Part Three
- Nursing care for an unconscious patient
Loss of consciousness
It occurs suddenly, spontaneously and for a short period
Its causes:
· Decrease in the amount of oxygen reaching the brain
· The amount of sugar in the blood decreases below (60 mg/100 ml of blood)
· Poisoning by drugs – alcohol
· Lung clots
· Seizures Epilepsy
· Severe infection
· Cerebrovascular diseases
· Severe decrease in blood pressure (less than 60 mm Hg)
· Lack of response in the case of mental illness
Symptoms:-
· Pale color
· Pulse rate falling below the lowest normal rate (60)
· Hypotension
· The person returns to his normal state after a short period. Meanwhile, the person sleeps in a shock position, and if he does not wake up, he must be examined.

· During shock or coma
· Observes the pupils, breathing, movement and level of consciousness
· He hears breathing, counts the heartbeats, and notes their regularity
Paramedic section
· Ensure safe breathing
· Note vital signs
· Shock mode
· Start giving solutions with Regers lactate or plasma, if available
· The patient is connected to a heart monitor
· Make an EKG
· Giving prescribed medications
· Trying to make the patient aware of what is around him, the place and the people around him
· Most cases of accidental fainting only require observation for an appropriate period and then the patient is discharged from the hospital in this case (the patient is accompanied by one of his family or relatives
In cases that threaten the patient’s life, such as:
· Acute coronary artery thrombosis
· Decreased and irregular heartbeat
· Severe bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract
· Lung clot
· Kidney failure
· Drug poisoning that causes severe collapse of the heart and lungs
· Pollution
Nursing care for diabetics
Diabetic coma:
Blood glucose level is higher than 300 mg/100 milliliters of blood.
Its causes:
Failure to follow diet and medication, lack of physical exercise, exposure to infection, and exposure to a severe psychological crisis.
How to avoid it:
Following a diet and treatment regimen, exercising daily (walking for an hour a day), continuous follow-up with urine and blood tests, training the patient to inject himself with insulin, and ensuring personal hygiene.
Its symptoms:
Increased urination, extreme hunger and thirst, blood pressure disturbances, constipation, difficulty breathing, tendency to vomit, abdominal pain, anxiety, dryness and redness of the skin, dizziness, and an apple-like odor emanating from the mouth.
Treatment: Water-based insulin: 1/3 of the daily dose, and the remaining 2/3 of the dose is given subcutaneously. A urine and blood sample for analysis.
Nursing care:
Taking a urine and blood sample for the following tests: blood glucose - blood salts - blood alkalinity - acetone - urea - hematocrit. Giving a dose of insulin and solutions and performing an EKG according to the instructions of the treating physician.
Observing and recording vital signs every 15 minutes and a fluid chart (according to the instructions of the treating physician) if he is in the hospital.
Educating the patient about (diet - exercise - following treatment - the importance of follow-up - the importance of personal hygiene and avoiding infection - how to analyze urine for sugar and acetone and give himself an insulin injection if he is able to do so).
2- Infection, cataracts, and complications of the retina, blood vessels, kidneys, and nervous system:
Purulent infections occur in diabetics due to the body's lack of resistance and the effect of all these previous complications on the patient's general condition, and may lead to gangrene or amputation of one of the limbs, especially the lower limbs.
Section: Nursing personnel in patient health education:
· Emphasize the importance of following the diet and treatment regimen and physical exercise appropriate to his age and health condition.
· How to conduct urine and blood tests and fill and inject insulin for himself if he is able to do so.
· Emphasize the importance of regular follow-up, personal hygiene, and staying away from sources of infection
Daily foot care:
· Washing using a good type of soap and lukewarm water, then drying well, especially between the fingers, using pressure and avoiding violent massage to maintain the integrity of the skin.
· Apply cream or edible oil to maintain the softness of the feet and reduce friction, and massage with alcohol once a week. The massage is from the toes to the top of the feet. If there are varicose veins, massage the feet very gently and do not massage the legs.
When taking care of nails:
· Immerse it for half an hour daily in lukewarm water with a teaspoon of Borax dissolved in it, then dry it with pressure and massage it around with nourishing oil or cream in order to strengthen the nails and prevent them from cracking.
· Nails are cut straight and not so short that they reach the soft tissues and do not cut the sides.
When choosing a shoe, make sure that it has a short, comfortable heel that does not put pressure on the toes. When using new shoes, make sure that they are worn for only half an hour on the first day, then for an hour on the second day.
To get rid of calluses:
Immerse the foot in lukewarm water and good-quality soap for ten minutes, then rub the excess tissue with a towel, avoiding causing skin inflammation and not cutting the callus.
To avoid blood division disorders:
· The patient is advised to abstain from smoking to prevent blood vessel constriction.
· Keeping feet warm.
· Do some exercises for the legs and avoid wearing anything that puts pressure on them to improve blood flow.
· Avoid taking any medication or placing it near hot water without consulting your physician.
· Make sure to change socks at least daily.
· If any wound occurs, it must be covered immediately with sterile or clean gauze and consult a doctor immediately.
· Do not use shoes if there is any wound on the feet.
· Inform the doctor when redness, blisters, pain, or swelling appear to avoid contamination that may lead to gangrene.
For the pubic area:
· It should be washed well after urinating or defecating and dried well with a soft cotton towel.
· Underwear should be changed daily and when needed, making sure it is cotton so that it can be washed in hot water and dried in the sun.
Take care to notice the presence of blisters or bumps and report them immediately to the treating physician.
Care steps that reduce eye risks:
· The entire eye should be examined every year.
· Tell your doctor if there is blurring or a dark spot, not seeing things clearly, a feeling of pressure or pain in the eye, difficulty seeing in dark light.
· Make a sectional measurement of intraocular pressure.
Dental Care:
· High blood sugar increases the risk of dental and gum problems. Good daily care at home and regular visits to the dentist will prevent these problems.
· Teeth should be brushed daily, and this is the best way to keep teeth and gums healthy.
· Visit the dentist every 6 months.
· The doctor must be informed that he is diabetic.
Ramadan fasting and diabetics:
· In the case of diabetes, it is undoubtedly useful in treating the second type, as it is an opportunity to apply the diet prescribed by the treating physician and thus reduce the patient’s weight, which may lead to recovery from the disease in simple cases in which the diet is used as the only treatment for the disease.
· In cases where blood sugar-lowering tablets are used, blood sugar decreases and the patient’s weight decreases, and thus the body responds more efficiently to blood sugar-lowering medications.
Unwell days:
He must analyze his urine daily, regardless of the amount of food, and he must continue taking diabetes medication and not change it except after the supervision of a doctor.
When any infection appears, regardless of its severity, the patient must quickly consult his doctor instead of neglecting it in the hope that it will improve automatically or treating it himself.
It must be treated according to the doctor's instructions, as he is able to judge and estimate the optimal treatment and the need for medical tests.
Therefore, a diabetic patient should avoid any wrong treatment that could have serious consequences.
Some daily guidelines that a diabetic patient must follow:
· Sugar pills should be taken in the prescribed dose.
· Tell your doctor when you feel tired or when you think there is some kind of infection.
· Do a blood sugar test approximately every 4 hours.
· Do a urine acetone test if the blood sugar level is higher than 240 milligrams.
· If the patient feels stomach fatigue, he should take fluids in small doses to avoid vomiting.
· Make sure to keep chocolate, candy, or a piece of sugar to use when needed.
· Keep a card on which is written that he is a diabetic patient, the type of treatment and dosage he is taking and the times of taking it, the doctor supervising his treatment or the hospital he visits.
Fainting and coma
Definition of fainting:-
It is when a person completely loses consciousness as a result of a lack of continuous supply of blood to brain cells
Types of fainting
1. In most cases, the person loses consciousness for a short period, and the person regains consciousness as soon as he falls to the ground, as a result of blood rushing to the brain from the extremities.
2. In other cases, the person loses consciousness and is like a deep sleeper (sleep), and you cannot wake him up by stabbing. In this case, the person either regains consciousness or enters a complete coma
3. The person completely loses consciousness and enters a coma
Signs and symptoms of fainting
· Paleness of the face
· Profuse and cold sweat with coldness in the extremities
· Dizziness or lightheadedness with difficulty concentrating, nausea
· Feeling numbness in the extremities and inability to hold anything
· Confusion of sight and confusion of thoughts
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
First aid:
◾ A] If the person feels that he will faint, do the following:
1. Help the injured person to sit, lean forward, and place his head between his knees
2. Ask the injured person to take a deep breath
3. Make sure there is fresh air
◾ B] If the person loses consciousness:
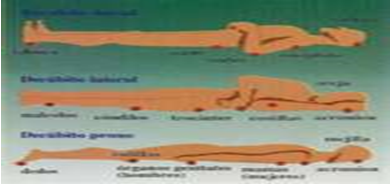
1. Place the patient on the floor lying on his back with the legs raised
2. Loosen the injured person’s tight clothing, especially around the neck
3. Break up any gathering around it to allow air to be renewed for the injured person
4. When the person begins to regain consciousness, explain what happened to him and look for other injuries
◾ C] First aid for a person in a coma:
1. Try to wake up the person in a coma by stimulating the sensory center by tugging on the ear to see if he reacts to the tugging or not.
2. If he does not react to pulling the ear, open the victim’s mouth and make sure that there is nothing blocking the airways
3. If you find an obstruction in the airways (the tongue or a piece of meat), push the injured person’s head back, insert two fingers into the injured person’s mouth, and remove the material causing the obstruction.
4. To open the airways, push the head back and the lower jaw forward, which helps the injured person breathe
5. Make sure that the injured person is breathing by:
¨ Look at the injured person’s chest
¨ And listen to the same afflicted person
¨ Place your hand above the chest to feel the air entering the chest
6. If the injured person is not breathing, begin artificial respiration immediately
If the injured person is breathing, place the injured person in the side-lying position. This position will help the injured person to breathe by placing the tongue and jaw in a forward position and helps fluids and vomit exit from the mouth so that there is no obstruction in the air passages.