sample collection and sample processing
- Methods used for collecting blood sample
1.Wing (brachial) vein method using a needle the brachial vein of the wing is an acceptable site for blood collection for birds 4 weeks and older. In younger birds, this vein is too small for efficient blood collection.
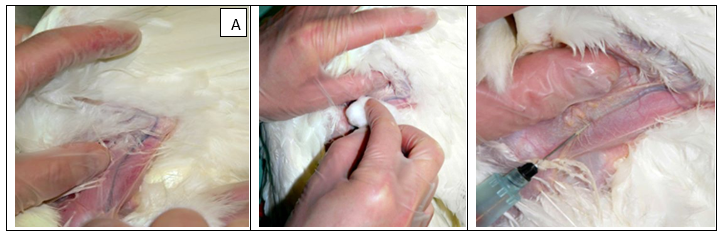
A)Wing vein prepared for puncture must disinfect area around the vein then inserted the syringe correctly.
2. Heart puncture collecting blood directly from the heart can provide rapid blood collection, and allow for collection of larger volumes of blood (4 to 10 mL). Additionally, cleaner blood samples can be collected compared with wing vein method. Cardiac puncture methods should only be practiced by trained personnel. Poor technique in needle placement and repeated attempts to locate the heart can result in fatal hemorrhage; however, this risk is minimized with practice. If fatal hemorrhage is suspected.
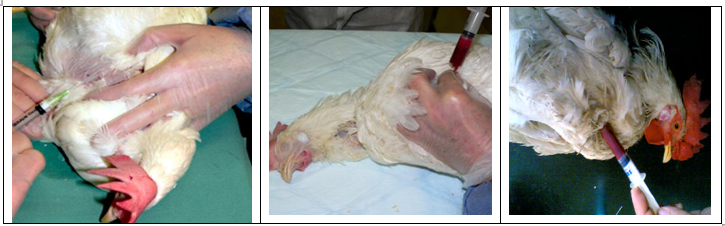
-The route of cardiac puncture was achieved by inserting the needle between the clavicles into the heart.
-Once a blood sample has been collected into a syringe, the sample should be carefully transferred to a tube to promote clot formation.
-Clotting occurs when all the cells in the blood are drawn together by the coagulation process and separates from the fluid portion of the blood (serum).
• The needle should be removed from the syringe before the blood is pushed into the clotting tube. Forcing the blood back through the needle will rupture red blood cells (hemolysis), resulting in a poor quality sample.
• Slowly inject the blood into the clot tube, allowing it to run down the side of the tube, which encourages clot formation. Blood must be placed in the clot tube before the coagulation process begins.
• Do not disturb the blood tubes while the clotting process is occurring. Tubes should be allowed to stay positioned nearly flat (horizontal) to maximize surface area of the clot as it forms. The amount of serum yielded from clotted blood depends on the surface area of the clot. Tubes held upright in the vertical position have little surface area and produce only a small quantity of serum. Use a test tube holder for keeping tubes in this flat position. If a test tube holder is not available, then a block of wood drilled with appropriate sized holes or a wire rack can be used.