Chapter one and two
- Communication methods
Definition of communication
Communication is the process of exchanging ideas, information, and trends verbally and non-verbally between individuals to achieve public or private purposes. Communication is a circular process and not a one-sided conversation . This means that the sender is at times a receiver and the receiver is at times a sender .
The importance of communication
• Forming relationships between community members.
• Exchange information, ideas and experiences.
• Conviction to change positive knowledge, attitude and behavior among individuals and groups
• Clarifying ideas, removing confusion, and correcting concepts .
• Increase culture.
• Influencing others through guidance and counseling.
• Transferring information, data, statistics and concepts through various channels to contribute to decision-making .
• A purposeful means to ensure interaction and joint exchange of the organization’s various activities .
• A way to motivate employees .
• Communication helps achieve goals .
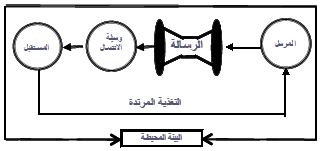
Components of the communication process:
• Sender
• the message
• Communication channel
• the future
• Feedback
• the environment
Types of communication:
1. Verbal
2. Non-verbal.
There are two types of communication:
First: Verbal communication:
• (talk - printed material to read - watching a television or radio program)
• Second: - Non-verbal communication:
• (body and hand movement - sitting - facial expressions such as joy and sadness - eye movement...etc. )
Communication skill:
1. Listening skill.
2. Speaking skill.
3. Persuasion skill.
4. The skill of asking questions.
5. Dialogue management skill.
6. Skill in dealing with others.
7. The skill of using body language.
· Listening skill
It is focusing attention on the opinions, thoughts, feelings, and linguistic and physical expressions of others. Do not rely on the content of the words, but try to reach the speaker’s directions .
The difference between listening and listening
- Listening : is limited to receiving the message organically through the ear .
- Listening : It is the use of the mind with its full capacity in everything that has been received, by processing the received message mentally with interpretation.
Types of listening:
Good listening is often accompanied by good thinking
Why don't we listen?
· Their inability to concentrate for any reason.
· Their intense preoccupation with themselves.
· They are too preoccupied with what they will say later.
· Their lack of confidence in what they are listening to and the reasons that make them listen to it.
· They do not have the ability to follow the points that the speaker is talking about.
· They do not care about what is said to them.
· We think seven times faster than we speak, and this makes us preoccupied with our judgments about the speaker’s speech?
· Our desire to express ourselves instead of listening (I want the opportunity to speak).
· Distraction due to side conversations or noise.
The importance of good listening
Good listening is the appropriate path for a leader or individual with strong relationships with others, as it saves a lot of time and effort in managing problems and conflicts, achieving goals, and negotiating with those around them, as listening leads to :
· It affects the validity and accuracy of the decision
· It makes the relationship mature and strong between individuals
· Generates the ability to innovate and create
· It makes the individual able to face problems and crises
· Makes the criteria for evaluating others more fair
· Listening means a permanent addition to a person’s ability to speak forcefully
· It reduces error and represents the key to safety for the individual’s intellectual growth.
How to become an effective listener?
· Search for the content of the topic and ignore the speaker’s manner or mistakes in speaking.
· Arrange the information you hear logically in your mind.
· Do not rush to judge.... Rather, let the speaker complete his speech.
· Do not turn your face away from the interlocutor (the eye sometimes listens).
· Ask your interlocutor if the conversation is not clear.
· Create an appropriate environment for yourself from the beginning that prevents you from focusing on things other than listening to the speaker.
· Make your place in the session suitable for following the speaker with your eyes and ears, and try to eliminate factors that could obstruct this, such as sunlight falling on you or the presence of some devices in front of you.
2- Speaking skill
How do you prepare yourself before starting the conversation?
· Determine your goal and benefit from communication
· Design your message to suit your listeners
· Good preparation of the topic of the conversation...it is the best source of trust.
· Have an idea in advance about the person you will be speaking to.
· Prepare supporting materials to support your speech.
· Mental and muscle relaxation.
To be a good speaker
· Avoid inexpressive faces - exaggerated expressions - distressed expressions.
· Avoid sharp glances or direct close-up looks.
· Avoid repetitive movements as a result of excessive nervousness (movement such as a pendulum clock, for example).
· Avoid inappropriate or exaggerated clothing.
· Avoid stuttering - low voice - continuing on one tone.
· Expand your circle of thinking and fully understand the information
· Use the recipient's language to convey the message clearly
· Ask questions and then let the speaker confirm to you that what you understood is in fact correct
· Do not say lightly: I do not know: many of us know very little about the world in which we live, and pretending to answer or fabricating it only doubles the problems.
· Pay your full attention to those you talk to: If you set aside time to communicate with a person, give him attention and attention. Join the conversation and participate in it when you see that it is of interest to the communication process.
3- Persuasion skill
It is one of the skills necessary for the communication process, and it is used in personal interviews, group discussions, and talking with leaders. Definition: Enticement through reason, logic, and knowledge to make others accept changes in their opinions, attitudes, or behaviors.
Stages of the persuasion process:-
· The attention stage: The individual is attracted to the new idea and shows enthusiasm for this idea.
· Interest stage: A stage in which the individual wants to know details about the idea and has a desire to analyze facts and collect information.
· Evaluation or mental comparison stage: In this journey, the individual performs a process of self-evaluation and comparison between the old and the new.
· Experimentation stage: In this journey, the individual tries to get rid of tension and attraction, so he experiments and applies the pleasure of the idea on a small scale.
· Adopting the idea/complete conviction: In this journey, the person is completely convinced of the idea and decides to continue implementing it.
The skill of asking questions
To keep the dialogue going, there must be a reaction from the other party that includes indicators that support that it received the message and helps the first party determine how to continue the dialogue. These indicators can be obtained through the optimal use of questions. The questions may be positive or negative. If they are positive, they explain the other party’s way of thinking and feeling, but if they are negative, they make him feel tense and embarrassed and push him to take a defensive position.
Therefore, the following must be taken into account:
· The goal of questions should be to reach agreement and not to interfere in personal matters.
· It is important not to ask questions that lead to anxiety and tension in the other party.
· Questions should help both parties, and not be used as maneuvering.
· Questions should aim to establish an atmosphere of cooperation by motivating the other party to respond frankly.
· Ensure that the questions are not deceptive, contrived, evasive, shameful, or worthless.
· Questions must be appropriate to the situation.
· Questions should also be appropriate to the other party’s personality and general aptitudes.
· The purpose of questions should be to achieve a goal and not simply to elicit a response.
· The need for a connection between the questions.
· Finally, it is required and usual that questions be characterized by tact and respect for the other party.
Specifications of successful communication:-
· That both the sender and the receiver must believe and be interested in the message
· Mutual respect between sender and receiver
The subject of the message is clear to both parties
· Use appropriate means for the sender, the recipient, the subject of the message, and the place where it is presented
· Communication is two-way, meaning there is interaction between the sender and the receiver
· Use verbal and non-verbal communication equally efficiently, as they complement each other
· The more senses we use, the more efficient the communication process becomes
· The message must be correct, accurate, clear, specific and short
· Do not be a continuous sender or receiver
· Set a clear goal for the communication process
· Choose the appropriate circumstance from an environmental, social and psychological perspective
· The language of communication must be appropriate for both parties
Specifications of successful communication
· That both the sender and the receiver must believe and be interested in the message
· Mutual respect between sender and receiver
The subject of the message is clear to both parties
· Use appropriate means for the sender, the recipient, the subject of the message, and the place where it is presented
· Communication is two-way, meaning there is interaction between the sender and the receiver
· Use verbal and non-verbal communication equally efficiently, as they complement each other
· The more senses we use, the more efficient the communication process becomes
· The message must be correct, accurate, clear, Specific and short
· Do not be a continuous sender or receiver
· Set a clear goal for the communication process
· Choose the environmentally appropriate condition, Social and psychological
· The language of communication must be appropriate for both parties
Basic principles for communicating clearly
In order for people to hear, see and understand the message you want to deliver to them, you must:
Choose words that are easy and simple to understand.
To avoid scientific and medical terminology.
Make sure that everyone present sees and hears what you are saying.
To present a message as short as possible without disturbing the content of the message.
Long messages lead to the attendees being distracted and not focusing on what you are saying and presenting. It also leads to them not remembering the message shortly after your speech.
You should talk to them about one topic at a time.