Chapter one and two
| Site: | EHC | Egyptian Health Council |
| Course: | Developing the administrative skills of nursing leaders |
| Book: | Chapter one and two |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Monday, 23 December 2024, 1:21 PM |
- Preparation
Kawthar Mahmoud Mahmoud
Dr. Camelia Fouad Abdullah, Professor in the Surgical Internal Medicine Department, Faculty of Nursing, Ain Shams University
Dr. Mona El-Shazly Mahmoud, Head of the Administration Department, Faculty of Nursing, AinShams University
Dr. Buthaina Nader Sadiq, lecturer in the Pediatrics Department, Faculty of Nursing, Ain Shams University
Dr. Samar Marzouk, lecturer in the Surgical Internal Medicine Department, Faculty of Nursing, Ain Shams University
Dr. Dina Mohamed Mohamed, lecturer in the Surgical Internal Medicine Department, Faculty of Nursing, Ain Shams University
Dr. Sarah Fathi, lecturer in the Internal Surgical Department, Faculty of Nursing, Ain Shams University
Development team at the Central Nursing Administration
Prof. Amany Farouk Mohamed, Senior Nursing Specialist at the Central Administration of Nursing
Prof. Azza Jalal Ahmed, nursing specialist at the Central Administration of Nursing
Prof. Hanan Amin Shousha, nursing specialist at the Central Administration of Nursing
Prof. Yasmine Sayed Abdel Basset, nursing specialist in the Central Administration of Nursing
Prof. Marwa Mohamed Hassan, nursing specialist at the Central Administration of Nursing
Prof. Ahmed Youssef Abdullah, nursing specialist in the Central Administration of Nursing
A.T. Angham Hamdy Abdel Khaleq, nursing specialist at the Central Administration of Nursing
Prof. Mohamed Abdel Ghani Youssef, nursing specialist in the Central Administration of Nursing
Prof. Taha Mohamed Ahmed, nursing specialist at the Central Administration of Nursing
Review and supervision
Dr. Kawthar Mahmoud Mahmoud, Head of the Central Administration for Nursing
Prof. Dr. Hisham Atta Youssef, Assistant to His Excellency Prof. Dr. Minister of Health and Population
For human resources development and training
Dr. Nevin Abd Rab Al-Nabi Muhammad, General Director of Therapeutic Nursing Department
Dr. Ali Abdel Azim, Director General of Quality Management, Ministry of Health and Population
- Introduction
The Ministry of Health (Central Administration of Nursing) has paid great attention to developing the information and skills of nursing staff members in various specialized and precise nursing fields. All of these specialties share the basic skills in practicing the nursing profession that relate to leadership and administrative skills, and these are of special importance to nursing leaders, whether on the The senior or middle management level, so nursing leaders’ knowledge of the management rules and systems that govern the practice of the nursing profession, which represents great importance in improving the health system.
From this standpoint, this guide has been prepared for chief nurses, agents and supervisors with the aim of increasing their administrative skills and practicing and working with management rules and systems, as this will reflect positively on performance.
Developing the administrative skills of nursing leaders
General goal:
This booklet aims to strengthen and update information, improve skills, and shed light on the concepts, foundations, and aspects related to nursing management topics to improve the nursing service provided .
The educational objectives of this booklet and how to use it and benefit from:
· Assisting nursing leaders to develop their necessary administrative skills related to the work and tasks assigned to them.
· The ability to self-educate and raise the level of professional performance.
· The ability to deliver skills and information to those working under their supervision (supervisors and department heads)
· Mentions the importance of management to achieve goals .
· Explains the concept of management and its importance.
· Discusses the principles and functions of management and how to apply them.
· Describes the responsibilities and duties of effective nursing leaders.
· Learn about the importance of planning.
· Enumerates the types of planning.
· Describes how planning is implemented.
· Know the concept of problem and decision making.
· Learn about the concept of organization.
· Discuss the benefits of organization.
· Knowledge of the steps/stages of organization.
· Knows the concept of guidance.
· Identify the elements of guidance.
· Definition and types of delegation.
· Identify the most important means of motivating subordinates.
· Defining the concept and steps of managing meetings.
· Discusses different styles of leadership.
· Designing job descriptions for nursing staff members.
· Describes the appropriate system for distributing nursing work within different units.
· Define the basic concepts of time management.
· Identify time wasters.
· Definition of what reports are.
· Discuss the importance of the report.
· Definition of what is meant by a hospital conditions report.
· Determine the purpose of using the hospital conditions report.
· Definition of what is meant by an accident report.
· Determine the importance of oversight.
· Learn about the concept of performance evaluation.
· Describes the advantages of performance evaluation.
· Focus on reading the summary of each chapter.
· Answer questions related to each chapter.
· Matching the answers to the questions with the model answer within the book after answering them yourself.
- Nursing ethics
Nursing ethics
introduction
God Almighty has granted the nursing staff the honor of the nursing profession, which transcends all considerations and rises to the level of a human being, providing comprehensive nursing care to him in cases of health and illness in his capacity as a human being, with justice and honesty
The nursing profession is based on a scientific and ethical foundation. The human being, in cases of illness in particular, deserves to be provided with nursing care at the best levels and the noblest methods of human interaction. The ethics of the nursing profession are an essential part of nursing care, treating patients, enhancing the health of individuals and communities, and relationships with members of the health team. The responsibilities of ethical nursing care. It is a duty for everyone involved in it to be a suitable environment for the work of nursing staff members
And the nursing staff members are the basis for encouraging all concerned to provide ethical professional conditions for their work and to provide nursing care. The Egyptian Code of Ethics for the Nursing Profession is the agreement and consensus of all Egyptian nursing and health leaders, nursing staff unions, and members of the Arab Nursing Staff Union, who look up to all members of the Arab Nursing Corps. And the Egyptian Council for commitment and awareness of it in order to achieve ethical scientific nursing care and achieve satisfaction among patients and members of society wherever nursing care is provided and satisfaction among service providers with the nursing service provided. The Egyptian General Union of Nursing and the Central Administration of Nursing at the Ministry of Health and Population were keen to bring nursing professional concepts closer between service providers and recipients and achieve Progress in all fields of the profession, advancement of its sciences and services with the highest possible degree of unification, and benefiting from the diversity and multiplicity of levels of progress that the Arab Republic of Egypt is expected to witness towards the nursing profession, and for Egypt to be a producer of nursing scientific knowledge towards universal benefit, in the belief of the
Egyptian Nursing Authority that science should be reflected in the service of humanity. Wherever he was, and to any nationality or religion, he was affiliated, and cooperation began by issuing the Charter of Ethics for the Egyptian Nursing Profession, to be the first charter issued by the General Syndicate of Nursing, and its main reference is the Charter of the Arab Nursing Federation, emphasizing the importance of professional ethics in work
The Egyptian Charter of Ethics for the Nursing Profession is of great importance, and the General Nursing Syndicate hopes that this Charter will receive the great attention of the Egyptian Nursing Authority, governments, health sectors, and all medical professionals throughout the country, and to emphasize adherence to it, disseminate it to all concerned, and encourage its use wherever necessary. It will be a permanent reference in work, planning, and education, and it will receive attention and be a subject of criticism and scientific research
First: Duties and responsibilities of the literary profession:
There are moral duties and responsibilities that govern and regulate the work of the nursing profession, in addition to the professional responsibilities and duties of nursing staff members. All organizations interested in the nursing profession, most notably the International Council of Nursing Staff, have paid attention to them, stressing the need for nursing staff members to adhere to the morals and ethics of the nursing profession. Therefore, it has drawn up a constitution and a code of ethics for the profession so that nursing staff members can be Nursing is aware to emulate and implement it, which will have an impact on the positive image of the nursing staff in society and their emergence as role models.
The most important provisions of this constitution are the following :
· Respecting life, alleviating suffering, and working to alleviate pain and raise the level of health
· Providing the highest level of nursing service and professional behavior
· To be prepared to practice the profession only and to work on acquiring information and skills
· Respecting the patient’s religious beliefs
· Keep all information she obtains through her work and do not disclose it except in accordance with the law
· Do not prescribe or give medical treatment without a doctor’s orders, except in emergency cases and notifying the doctor immediately
· You are committed to carrying out the doctor’s orders intelligently and obediently and refuse to participate in any unethical actions
· Gain the trust of the doctor and members of the health team
· Do not allow their names to be used in advertising products or in any form of personal advertising
· Cooperating with members of other professions and with her nursing colleagues
· Adhering to the standards of personal etiquette in her private life
· Citizens and members of other health professions participate in their efforts to meet the health needs of the local, national and global community
Thus, the nurse has many responsibilities and duties towards the patient, herself, her colleagues, her workplace, society, and her profession in which she works.
The following are the most important ethical responsibilities of nursing staff members:
The most important responsibilities of nursing staff towards their patients are:
· To keep in mind that healing the patient and maintaining his health is their primary goal, without other considerations such as religion, color, gender, or politics.
· To be the place of trust placed by the patient in terms of his recovery.
· To be kind-hearted in their treatment and to act wisely and accurately towards their patients, and to give the patient hope for recovery, whether physical or psychological, and to maintain absolute confidentiality of everything you know about the patient, and to participate with the patient in making some decisions related to his treatment.
· They should be responsible for health education for the patient and providing him with complete information regarding his illness, how to cope with it, and what are the means of avoiding complications resulting from it, and not just giving him medication .
Responsibility of nursing staff towards themselves:
· Nursing staff members must work to improve their scientific level by constantly being informed of everything new in the general natural sciences and special nursing sciences.
· Completing studies to obtain available academic degrees such as a specialized diploma, master’s and doctorate.
· Attending seminars, scientific conferences and seminars organized by medical and nursing societies and participating in scientific research that helps advance the nursing and health care profession.
· To be fully convinced of the nursing profession and to bear in mind that this profession has its own respect, dignity and dignity, and to be of good conduct and behavior in their public and private lives.
Responsibilities of nursing staff towards their colleagues at work:
· Sincere cooperation with members of the health team, which helps provide health care to citizens
· They treat their co-workers as they would like to be treated and avoid bad talk about them and any comment or remark that would detract from the skill or opinion of any co-worker.
· Fully prepared to teach recent graduate colleagues all the foundations and concepts of modern nursing
Responsibility of nursing staff towards the institution in which they work:
· Respecting the organization’s work laws and rules.
· Respect all employees of the organization and cooperate with their superiors.
· Respect the full uniform while working.
· Proper use and preservation of work tools, and reporting in the event of loss or damage to any of the devices and tools
Responsibility of nursing staff towards society:
· To be good citizens who respect the traditions and customs of society.
· Not participating in work that affects the honor and dignity of citizens.
· To have sufficient knowledge of the state’s laws and legislation.
Responsibility of nursing staff towards the nursing profession:
· Paying attention to their appearance, adherence to dress, cleanliness and grooming.
· Stay away from any action that raises suspicions around her and have good behavior.
· They must be convinced of the profession and that it is a humane job that is respected.
· Raising the level of the scientific profession through scientific research while communicating information to other groups.
· Working to improve the physical, economic and social conditions of workers in the profession.
· Improving the level of performance of nursing services in their workplace, as well as improving the selection of workers
The following are the most important qualities necessary for nursing staff members:
Nursing staff members must have the most beautiful qualities that qualify them to carry out their mission in the best way, such as:
1- Healthy body and mind.
2- Be mature in thinking and acting.
3- They have basic information about the profession as well as general information.
4- They have skills specific to the nursing profession.
5- They have the ability to gain the trust of others and teach others.
6- They have sound attitudes towards their profession.
7- Role models in their cleanliness and good appearance.
8-A Strong observation and smart people.
9- To be firm.
10- Conscientious and cooperative .
11- His ability to make decisions and have emotional stability, especially in crises and critical situations.
12 - Quick intuition and quick action.
13- Self-confidence.
- Communication methods
Definition of communication
Communication is the process of exchanging ideas, information, and trends verbally and non-verbally between individuals to achieve public or private purposes. Communication is a circular process and not a one-sided conversation . This means that the sender is at times a receiver and the receiver is at times a sender .
The importance of communication
• Forming relationships between community members.
• Exchange information, ideas and experiences.
• Conviction to change positive knowledge, attitude and behavior among individuals and groups
• Clarifying ideas, removing confusion, and correcting concepts .
• Increase culture.
• Influencing others through guidance and counseling.
• Transferring information, data, statistics and concepts through various channels to contribute to decision-making .
• A purposeful means to ensure interaction and joint exchange of the organization’s various activities .
• A way to motivate employees .
• Communication helps achieve goals .
Components of the communication process:
• Sender
• the message
• Communication channel
• the future
• Feedback
• the environment
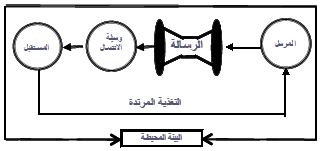
Types of communication:
1. Verbal
2. Non-verbal.
There are two types of communication:
First: Verbal communication:
• (talk - printed material to read - watching a television or radio program)
• Second: - Non-verbal communication:
• (body and hand movement - sitting - facial expressions such as joy and sadness - eye movement...etc. )
Communication skill:
1. Listening skill.
2. Speaking skill.
3. Persuasion skill.
4. The skill of asking questions.
5. Dialogue management skill.
6. Skill in dealing with others.
7. The skill of using body language.
· Listening skill
It is focusing attention on the opinions, thoughts, feelings, and linguistic and physical expressions of others. Do not rely on the content of the words, but try to reach the speaker’s directions .
The difference between listening and listening
- Listening : is limited to receiving the message organically through the ear .
- Listening : It is the use of the mind with its full capacity in everything that has been received, by processing the received message mentally with interpretation.
Types of listening:
Good listening is often accompanied by good thinking
Why don't we listen?
· Their inability to concentrate for any reason.
· Their intense preoccupation with themselves.
· They are too preoccupied with what they will say later.
· Their lack of confidence in what they are listening to and the reasons that make them listen to it.
· They do not have the ability to follow the points that the speaker is talking about.
· They do not care about what is said to them.
· We think seven times faster than we speak, and this makes us preoccupied with our judgments about the speaker’s speech?
· Our desire to express ourselves instead of listening (I want the opportunity to speak).
· Distraction due to side conversations or noise.
The importance of good listening
Good listening is the appropriate path for a leader or individual with strong relationships with others, as it saves a lot of time and effort in managing problems and conflicts, achieving goals, and negotiating with those around them, as listening leads to :
· It affects the validity and accuracy of the decision
· It makes the relationship mature and strong between individuals
· Generates the ability to innovate and create
· It makes the individual able to face problems and crises
· Makes the criteria for evaluating others more fair
· Listening means a permanent addition to a person’s ability to speak forcefully
· It reduces error and represents the key to safety for the individual’s intellectual growth.
How to become an effective listener?
· Search for the content of the topic and ignore the speaker’s manner or mistakes in speaking.
· Arrange the information you hear logically in your mind.
· Do not rush to judge.... Rather, let the speaker complete his speech.
· Do not turn your face away from the interlocutor (the eye sometimes listens).
· Ask your interlocutor if the conversation is not clear.
· Create an appropriate environment for yourself from the beginning that prevents you from focusing on things other than listening to the speaker.
· Make your place in the session suitable for following the speaker with your eyes and ears, and try to eliminate factors that could obstruct this, such as sunlight falling on you or the presence of some devices in front of you.
2- Speaking skill
How do you prepare yourself before starting the conversation?
· Determine your goal and benefit from communication
· Design your message to suit your listeners
· Good preparation of the topic of the conversation...it is the best source of trust.
· Have an idea in advance about the person you will be speaking to.
· Prepare supporting materials to support your speech.
· Mental and muscle relaxation.
To be a good speaker
· Avoid inexpressive faces - exaggerated expressions - distressed expressions.
· Avoid sharp glances or direct close-up looks.
· Avoid repetitive movements as a result of excessive nervousness (movement such as a pendulum clock, for example).
· Avoid inappropriate or exaggerated clothing.
· Avoid stuttering - low voice - continuing on one tone.
· Expand your circle of thinking and fully understand the information
· Use the recipient's language to convey the message clearly
· Ask questions and then let the speaker confirm to you that what you understood is in fact correct
· Do not say lightly: I do not know: many of us know very little about the world in which we live, and pretending to answer or fabricating it only doubles the problems.
· Pay your full attention to those you talk to: If you set aside time to communicate with a person, give him attention and attention. Join the conversation and participate in it when you see that it is of interest to the communication process.
3- Persuasion skill
It is one of the skills necessary for the communication process, and it is used in personal interviews, group discussions, and talking with leaders. Definition: Enticement through reason, logic, and knowledge to make others accept changes in their opinions, attitudes, or behaviors.
Stages of the persuasion process:-
· The attention stage: The individual is attracted to the new idea and shows enthusiasm for this idea.
· Interest stage: A stage in which the individual wants to know details about the idea and has a desire to analyze facts and collect information.
· Evaluation or mental comparison stage: In this journey, the individual performs a process of self-evaluation and comparison between the old and the new.
· Experimentation stage: In this journey, the individual tries to get rid of tension and attraction, so he experiments and applies the pleasure of the idea on a small scale.
· Adopting the idea/complete conviction: In this journey, the person is completely convinced of the idea and decides to continue implementing it.
The skill of asking questions
To keep the dialogue going, there must be a reaction from the other party that includes indicators that support that it received the message and helps the first party determine how to continue the dialogue. These indicators can be obtained through the optimal use of questions. The questions may be positive or negative. If they are positive, they explain the other party’s way of thinking and feeling, but if they are negative, they make him feel tense and embarrassed and push him to take a defensive position.
Therefore, the following must be taken into account:
· The goal of questions should be to reach agreement and not to interfere in personal matters.
· It is important not to ask questions that lead to anxiety and tension in the other party.
· Questions should help both parties, and not be used as maneuvering.
· Questions should aim to establish an atmosphere of cooperation by motivating the other party to respond frankly.
· Ensure that the questions are not deceptive, contrived, evasive, shameful, or worthless.
· Questions must be appropriate to the situation.
· Questions should also be appropriate to the other party’s personality and general aptitudes.
· The purpose of questions should be to achieve a goal and not simply to elicit a response.
· The need for a connection between the questions.
· Finally, it is required and usual that questions be characterized by tact and respect for the other party.
Specifications of successful communication:-
· That both the sender and the receiver must believe and be interested in the message
· Mutual respect between sender and receiver
The subject of the message is clear to both parties
· Use appropriate means for the sender, the recipient, the subject of the message, and the place where it is presented
· Communication is two-way, meaning there is interaction between the sender and the receiver
· Use verbal and non-verbal communication equally efficiently, as they complement each other
· The more senses we use, the more efficient the communication process becomes
· The message must be correct, accurate, clear, specific and short
· Do not be a continuous sender or receiver
· Set a clear goal for the communication process
· Choose the appropriate circumstance from an environmental, social and psychological perspective
· The language of communication must be appropriate for both parties
Specifications of successful communication
· That both the sender and the receiver must believe and be interested in the message
· Mutual respect between sender and receiver
The subject of the message is clear to both parties
· Use appropriate means for the sender, the recipient, the subject of the message, and the place where it is presented
· Communication is two-way, meaning there is interaction between the sender and the receiver
· Use verbal and non-verbal communication equally efficiently, as they complement each other
· The more senses we use, the more efficient the communication process becomes
· The message must be correct, accurate, clear, Specific and short
· Do not be a continuous sender or receiver
· Set a clear goal for the communication process
· Choose the environmentally appropriate condition, Social and psychological
· The language of communication must be appropriate for both parties
Basic principles for communicating clearly
In order for people to hear, see and understand the message you want to deliver to them, you must:
Choose words that are easy and simple to understand.
To avoid scientific and medical terminology.
Make sure that everyone present sees and hears what you are saying.
To present a message as short as possible without disturbing the content of the message.
Long messages lead to the attendees being distracted and not focusing on what you are saying and presenting. It also leads to them not remembering the message shortly after your speech.
You should talk to them about one topic at a time.
- Management science
Introduction to management science
Definition of management:
There are several definitions of management, and you can acquire one or more.
Management is a science : it means that it depends on the scientific method when observing, analyzing and interpreting administrative problems and arriving at results that can be generalized.
Management is a science : that is, it has principles, rules, schools, and theories that govern administrative work, and the application of these principles and theories leads to specific results.
Management is an art: that is, the manager needs experience, skill, and intelligence in practicing his work, and in dealing with the human element to motivate him to achieve organizational goals, because not everyone who has studied management science is able to apply it. The art of management is the ability to apply management in different fields.
Management is both an art and a science : From all of the above, we can say that management is both an art and a science. The administrator must rely on books and administrative theories in addition to practical experience that is indispensable.
• The process of setting goals and making the necessary decisions for the profession and achieving them at a specific time through the optimal use of material and human capabilities.
• The process of making decisions and finding alternatives to achieve the desired goal with the highest efficiency and lowest cost.
• The process of achieving specific goals at a specific time by using the efforts and leadership of individuals and making use of available material resources, aiming for perfection, speed, and economy as much as possible.
• The origin of the word administration) Latin meaning ( To Serve(i.e. (in order to serve)) and administration thus means “service” on the basis that whoever works in administration is based on serving others.
• Management means forecasting, planning, organizing, coordinating, issuing orders and controlling .
• Management is the process of planning, organizing, leading and controlling the activities and members of the organization, and using all organizational resources - human, financial, material and information - for the purpose of achieving the organization’s goals efficiently and effectively.
Effectiveness: Effectiveness means the extent to which the organization's goals are achieved
Doing the right things. That is, choosing the right goals
Efficiency : Efficiency .
• It means the economic use of resources: that is, economic use of resources and making good use of them ( doing things in the right way, that is, achieving the best results with the least effort, time, and cost ) .
Administrative qualities that an administrator must possess:
· Honesty, justice and sincerity in work.
· Mental and intellectual qualities, meaning that he must be intelligent .
· Physical characteristics to bear the workload
· Technical qualities, meaning that he must be familiar with the specialty in which he works .
· Cultural qualities such that he is familiar with other sciences.
· Human qualities through which he can deal with the human element .
· Qualities related to experience, which are qualities that arise as a result of practicing the work .
The role of the head nurse as an administrator :
Planning :
- The head nurse must be familiar with the goals of the health unit and nursing services to achieve better nursing care and meet the needs of patients.
- Be familiar with the numbers of patients and nurses, the budget, the number of beds, and the regulations and laws of the hospital
- Planning is used to determine:
- Duties and responsibilities of nurses
- Setting the budget and reporting to the hospital director on budgetary needs
- Guiding nurses in the optimal use of machines and tools
- Develop training programs for nurses
Organization :
- It organizes nurses, capabilities, machines and tasks according to needs to achieve goals .
Guidance:
- Supervising the action plan and ensuring that the nurses have implemented the plan to the fullest extent.
Monitoring:
- This is done through error correction and continuous evaluation.
Skills necessary to practice the administrative process :
1- Conceptual Skills
2- Behavioral or human skills
3- Technical skills Technical Skills
Intellectual skills: Conceptual Skills
It is represented by the ability to have a comprehensive vision for the organization as a whole and the ability to link ideas and interrelation between parts of the organization with each other. These skills are more required in senior management: (senior management, especially the general manager
• Human Skills: Human Skills
In short, it is represented by the manager's ability to deal with all employees in the organization, and this quality is required at all administrative levels. (All administrative levels, especially human resources management
– Technical Skills: Technical Skills
It is represented by the extent to which the manager has the ability to use technologies such as computers, language skills, and accounting, and these skills are required at most of the lower administrative levels. (lower management)
Especially the CEO
· Lower management level : They are the people who actually direct and coordinate the organization’s production and service work, and they are not managers. They report to the middle management manager . They are called department heads . . .
· Middle management level . They are the managers responsible for directing, coordinating and monitoring the activities and activities of lower management managers . They interpret and explain the directives, policies and decisions of upper management to lower management managers . They are responsible to their superiors in senior management. They are called role supervisors and quality and infection coordinators.
· Senior management level ) It includes a limited group of individuals that usually includes the president, his deputy, the general manager, and the executive director. They are responsible for the overall general direction and supervision of the organization through middle managers.
Components of the administrative process:
The foundations of management include the following main components:
Planning : developing the necessary plans to achieve goals and determining in advance what must be done, how it will be done, when it will be done, and by whom .
Organization : It includes setting the organizational structure, defining competencies, and setting systems and regulations. A process that includes defining work, dividing activities, assigning responsibilities, using and arranging the organization’s human and material resources in order to implement plans and achieve the desired goals .
Directing: It is the method by which individuals are guided, supported, and mobilized to achieve the organization's goals by building strong work teams. Delegation of authority, effective communication, and conflict resolution through a competent supervisor.
Oversight: Oversight is measuring and correcting the performance of subordinates for the purpose of ensuring that the goals of the health facility have been achieved .