Part Three
- Standard measures to combat infection
Infection control in the operational unit
Introduction
The infection that occurs at the place of surgery in the patient's body is one of the common infections associated with health care and this infection causes a large percentage of complications and there are many factors that cause this infection, which when it occurs deep in the place of surgical intervention, it may cause death, and often the entry of microbes Therefore, to reduce the risk of infection at the surgical site, it is necessary to apply a specific preventive program, realizing that these risks are affected by the patient's condition at the time of surgery, the type of operations, personnel and health facility.
Sources of infection of surgical sites :-
1-internal sources :-
The microbes that cause most cases of surgical site infection come from bacteria colonizing the patient's skin, mucous membranes or intestines (normal flora) and when there is a cut in the skin or mucous membrane, the tissues are at risk of contamination with these bacteria and usually these bacteria are from Gram-positive staphylococci (such as staphylococci) but may include colonized bacteria For feces (such as anaerobic bacteria and Gram-negative aerobic bacteria), when wounds occur near the anus or groin, and in the digestive tract processes, bacilli are Gram-negative, such as enterococci, sometimes anaerobic bacteria such as fragile Bacillus are usually isolated from surgical site infections .
2-external sources :-
It includes surgical personnel (especially members of a surgical team), the operating room environment, and all tools, devices, and materials that enter the field during the surgery procedure, and infection often occurs from aerobic bacteria, especially a positive response to Gram Stain
Therefore, it is necessary to prevent infection of the surgical site :-
◾ - Reducing or reducing microbial contamination of patient tissues or sterile surgical instruments
◾ - The use of preventive antibiotics before surgery
◾ - Proper surgical technique
◾ - Proper ventilation system for the operating room .....................Etc
◾ - infection control for surgery, such as patient preparation, skin disinfection, care team, proper timing of preventive antibiotics, and operating room preparation is easier if compared to controlling the patient's risk factors .
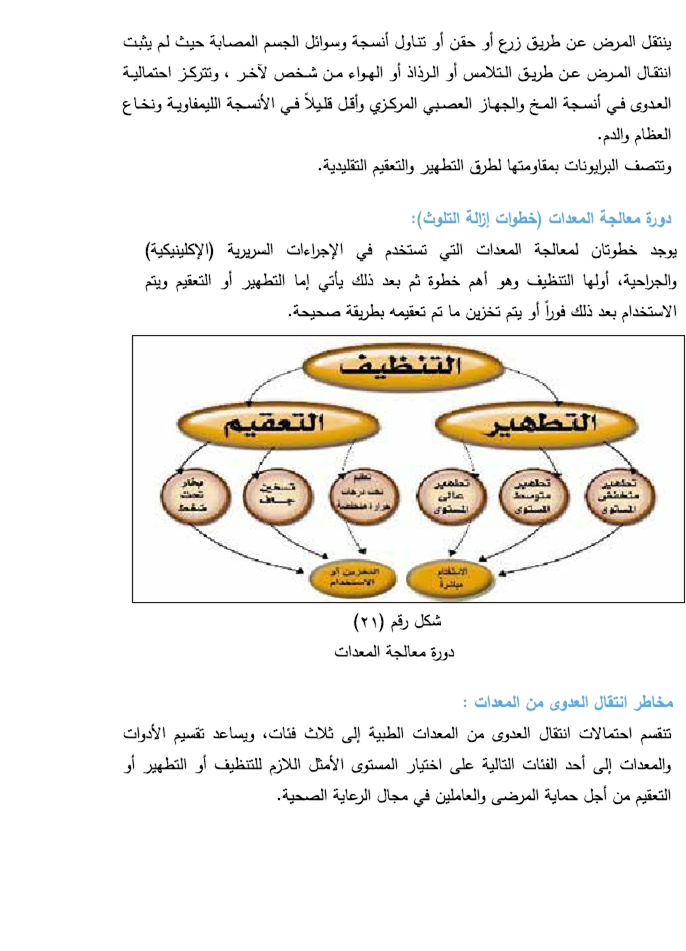
Control of the environment within the operations suite:-
Providing a safe environment in the operations suite:
◾ Specific rooms should be allocated for the implementation of surgical and medical interventions and the allocation of rooms for other services, as well as the control of traffic directions, movement and activities in those areas
◾location of the operations wing
◾wards and operating rooms should be located in specially prepared places for this purpose
◾ These wards should be located so that they are easily accessible from the surgical departments and the accident and emergency department and so that they are separated from the main traffic route of the hospital and the main roads at the same time
◾floors and walls must be antistatic or antistatic and antimicrobial together
◾ the angles between the floors and the walls and between the walls and some of them must be round (non-sharp angles), which leads to reducing the rates of accumulation of dust and liquids and allows frequent cleaning and disinfection
◾ process ceilings should not be of the suspended ceiling type, and if this is not possible, they should be of long slats in order to reduce the number of breaks.
Operations suite design:-
The operations wing should be divided into the following areas :-
1-the non-restricted area :
This area could include
◾ a : main entrance door
◾a store for medical and surgical supplies and devices
◾changing rooms and attached bathrooms
◾a temporary storage warehouse for contaminated furniture as well as for medical waste
2-the semi-restricted area:
◾ It could cripple this area
◾ - Store of sterile tools and supplies
◾ - Nesthesia room (patient preparation)
◾ - Wake up area
◾ - Hand washing and disinfection area
◾- a rest room for the Working Group
◾ entering this area requires wearing an operating suit, foot protectors and headgear, but there is no need to wear masks, gloves or a surgical gown ( except in the case of entering an operating room) there should be a one-way entrance to the restricted area (operating room), preferably not a hand cleaning area, and access to the operating room is limited to a group of employees Participants in the operation that is already being conducted.
3-restricted area:-
Access to this area is limited to the work team and this area includes:
Operating room .
Temporary storage of sterile tools and supplies intended for daily use.
Remember :
◾ sterile and clean supplies should be brought to the operating room from the supply storage area or the machine reprocessing area outside the ward on a covered cart .
◾ contaminated instruments and machines must be transported inside covered containers from the operating room to the central sterilization Department .
Temperature and humidity
◾ Temperature and humidity play a very important role in providing a sense of comfort for the patient and staff, so they must be organized and monitored carefully.
The humidity should be controlled
◾ it remains between 30-60 %
◾ The temperature should be controlled and kept between 20-24 degrees Celsius and the temperature of the operating room should be at least one degree Celsius lower than the temperature of the external lobbies, as this helps to move the air to the outside .
Perfect ventilation in operating rooms :-
◾ Positive pressure ventilation.
◾ It is necessary to maintain positive pressure ventilation in the operating room compared to the related lobbies and adjacent areas, and the number of operating rooms equipped with air treatment units should correspond to the number set by the manufacturer of air treatment units, as well as periodic maintenance of air treatment units ( filters and others)
◾ Also, the temperature, humidity and pressure should be recorded before the start of each surgical operation in a special log
The criteria to be met, if possible, based on the available resources are :-
◾ Air change rate: change the air from 15-20 times per hour, provided that at least three times of it have fresh air from the outside and filtered
◾ Air purification : air filtration with high-efficiency filters, especially in cases of Marrow Transplantation, organs, brain and nerve operations and some orthopedic operations
◾ Air supply: it should be ensured that there is one direction of air entry and exit, provided that the air outlet openings are at a distance of 20-30 centimeters from the ground, taking into account the absence of furniture or movable objects in front of the air outlet openings, as they work to prevent air from circulating in the operating room, and then they should be minimized .
◾ The entrance to each operating room should have indicators for measuring pressure, temperature and humidity inside the room
◾ doors : the doors of the operating rooms must be self-closing .
◾ traffic: access to the operating room is limited to the people required to be present in the surgical procedure, as the percentage of microbes increases with the increase in the number of people moving in the operating room .
Infection prevention in operating rooms
◾ infection prevention is achieved inside the operating room by carefully following the methods of preventing contamination
◾ proper hand washing for the nature of the procedure
◾ use personal protective equipment appropriate to the nature of the procedure
◾ isolation of the surgical site from the surrounding non-sterile environment
◾ Create a sterile area and keep it sterile for the duration of the surgery.
First : hand care before performing surgical operations
Washing the surgical team's hands is one of the most effective ways to reduce the risk of infection.
Second: personal protective equipment used in operating rooms
The use of personal condoms reduces the patient's exposure to microbes that fall from the skin, mucous membranes or hair of surgical team members, and also protects surgical team members from exposure to blood and other body fluids .
Foot protectors: employees must adhere to wearing foot protectors ( neck protectors of appropriate length or soap ) to protect the feet from exposure to liquids and sharp tools.
Headgear :-
The head should be completely covered using single-use caps , these caps reduce contamination in the surgical area, which may result from carburetors in the hair and human cells falling from the scalp
Hair covers should be worn first, so that the hairs do not fall over the clean clothes of the operating room.
Standard surgical masks :
◾ These masks must cover the nose and mouth all the time of work and it is not allowed to wear them at all up to the nose and mouth or put them in pockets for reuse
◾ masks should be constantly evaluated if exposed to moisture and wetness, and they should also be changed between different suits and when leaving the room
◾ High-efficiency masks should be available for use during surgical operations for patients who are likely or confirmed to have an airborne microbial infection (such as bacteria that cause tuberculosis ,)
◾ Special surgical masks should be used for service providers with beards .
Eye and face protectors: eye protectors ( eye protectors ) or eye and face protectors ( face protectors ) should be worn to protect the eyes, nose and mouth of the work team when splashing of blood and other body fluids is an expected
event .
Surgical gown ( Gaon): sterile surgical gown made of non-permeable fabric prevents contamination of the forearm, chest or clothes of any member of the surgical team with blood or other body fluids, it also limits the transmission
of microbes from the surgical team to patients, and a single-use plastic bib should be worn under the Gaon if the cloth made of it The Gaon is an outlet for liquids .
Surgical gloves: the surgical staff should wear sterile gloves that fit the exact size of the hand, in order to reduce the transmission of microbes from the hands of the team members with blood and other body fluids , and gloves should
be changed if contaminated or there is a doubt about their safety .
|
Wash the hands surgically, dry them with a sterile towel, then the nursing caretaker opens the outer cover of the glove package. |
|
|
Provide and maintain a sterile area
A sterile area should be provided and maintained to reduce the risk of contamination of the subject of surgery, this is achieved by placing sterile pads impermeable to liquids ( or using sterile transparent plastic adhesive insulating materials intended for this purpose) around the subject of the operation
The patient should be fully brushed so that the only place that is not covered is the surgical cut
A sterile field can be maintained by :
◾ sterile machines and instruments should be placed only inside the sterile field
◾ opening, distributing and transporting sterile instruments without contamination
◾ consider everything that is below the level of the patient covered with sterile mattresses as non-sterile (outside the sterile field)
◾ not to allow people who are not involved in surgery to penetrate the sterile field or touch sterile instruments
◾ It is forbidden to touch the sterile area of the Gaon facing the sterile area when wearing and this area extends from the chest to the waist and sleeves for a distance of 5 cm above the elbow to the hemmed end of the wrist ( bracelet) and the neck, shoulder and back areas are not considered within the sterile area and the position of the body must be Placing disinfectant liquids or any other type of liquid on the floor of the machines .
◾ When the safety of sterile instruments and supplies is in doubt, they are considered contaminated and are not used .
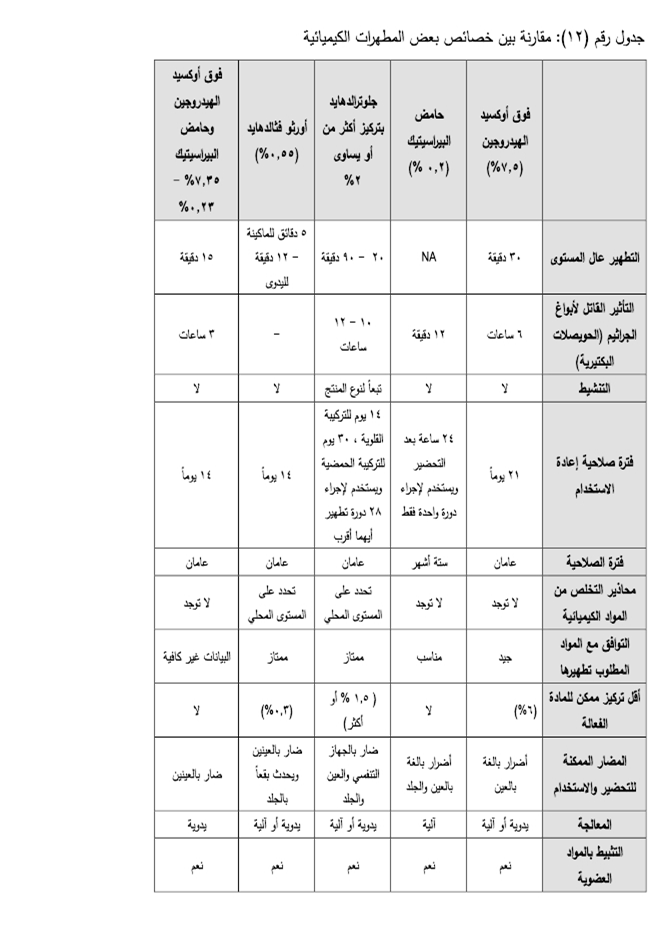
Disinfectants for the preparation of the patient's skin and the hands of the staff before the surgical procedure :
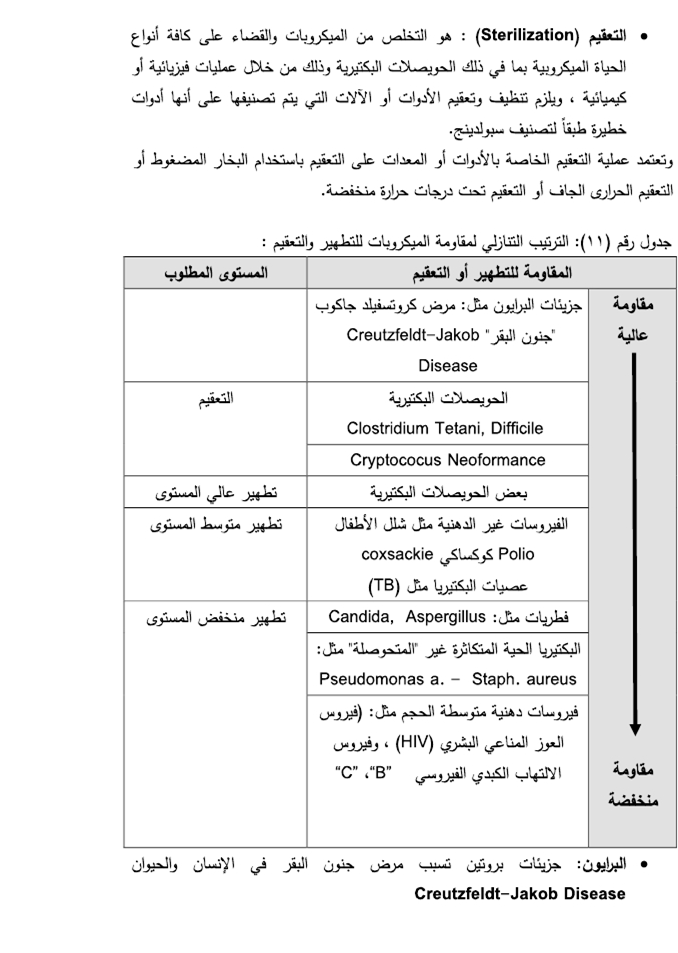
They are substances that stop the growth or work of microbes , whether by stopping their activity or destroying them , and are used objectively on living tissues and are not intended for those disinfectants that are used to disinfect unnecessary things such as tools and surfaces .
|
|
|
|
Maintenance in the operating room :
◾ devices and equipment must be checked weekly or according to the terms of the maintenance contract
◾ the ventilation system ( such as : the relationship between pressures , Air change processes / hour ) should be checked periodically and the filters should be changed if necessary and according to the manufacturer's instructions
◾ the infection control team should be informed when disconnecting the ventilation system during system maintenance or fault repair
◾ the infection control team in cooperation with the engineers of the unit should help determine the need for Environmental Control required when reinstalling the ventilation system
◾ filters should be checked for air change operations before using the operating room after the work interruption period
Sampling from the operating room :-
It is not recommended to routinely take air samples or operating room surfaces
Samples should be taken in cases of an outbreak of infection or after a change in the ventilation system ( such as the installation of a new Air Treatment Unit) or after the construction of new rooms or any infrastructure development
Processes of changing and checking air currents : -
Tests must be carried out ( such as : smoke test and others ) to ensure the movement of air currents, as well as to ensure that the new filters will not reduce the rates of Air change, and any difference in these rates must be corrected immediately with registration and documentation .
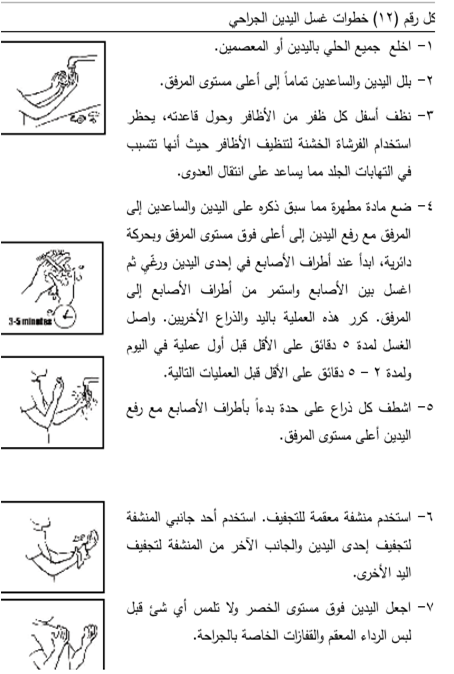
Hand washing
(Surgical hand washing )
The goal of hand washing is to :
The warm humid atmosphere inside the surgical glove promotes the rapid growth of microbes on the hands inside the glove .
Therefore, the surgical washing process using an antiseptic before the start of the surgical procedure helps to prevent this rapid growth of microbes for a while, which reduces the risk of infection for patients in the event of a puncture or laceration of the glove during the operation .
Surgical hand washing :
1-rings, bracelets or a watch should not be worn in the operations and Surgery Unit .
2-the nails should not be touched .
3-it should not be greased with nail polish .
4-there should not be any artificial nails.
5-it is preferable to wash hands between each operation and the other, but 3-5 mm of alcohol can be used
(Alcohol hand rub) between operations and rub it with hands well until dry, when there is a lot of pressure behind some operations to prevent skin infections as a result of using Betadine too much .
6-Betadine is used in hand washing surgically, but the latest now is hand washing with warm water and liquid soap and then rubbing with alcohol (Alcohol hand rub).
7 - Always raise the hands above the elbow level so that the water flows from the hands ( the least polluted ) to the arms (the most polluted ) .
Recent studies have shown that the use of soft brushes in rubbing hands does not affect the reduction of microbes more, on the contrary, it may lead to cracks, micro-wounds and irritation of the skin, which leads to the opposite result .
When is surgical washing done :
◾ Before surgical interventions.
◾ Before the installation of urinary catheters.
◾ Before installing a central venous catheter.
◾ Pre-spare on deep wounds and burns.
Steps of massaging hands with alcohol in preparation for surgical intervention :
◾ Before doing the first cleansing of the hands, they should be thoroughly washed using ordinary soap in the same way as the previous steps.
◾ Making sure the hands are well dried and then pour about 5 ml of alcohol into one of the palms.
◾ Massage the hands with alcohol and make sure that it reaches the areas under the nails and on top of the forearm.
◾ Repeat the procedure on the other hand and forearm.