Chapter Three
- Problem Solving
introduction:
Solving administrative problems and making decisions are an integral part of the functions of the administrative process and can be considered as two basic activities that the manager performs on an ongoing basis in their organizational units to confront undesirable situations or levels of performance that constitute an obstacle that prevents reaching the specified goals efficiently and effectively.
Charles says
• (When we write down the details of the problem, we have achieved half of its solution)
Definition of the problem :
• A problem is a state of discrepancy or difference between a current or future reality and a goal that we seek to achieve. There are usually obstacles between reality and the target, and the obstacles may be known or unknown .
. It is a state of dissatisfaction or tension that arises from the awareness of the presence of obstacles to reaching the goal or the expectation that better results can be obtained by making better and more efficient use of familiar processes and activities
The problem can be defined from another perspective as an unsatisfactory or undesirable result that arises from the presence of one or several known or unknown causes that need to be studied to identify them so that they can be influenced. Problems also differ in terms of their degree of severity or impact.
Problem solving concept :
That it is a thinking process in which the individual uses his previously acquired knowledge and skills in order to respond to the requirements of a situation that is unfamiliar to him. The response is to initiate action aimed at resolving the ambiguity or ambiguity contained in the situation
Problem solving steps:
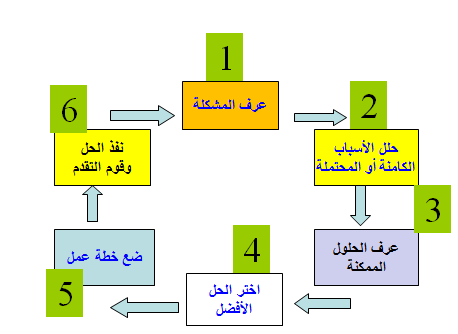
. Practical steps to solve the problem:
. Identify and describe the problem:
The first step in solving the problem is to identify it, and this is done by reviewing the indicators, data, and facts in the situation. Here, management must distinguish between two things:
· The real problem: This includes the main factors that hinder the establishment from achieving a specific goal, and the goal cannot be achieved unless they are solved.
·Sub-problem: It is a temporary symptom that arises as a result of the real problem and disappears with its disappearance
Therefore, solution efforts should be directed to the real problem, not to its branches. The first step in solving the problem is to feel its existence, and this is done by noticing a difference or deviation between the results achieved and the desired goals.
. Analysis of the facility’s capabilities and resources:
This is an important step to determine the possibilities for implementing solutions before thinking about them. This is done by identifying the basic strengths and weaknesses related to the problem in the facility.
. Find the causes of the problem:
Problems do not arise in a vacuum, but rather they have causes. Usually, the causes that create a problem are multiple, and these causes may overlap and interact. Therefore, supervisors must search for these causes and rank their relative importance in causing the problem, as well as clarify the overlapping relationships between them.
. Develop alternative solutions:
Any alternative solution must be characterized by the following:
· It contributes to some degree to solving the problem, but does not necessarily solve it completely
· It must be practically applicable or financially feasible.
· To be socially acceptable
· Does not create other problems, even if it helps solve the main problem
After presenting the alternative solutions, they must be compared. This comparison mainly focuses on important elements that should be present in the most appropriate alternative, which are:
· The extent to which each of the proposed solutions contributes to solving the problem
· The cost or burdens incurred by implementing each solution
· Special requirements that must be provided to implement each solution
· The expected time period for the solution to produce its effects
· Side problems that may arise from implementing each solution
. Put the solution into an application:
There is no doubt that choosing a solution does not solve the problem in itself, but it must be implemented correctly and completely in order for it to have its intended effect and eliminate or alleviate the problem. Therefore, the process of solving problems took place in several important stages, each of which is a link in an integrated chain. Each stage depends on the previous stage, meaning The quality and effectiveness of problem solving as an administrative basis depends on the efficiency of all stages.

• Use one type of thinking .
• Absence or limited participation of concerned parties.
• Fear of failure, innovation, and exchanging ideas .
• Lack of information or poor analysis of the problem .
• Lack of commitment to solving the problem.
• Misinterpreting the problem.
• Lack of knowledge of methods (techniques) and processes for solving the problem.
• Inability to use methods effectively.
• Not using the appropriate method for a specific problem.
• Insufficient or incorrect information.
Methods for solving administrative problems :
• You must realize that there is a problem and it must be identified quickly, and you must decide to confront the problem and confront it.
• You must understand that solving problems involves making a certain effort, and you must relax and develop your mind before acting on the problem.
• You should be convinced that making a decision is better than doing nothing and you should be determined to address the problem as early as possible.
• You must appreciate the existence of a situation to identify the problem before rushing to address and eliminate it.
• You must make a list of facts and information related to the problem as you see it. This helps you understand the problem and allows you to determine what is actually happening.
• It is also important to determine the pros and cons of the available options and alternatives and their solutions.
• You must know the possible chances of success and failure in certain proportions and know whether there is a solution to the problem left after all that
• You must make a logical decision about the effectiveness of your decision and must consult with others who will be affected by this decision.
• You must carefully consider the effectiveness of your decision
• You should take into account whether the problem requires a temporary or long-term solution, while ensuring that your decision solves the problem permanently.
The importance of developing the ability to solve problems:
Developing your ability to solve problems is beneficial in many ways, as you will be able to:
• Anticipates specific problems and takes preventive action.
• Problems are solved quickly and with less effort.
• Reduces stress.
• Develop your performance at work and your relationships with colleagues.
• Create opportunities and exploit them.
• Solve the most pressing problems.
• You exercise more control over major or vital aspects of your life.
• Achieve more personal satisfaction.