Part One
- Quality and improving the work environment
Introduction:
There are multiple definitions of quality, and some or all of these definitions may apply to many topics or services. Each person’s expectations about the expected quality of the service or product depend on several factors such as his individual needs, personal experiences, and the influences of others on him. These factors help to form a set of characteristics that On the basis of which the quality of services provided to him is evaluated.
The perspective and judgment of quality may differ from the perspective of the patient, provider, hospital administration, and community.
Quality is the basis of providing health services, and to confirm the meaning of doing the right thing the right way the first time, we must ensure that things are done in a better way every day, ensure that we obtain the best clinical result for the patient, satisfy all our customers, maintain distinguished workers, and finally ensure the optimal use of available capabilities.
Definitions of quality
• Quality is conformity with needs and specifications.
• It is doing the right thing right the first time.
Quality and health services
• Making sure things are done better every day.
• Ensuring the best clinical result is obtained.
• Ensuring the satisfaction of all our customers.
• Ensuring we retain outstanding employees.
• Ensure optimal use of available capabilities.
Quality and cost
introduction:
The means and methods of providing high-quality health services vary, starting from working in a method of observation and discovering the problems that occur during the application of the system, then eliminating these problems and planning to develop systems that achieve high quality in the service provided, in a way that ensures reducing expenses and saving resources, and even increasing income and returns, through... Eliminate unnecessary and harmful procedures and improve efficiency.
The relationship between quality and cost
Methods and approaches to providing high-quality health services vary as follows:
1. The method of observing and discovering problems that occur during the implementation of the system and then eliminating these problems during work (leads to raising the level of service).
2. The method of taking preventive measures during the implementation of the system to identify the systems that lead to reduced quality and then work to develop these systems (leading to reducing service expenses).
3. The method of advance planning to establish systems that achieve high quality in the service provided, ensuring reduced expenses, saving resources, and even increasing income and returns. From the above it is clear that ensuring quality leads to:
• Eliminate unnecessary procedures.
• Eliminate harmful actions.
• Improving efficiency. (It achieves increased income and resources and reduced expenses).
Quality assurance
The four characteristics of quality assurance:
• Awareness of meeting the needs and expectations of the patient and society.
• Focus on systems and chains of procedures.
• Using data to analyze health service provision chains.
• Encouraging teamwork to solve problems and develop and improve quality.
Quality assurance
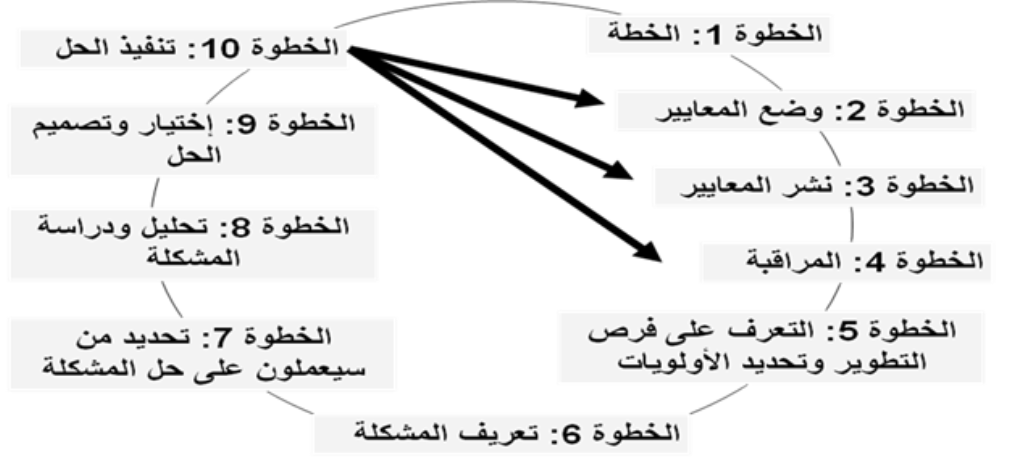
The quality assurance division consists of three stages that include ten steps:
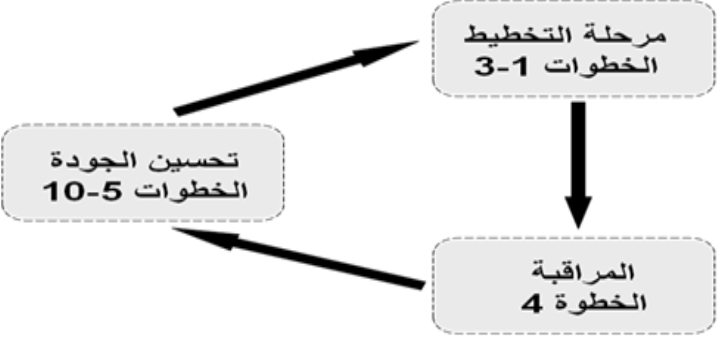
The ten steps to ensure quality
Characteristics based on which the starting point is determined:
Most frequent cases:
• These are activities that will affect a large number of people or their incidence will increase.
Conditions accompanied by problems:
• These are cases in which problems occur repeatedly, whether for workers or patients.
Cases most at risk:
• These are the activities that make the patient more exposed to danger:
1. Failure to provide health services.
2. Not providing the service when it is needed.
3. Providing an unnecessary service.
Standard
What is the standard:
• A standard is a statement that defines expected quality.
Why standard standards:
• Defining and defining quality “How are activities carried out?”
• Quality assessment “How well were the activities implemented?”
What is the standards section in determining quality?
• Identify important inputs.
• Identify the series of actions necessary to achieve the desired results.
• Describe the desired outcomes.
Types of standards
• Clinical work manual.
• Administrative work rules.
• Specifications.
• Performance Standards.
Standards sources
• Standards previously prepared.
• Local and internal standards.
• International standards.
• Educational bodies and institutions.
• Educational institutes and institutions.
Standards published by:
• Detailed explanation.
• A clear plan for implementation.
• Use of incentives.
Disseminate standards by:
• Written letters.
• Conferences and meetings.
• Friendly meetings.
• Work manual.
• Training.
• Monitoring and supervision.
Monitoring
It is the departmental process of collecting and analyzing data on specific indicators to help managers determine the extent to which the main activities are implemented according to the plan and the extent of their impact on the targeted sector of service beneficiaries.
To design a good monitoring program you must:
• Focus on key indicators.
• Collect only the required data.
• Not exhausting workers.
• Collecting data that can be collected, studied and inferred.
• Feedback.
Division improves quality
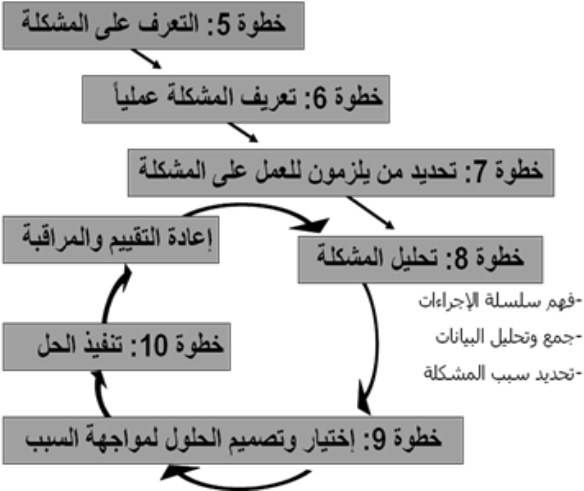
Step five
Recognize the problem or improvement opportunity:
By knowing the types of data to be collected.
There are two types of data:
Quantitative data:
- Surveillance system.
- Surveys.
- Evaluation results and assessment of the situation in special cases.
Qualitative data:
Step six
Definition of the problem in practice:
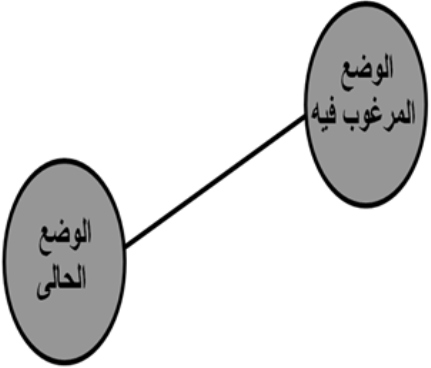
It expresses the difference and gap between the desired performance
And the current situation
Step seven
Determine who will work to solve the problem:
By choosing a team that has the following characteristics:
• Who understand the problem.
• Who can help.
• Those who have technical experience.
Step eight
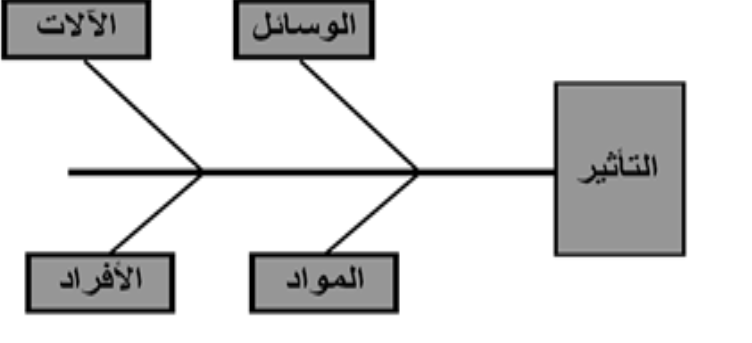
Analyze the problem to find out the root causes:
By using tools to analyze problems:
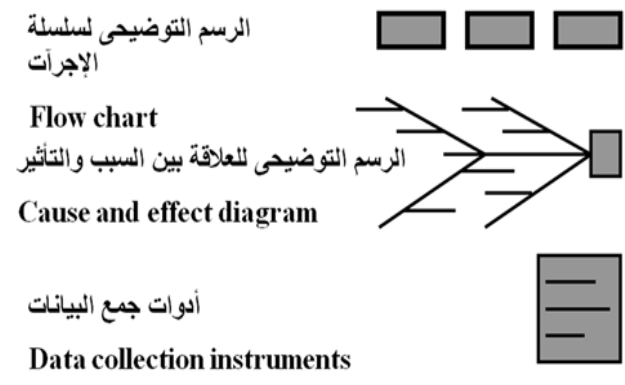
Illustration of the series of procedures (implementation steps):
Illustration of the relationship between cause and effect:
Step nine
Design and develop solutions:
By setting specifications for the solution and identifying the obstacles:
Choose the best solution based on criteria such as:
• Ability to implement the solution.
• The solution is free from a negative impact on other activities.
• Workability of the solution.
• Management support for the solution.
• Community support.
• ---------etc
Step ten
Apply solutions
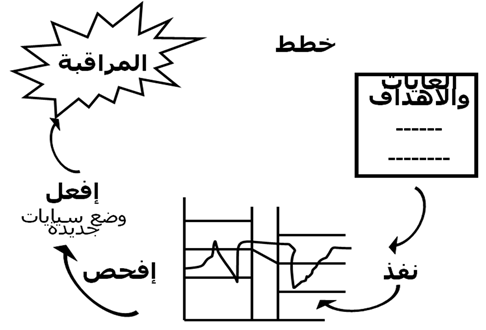
Follow up on solution implementation:
• Did the solution achieve the desired results?
• Did the steps go correctly?
• Are there steps that were difficult?
• Did any problems arise during implementation?
• Is there opposition from other parties and what is the reason for it?
Building a quality assurance program
• Strengthening connection and loyalty to quality.
• Implement an initial review process for quality-related activities.
• Establishing a future vision and program objectives.
• Determine the level and areas of activities.
• Defining the responsibilities.
• Resource allocation.
• Strengthening important administrative skills and systems related to quality.
• Prepare a written plan.
Common errors when implementing the program
• Leaders’ lack of belonging.
• Lack of patience among senior management.
• Lack of specific strategy or methods.
• Rushing into action before fully understanding.
Quality improvement story:
• Telling the story of quality improvement is characterized by simplicity, clarity, and the use of sentences and diagrams. It helps to:
• Visual documentation.
• Strengthening the use of statistical methods.
• Strengthening communications and reducing duplication.
• Preparing presentations and reports.
• Strengthening the use of the surveillance system.
• Help the team understand the differences between procedures and tools.
• Providing a unified approach.
• Report on quality improvement activities

Monthly report on quality activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
Definition of Kaizen philosophy:
It is a compound word of two parts that means “change for the better.” It is a primary means for achieving continuous improvement. It includes many of the improvement tools used in management, and one of these tools is 5S.
Five S?
5S is the philosophy of taking care of the workplace by organizing and cleaning it. It consists of five basic steps, and each step is called in Japanese with a word that begins with the letter S, hence the name 5S. This philosophy became known worldwide by this name, so much so that these five Japanese words were translated into English words starting with the letter S in order for the name to be valid. We can translate these five words into Arabic words that begin with the letter T, which are classification, organization, cleaning, standardization, and stabilization.
The five elements of this philosophy:
Five T consists of five elements:
1- Sorting classification, which is in Japanese: Seiri:
Taking care of the workplace begins with classifying everything in it.
Meaning of classification: Classification here means that we classify things into things that are necessary for work at the present time and things that are not necessary for work. After that, we get rid of the things that are not needed for work and keep those that are necessary for work. Such as: tools, files, materials, waste, papers, and equipment.
The classification process is the first step in this process
2- Set in Order, which is in Japanese: Seiton:
After that comes the organization process, which aims to preserve the things that we decided to keep in an organized way that helps us perform the work efficiently. The organization process does not only include arranging tools or files on the shelves, but it also leads to reconsidering the general plan of the workplace itself. We have to think about the most appropriate way to organize the workplace based on our current work.
3- Cleaning or polishing (Shining) in Japanese: Seiso:
The goal is a very clean work environment. This process is a process that is carried out in sections every shift or every day. There are things that must be cleaned by the person who uses them or handles them, such as work tools, including keys, tools, and supplies that he uses.
4-Standardization, which is called Seiketsu in Japanese:
After all this effort and experience in organizing and cleaning, specific rules should be established for what the workplace should be like. This includes defining the responsibilities of each individual, setting standard methods for the cleaning process, and announcing all of this so that each individual knows what duty he has in his department and how to perform it. This ensures that the situation will continue in this good manner and we will not return to old habits again.
5- Install Sustain, which is Shitsuke in Japanese:
We come to the final step, which is establishing systems to ensure the continuity of this entire process. For example, systems are put in place to review the cleanliness of places. An effective method is for one party to inspect another party, and a representative from one department inspects the process of filing files in another department or the cleanliness of the work site.
Five s benefits:
There are many benefits from it
1- Reducing time wasted searching for documents or tools
2- Reducing injuries due to the cleanliness of the floors, the absence of anything lying here and there, and the clarity of safe passage places
3- Reducing equipment malfunctions due to their early detection
4- Eliminate excess effort and unnecessary movements through a serious process of organization
5- Feeling a beautiful work environment as a result of the cleanliness and organization
6- Replace damaged tools as soon as they are damaged, instead of discovering it late and disrupting work
7- Easily discover lost things
8- Reducing the malfunctions that occurred after maintenance operations as a result of some dust entering the delicate components (and this has been mentioned in other fields)
9- Reducing quality problems that occurred due to pollution and dust.