• Human relations in the health organization.
• Lack of appropriate services.
• work stress. - Lack of technical and administrative competencies .
• Environmental factors.
• Lack of supervision and inspection.
• Weak administrative experience. - Poor distribution of workers
• Difference in specialization. - Poor planning and poor coordination
• Regulations and laws. - Routine and length of procedure
- Problem Solving
introduction:
Solving administrative problems and making decisions are an integral part of the functions of the administrative process and can be considered as two basic activities that the manager performs on an ongoing basis in their organizational units to confront undesirable situations or levels of performance that constitute an obstacle that prevents reaching the specified goals efficiently and effectively.
Charles says
• (When we write down the details of the problem, we have achieved half of its solution)
Definition of the problem :
• A problem is a state of discrepancy or difference between a current or future reality and a goal that we seek to achieve. There are usually obstacles between reality and the target, and the obstacles may be known or unknown .
. It is a state of dissatisfaction or tension that arises from the awareness of the presence of obstacles to reaching the goal or the expectation that better results can be obtained by making better and more efficient use of familiar processes and activities
The problem can be defined from another perspective as an unsatisfactory or undesirable result that arises from the presence of one or several known or unknown causes that need to be studied to identify them so that they can be influenced. Problems also differ in terms of their degree of severity or impact.
Problem solving concept :
That it is a thinking process in which the individual uses his previously acquired knowledge and skills in order to respond to the requirements of a situation that is unfamiliar to him. The response is to initiate action aimed at resolving the ambiguity or ambiguity contained in the situation
Problem solving steps:
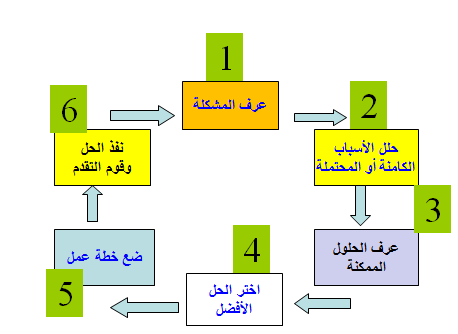
. Practical steps to solve the problem:
. Identify and describe the problem:
The first step in solving the problem is to identify it, and this is done by reviewing the indicators, data, and facts in the situation. Here, management must distinguish between two things:
· The real problem: This includes the main factors that hinder the establishment from achieving a specific goal, and the goal cannot be achieved unless they are solved.
·Sub-problem: It is a temporary symptom that arises as a result of the real problem and disappears with its disappearance
Therefore, solution efforts should be directed to the real problem, not to its branches. The first step in solving the problem is to feel its existence, and this is done by noticing a difference or deviation between the results achieved and the desired goals.
. Analysis of the facility’s capabilities and resources:
This is an important step to determine the possibilities for implementing solutions before thinking about them. This is done by identifying the basic strengths and weaknesses related to the problem in the facility.
. Find the causes of the problem:
Problems do not arise in a vacuum, but rather they have causes. Usually, the causes that create a problem are multiple, and these causes may overlap and interact. Therefore, supervisors must search for these causes and rank their relative importance in causing the problem, as well as clarify the overlapping relationships between them.
. Develop alternative solutions:
Any alternative solution must be characterized by the following:
· It contributes to some degree to solving the problem, but does not necessarily solve it completely
· It must be practically applicable or financially feasible.
· To be socially acceptable
· Does not create other problems, even if it helps solve the main problem
After presenting the alternative solutions, they must be compared. This comparison mainly focuses on important elements that should be present in the most appropriate alternative, which are:
· The extent to which each of the proposed solutions contributes to solving the problem
· The cost or burdens incurred by implementing each solution
· Special requirements that must be provided to implement each solution
· The expected time period for the solution to produce its effects
· Side problems that may arise from implementing each solution
. Put the solution into an application:
There is no doubt that choosing a solution does not solve the problem in itself, but it must be implemented correctly and completely in order for it to have its intended effect and eliminate or alleviate the problem. Therefore, the process of solving problems took place in several important stages, each of which is a link in an integrated chain. Each stage depends on the previous stage, meaning The quality and effectiveness of problem solving as an administrative basis depends on the efficiency of all stages.

• Use one type of thinking .
• Absence or limited participation of concerned parties.
• Fear of failure, innovation, and exchanging ideas .
• Lack of information or poor analysis of the problem .
• Lack of commitment to solving the problem.
• Misinterpreting the problem.
• Lack of knowledge of methods (techniques) and processes for solving the problem.
• Inability to use methods effectively.
• Not using the appropriate method for a specific problem.
• Insufficient or incorrect information.
Methods for solving administrative problems :
• You must realize that there is a problem and it must be identified quickly, and you must decide to confront the problem and confront it.
• You must understand that solving problems involves making a certain effort, and you must relax and develop your mind before acting on the problem.
• You should be convinced that making a decision is better than doing nothing and you should be determined to address the problem as early as possible.
• You must appreciate the existence of a situation to identify the problem before rushing to address and eliminate it.
• You must make a list of facts and information related to the problem as you see it. This helps you understand the problem and allows you to determine what is actually happening.
• It is also important to determine the pros and cons of the available options and alternatives and their solutions.
• You must know the possible chances of success and failure in certain proportions and know whether there is a solution to the problem left after all that
• You must make a logical decision about the effectiveness of your decision and must consult with others who will be affected by this decision.
• You must carefully consider the effectiveness of your decision
• You should take into account whether the problem requires a temporary or long-term solution, while ensuring that your decision solves the problem permanently.
The importance of developing the ability to solve problems:
Developing your ability to solve problems is beneficial in many ways, as you will be able to:
• Anticipates specific problems and takes preventive action.
• Problems are solved quickly and with less effort.
• Reduces stress.
• Develop your performance at work and your relationships with colleagues.
• Create opportunities and exploit them.
• Solve the most pressing problems.
• You exercise more control over major or vital aspects of your life.
• Achieve more personal satisfaction.
- Table of shifts
The shift schedule is a timetable for distributing work alternately and equally among nurses and arranging shifts. This schedule is used for three purposes:
. Distributing work in excess of normal working hours fairly and equally among nurses, such as: staying up late - weekends - working with overtime pay
. Distributing difficult or undesirable work equally among nurses, such as home visits and childbirth in health units
. Divide excess duties among all employees.
. Rules for making shift schedules
There are two basic rules that must be respected when distributing different tasks alternately among employees:
. The shift work period must be equal to the same schedule, and the work period may be a day, a week, or a month.
. The number of nurses working in shifts must be equal to the number of work periods or the number of activities
. When setting a shift schedule, the following must be taken into account
. The start date of the shift week is written in the column to the right
. The place of work or its period is written horizontally in the table
. Fill in from right to left, beginning each new line with the last name in the previous column.