parasitic diseases of slaughtered food animals
- III. Parasites not transmissible to man
A. Nematode
1- Ascaris (toxocara)
Cause: Ascaris suum (suis) in pig. Ascaris ovis in sheep. Neoscaris(toxocara) vitulorm in calve.
P/M: Intestinal obstruction. Flesh: Characteristics odor (toxic substance and volatile acid)-poor. Liver: The early stage is congested and chronic cases make milk spots. Lung: Edema, hemorrhage, and parasitic pneumonia.
Judgement:
1. Condemnation of affected intestine and liver
2. Boiling and roasting test must be applied for detection of any abnormal odor & taste.
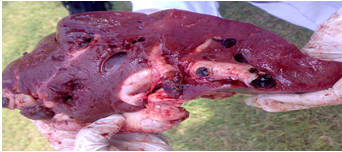
2- Lungworm Cause:
Dictyocaulus viviparous in cattle. Dictyocaulus filaria in sheep.
Metastrongylus elongatus in pig P/M:
Yellow or reddish brown foci (adult parasite)/surface of the lung just beneath
pleura. Catarrhal bronchitis and pneumonia (exudates contain the parasites).
Emaciated animal Judgement: Lung: o
Slight
infestation: condemnation of affected part o
Heavy
infestation: condemnation of lung Carcass:
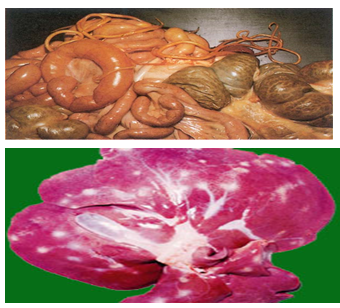
If there is anemia and emaciation make T B- Cestodes 1- Sheep measle 2-Camel measle 3-Cysticerus tenuicollis 4-Coenurus cerebralis Cause C. Ovis C. cameli or
dromedarri C. tenuicollis (largest) Multiceps multiceps or Coenurus cerebralis Adult worm T. ovis T. hyaena T.hydatigena (marginata)
largest tape worm in dog T. multicepes (T. coenurus) Habitat Heart-
Masseter-Tongue- Diaphragm Heart- Masseter-Skeletal Ms- Liver Liver-Mesentery & its L. node- Omentum Brain &spinal cord F.H Dog Hyaena or dog Dog Dog I.M.H Sheep and goat Camel Ox, sheep, goat, pig, and camel Sheep, and goats. Rare in ox, horses, and man Judgement Organ: condemned Carcass: Light:
remove the affected part Heavy: (T) as c. bovis Organ: Light:
cyst. Heavy:
whole organ Carcass: A Early before emaciation remove head.
With emaciation (T) N.B: Gid=sturdy=turnsick= circling disease C- Arthropods 1- Oestrus bovis 2- Oestrus ovis Cause - Hypoderma bovis (cattle) - H. linatum - Sheep nasal fly / False gid Predilection
seat/ host - Muscle of belly (butcher's jelly) - S/C in goat - Carcass unmarketable - Sheep - Camels, dogs, and man (Sometimes) A/M and P/M - Swelling or
eroded skin back (Larvae protruding) - Cattle kick the
abdomen- erected tail - Paralysis
(lower body, legs) (spinal cord) - Hemorrhagic
edema -
Edema and
inflammation in s/c tissue around larvae (butcher ̓s jelly) - Symptom of brian irritation - Tozzing of head - Sneezing - Loss of appetite and emacaciation Judgement Trimming of the affected parts - Condemnation of
head - Carcass
approved (no emaciation) D- Trematode: Fascioliasis: Cause: Fasciola gigantica “Giant liver”, Fasciola hepatica, or Fascioloides
magna M.O.I: EMC on grass (animal, human). Not by adult fluke Acute Subacute Chronic - Immature - Haemorrhagic tracts - Swelling, congestion, Hg. on liver capsule - Soapy touch of muscle - Death from liver rupture - Differs from
the acute type in that symptoms are more protracted - Adult flukes in the bile ducts (mechanical
irritation) - Hard
liver and atrophy - The
cirrhotic areas (greyish color) Fasciola in different species: Cattle: Bile duct: Pipe
appearance/sand sound by knife. Liver tissue: Cirrhosis. Lung: Nodule (immature
fluke that failed to reach bile duct and liver) Sheep: Bile duct: Thickening &
dilatation. Liver tissue: Fibrosis. Lung: Rare nodule

Pig: Immature fluke encysted in
liver tissue & fail to reach bile duct. Judgement: Organ o Acute: Condemnation o Chronic: Light
infestation: Condemnation of the affected part. Heavy infestation: Condemnation
of the whole liver Carcass: o
Examined
for jaundice, emaciation & oedema "Cattle" o
Examined
for edema, emaciation, and jaundice "Sheep"